Product Description
Ball Screw with Nut details
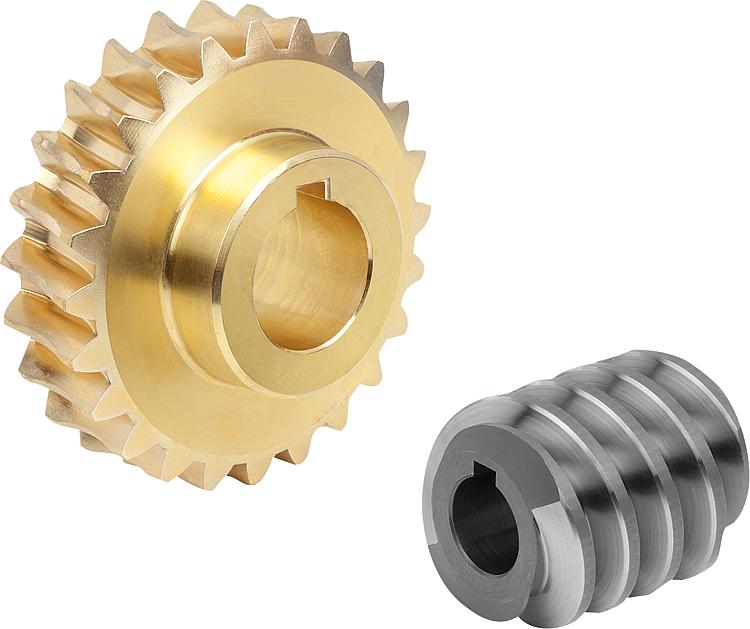
Ball screw is made of screw, nut and ball. The function is to turn the rotary motion into liner motion, which is a further extension and development of ball screw. The significance of this development is to move into a rolling bearing from sliding action; With little friction, ball screws are widely used in various industrial equipment and precision instruments.
WHAT CAN WE SUPPLY?
-1.We have TBI or CHINAMFG sizes for your selection.
Our ball screws and nuts are the same sizes as TBI or CHINAMFG ,they can be interchanged with TBI or THK.
TBI sizes have enough inventory in stock.
CHINAMFG sizes are produced on request.
-2.We are able to machine the 2 end sides of ball screws according to your requirements.
-3.We have full range of products what can be matched with ball screws.
We are able to match for you completely, including Machined Ball screw, Ball screw Nut, Nut housing/Nut Bracket, Shaft Coupler, End support unit.
-4.We provide many different series of ball screws and screw nuts, like SFU,SFK,SFS,SFI,SFY,SFA,DFU,DFI series and so on.
| SFU Ball Screw Nut Model No.(plastic deflector or metal deflector ) |
| SFU1204-3;SFU1605-3;SFU1605-4; SFU1610-2; SFU2005-3;SFU2005-4;SFU2505-3;SFU2505-4;SFU2510-4;SFU3205-3; SFU3205-4;SFU4005-4;SFU4571-4; SFU5571-4;SFU6310-4;SFU8571-4 |
| SFK Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFK0601;SFK0801;SFK0802;SFK082.5;SFK1002;SFK1004;SFK1202;SFK1402 |
| SFS Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFS1205;SFS1210;SFS1605;SFS1610;SFS1616;SFS1620;SFS2571;SFS2510;SFS2525;SFS3210;SFS4571 |
| SFI Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFI1605;SFI1610;SFI2005;SFI2505;SFI2510;SFI3205;SFI3210;SFI4005;SFI4571 |
| SFE Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFE1616;SFE2571;SFE2525;SFE3232;SFE4040 |
| SFY Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFY1616;SFY2571;SFY2525;SFY3232;SFY4040 |
| SFA Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFA1610;SFA1620;SFA2571;SFA2510;SFA2525 |
| Ball Screw End Supports Model No. |
| BK10 BF10, BK12 BF12, BK15 BF15, BK17 BF17, BK20 BF20, BK25 BF25,BK30 BF30, BK35 BF35, BK40 BF40 |
| EK06 EF06, EK08 EF08, EK10 EF10, EK12 EF12, EK15 EF15, EK20 EF20; EK25 EF25 |
| FK06 FF6, FK08 FF08,FK10 FF10, FK12 FF12, FK15 FF15, FK20 FF20, FK25 FF25, FK30 FF30 |
| Ball Screw Nut Housings Model No. (Aluminium or Iron) |
| DSG12H(1204),DSG16H(1605/1610), DSG20H(2005/2571), DSG25H(2505/2510), DSG32H(3205/3210), DSG40H(4005/4571),DSG50H(5005/5571) |
Each series has its own characteristics. The following table list the differences in appearance and characteristics for your reference.
Rolled Ball Screw Application:
1. Engraving machines; 2. High speed CNC machinery;
4. Auto-machinery. 3. Semi-Conductor equipment;
5. Machine tools; 6. Industrial Machinery;
7. Printing machine; 8. Paper-processing machine;
9. Textiles machine; 10. Electronic machinery;
11. Transport machinery; 12. Robot etc.
Rolled ball screws can not only be used in above general machinery, but also in many advanced industries. Rolled ball screw with a motor assembles electrical-mechanical actuator, which is more eco-friendly than hydraulic pump system. Nowadays it’s applied to electric vehicles, solar power plants, railway devices and many medical and leisure equipments.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C7 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 31-40mm |
| Flange: | Without Flange |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What are the common issues or failures associated with worm screws?
Worm screws, like any mechanical component, can experience certain issues or failures over time. Understanding these common problems is important for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Here are some common issues or failures associated with worm screws:
- Wear and Surface Damage: Due to the sliding contact between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel, wear can occur over time. This wear can lead to surface damage, such as pitting, scoring, or galling. Excessive wear and surface damage can affect the performance and efficiency of the worm screw gear system, resulting in increased backlash, decreased torque transmission, and potential failure.
- Lubrication Problems: Inadequate or improper lubrication is a common cause of issues in worm screw systems. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and accelerated wear. On the other hand, over-lubrication can cause excessive drag and fluid churn, leading to inefficient power transmission. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals, types of lubricants, and proper lubrication techniques to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the worm screw system.
- Backlash and Inaccuracy: Backlash refers to the play or clearance between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. Excessive backlash can result in reduced accuracy, loss of motion control, and diminished overall system performance. Backlash can be caused by factors such as wear, misalignment, or improper assembly. Regular inspection and adjustment of backlash are necessary to maintain the desired precision and minimize the effects of backlash-related issues.
- Misalignment: Misalignment between the worm screw and the worm wheel can result in increased friction, wear, and inefficiencies. Misalignment can occur due to factors such as improper installation, component deformation, or external forces. It is essential to ensure proper alignment during installation and periodically check for misalignment during routine maintenance. Adjustments should be made as necessary to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
- Overloading: Subjecting the worm screw gear system to excessive loads beyond its design limits can lead to failure. Overloading can result in accelerated wear, tooth breakage, or component deformation. It is important to operate the system within the specified load limits and consider factors such as shock loads, dynamic loads, and variations in operating conditions. If higher loads are required, it may be necessary to select a worm screw system with a higher load capacity or redesign the system accordingly.
- Corrosion and Contamination: Corrosion and contamination can negatively impact the performance and lifespan of worm screw systems. Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles can lead to corrosion, rusting, or damage to the surfaces of the worm screw and worm wheel. Contamination can interfere with smooth operation and cause accelerated wear. Proper environmental protection, regular cleaning, and appropriate sealing measures can help mitigate the effects of corrosion and contamination.
- Insufficient Stiffness: Worm screws rely on proper support and stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and prevent deflection. Inadequate stiffness in the supporting structure or mounting arrangement can result in excessive deflection, misalignment, and decreased performance. It is crucial to ensure that the worm screw system is properly supported and mounted to maintain the required rigidity and stiffness for optimal operation.
It’s important to note that the specific issues or failures associated with worm screws can vary depending on factors such as the application, operating conditions, maintenance practices, and the quality of the components. Regular inspection, proper lubrication, alignment checks, load monitoring, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for minimizing the occurrence of these issues and ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of worm screw systems.

What are the latest innovations in worm screw design and materials?
In recent years, there have been several notable innovations in worm screw design and materials that aim to improve performance, efficiency, durability, and overall functionality. Here are some of the latest advancements in this field:
- Advanced Materials: One of the significant trends in worm screw design is the use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring materials with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and fatigue properties. For example, advanced alloys and composite materials are being employed to improve load capacity, reduce weight, and increase the longevity of worm screws. Additionally, advancements in material science and engineering are leading to the development of self-lubricating materials, which can minimize friction and improve efficiency by reducing the need for external lubrication.
- Improved Thread Geometries: Innovations in thread geometries have focused on optimizing load distribution, reducing friction, and improving efficiency. Researchers and engineers are developing novel thread profiles and forms that enhance contact between the worm screw and the worm wheel. These designs help minimize backlash, increase load-carrying capacity, and improve overall system performance. Additionally, advancements in computer simulations and modeling techniques enable more accurate analysis and optimization of thread geometries for specific applications.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Surface treatments and coatings are being applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. For instance, advanced coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings or specialized lubricious coatings help reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and minimize the need for external lubrication. Surface treatments like nitriding or carburizing can improve hardness and provide resistance against abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of worm screws.
- Precision Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing processes and technologies have enabled the production of worm screws with higher precision and tighter tolerances. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC grinding and high-precision gear hobbing, allow for the creation of worm screws with superior dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and better tooth profile control. These manufacturing advancements contribute to enhanced performance, reduced backlash, and increased overall system efficiency.
- Computer-Aided Design and Simulation: The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools has revolutionized worm screw design and optimization. Engineers can now create virtual models, simulate the behavior of worm gear systems, and analyze various design parameters to optimize performance before physical prototypes are manufactured. This iterative design process helps reduce development time, minimize costs, and improve the final design and performance of worm screws.
- Integration with Digitalization and Automation: The integration of worm gear systems with digitalization and automation technologies is another area of innovation. Worm screws are being designed to work seamlessly with sensor technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load. This data can be utilized for predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and optimization of the overall system performance.
It’s important to note that the field of worm screw design and materials is continuously evolving, and new innovations are being introduced regularly. Keeping up with the latest research, advancements, and industry developments is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in worm gear system applications.
How do you calculate the gear ratio for a worm screw and gear setup?
In a worm screw and gear setup, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the worm wheel (gear) and the number of threads on the worm screw. The gear ratio represents the relationship between the rotational speed of the worm screw and the resulting rotational speed of the worm wheel. The formula to calculate the gear ratio is as follows:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Worm Wheel / Number of Threads on Worm Screw
Here’s a step-by-step process to calculate the gear ratio:
- Count the number of teeth on the worm wheel. This can be done by visually inspecting the gear or referring to its specifications.
- Count the number of threads on the worm screw. The threads refer to the number of complete turns or helical grooves wrapped around the cylindrical body of the worm screw.
- Divide the number of teeth on the worm wheel by the number of threads on the worm screw.
- The result of the division is the gear ratio. It represents the number of revolutions of the worm screw required to complete one revolution of the worm wheel.
For example, let’s say the worm wheel has 40 teeth, and the worm screw has 2 threads. Using the formula, we can calculate the gear ratio as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 teeth / 2 threads = 20
In this case, for every full revolution of the worm screw, the worm wheel will rotate 1/20th of a revolution. This indicates a significant speed reduction, resulting in high torque output at the worm wheel.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio calculated using this formula assumes an ideal scenario without considering factors like friction, efficiency losses, or the pitch diameter of the gears. In practical applications, these factors may affect the actual gear ratio and performance of the worm screw and gear setup.


editor by CX 2024-03-23
China Hot selling C7 Precision Rolled Thread Double Nut Ball Screw
Product Description
Ball Screw with Nut details
Ball screw is made of screw, nut and ball. The function is to turn the rotary motion into liner motion, which is a further extension and development of ball screw. The significance of this development is to move into a rolling bearing from sliding action; With little friction, ball screws are widely used in various industrial equipment and precision instruments.
WHAT CAN WE SUPPLY?
-1.We have TBI or CHINAMFG sizes for your selection.
Our ball screws and nuts are the same sizes as TBI or CHINAMFG ,they can be interchanged with TBI or THK.
TBI sizes have enough inventory in stock.
CHINAMFG sizes are produced on request.
-2.We are able to machine the 2 end sides of ball screws according to your requirements.
-3.We have full range of products what can be matched with ball screws.
We are able to match for you completely, including Machined Ball screw, Ball screw Nut, Nut housing/Nut Bracket, Shaft Coupler, End support unit.
-4.We provide many different series of ball screws and screw nuts, like SFU,SFK,SFS,SFI,SFY,SFA,DFU,DFI series and so on.
| SFU Ball Screw Nut Model No.(plastic deflector or metal deflector ) |
| SFU1204-3;SFU1605-3;SFU1605-4; SFU1610-2; SFU2005-3;SFU2005-4;SFU2505-3;SFU2505-4;SFU2510-4;SFU3205-3; SFU3205-4;SFU4005-4;SFU4571-4; SFU5571-4;SFU6310-4;SFU8571-4 |
| SFK Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFK0601;SFK0801;SFK0802;SFK082.5;SFK1002;SFK1004;SFK1202;SFK1402 |
| SFS Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFS1205;SFS1210;SFS1605;SFS1610;SFS1616;SFS1620;SFS2571;SFS2510;SFS2525;SFS3210;SFS4571 |
| SFI Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFI1605;SFI1610;SFI2005;SFI2505;SFI2510;SFI3205;SFI3210;SFI4005;SFI4571 |
| SFE Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFE1616;SFE2571;SFE2525;SFE3232;SFE4040 |
| SFY Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFY1616;SFY2571;SFY2525;SFY3232;SFY4040 |
| SFA Ball Screw Model No. |
| SFA1610;SFA1620;SFA2571;SFA2510;SFA2525 |
| Ball Screw End Supports Model No. |
| BK10 BF10, BK12 BF12, BK15 BF15, BK17 BF17, BK20 BF20, BK25 BF25,BK30 BF30, BK35 BF35, BK40 BF40 |
| EK06 EF06, EK08 EF08, EK10 EF10, EK12 EF12, EK15 EF15, EK20 EF20; EK25 EF25 |
| FK06 FF6, FK08 FF08,FK10 FF10, FK12 FF12, FK15 FF15, FK20 FF20, FK25 FF25, FK30 FF30 |
| Ball Screw Nut Housings Model No. (Aluminium or Iron) |
| DSG12H(1204),DSG16H(1605/1610), DSG20H(2005/2571), DSG25H(2505/2510), DSG32H(3205/3210), DSG40H(4005/4571),DSG50H(5005/5571) |
Each series has its own characteristics. The following table list the differences in appearance and characteristics for your reference.
Rolled Ball Screw Application:
1. Engraving machines; 2. High speed CNC machinery;
4. Auto-machinery. 3. Semi-Conductor equipment;
5. Machine tools; 6. Industrial Machinery;
7. Printing machine; 8. Paper-processing machine;
9. Textiles machine; 10. Electronic machinery;
11. Transport machinery; 12. Robot etc.
Rolled ball screws can not only be used in above general machinery, but also in many advanced industries. Rolled ball screw with a motor assembles electrical-mechanical actuator, which is more eco-friendly than hydraulic pump system. Nowadays it’s applied to electric vehicles, solar power plants, railway devices and many medical and leisure equipments.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C7 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 31-40mm |
| Flange: | Without Flange |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can worm screws be used for high torque applications?
Yes, worm screws can be used for high torque applications. The design of a worm screw mechanism allows for efficient torque transmission and multiplication, making it suitable for applications that require high torque output. Here are some key points to consider regarding the use of worm screws in high torque applications:
- Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio, which results in a lower output speed and higher output torque. This gear reduction capability allows worm screws to generate and transmit substantial torque, making them well-suited for high torque applications.
- Efficiency: While worm screws can provide high torque output, it’s important to consider the mechanical efficiency of the system. The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. It’s crucial to ensure that the efficiency of the worm screw mechanism meets the requirements of the specific high torque application.
- Load Holding: Another advantage of worm screws is their self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel, which provides resistance against backward rotation. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads in a fixed position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. In high torque applications where load holding is required, worm screws can provide reliable and secure positioning.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the worm screw and worm wheel should be carefully selected to withstand high torque loads. Both components should have sufficient strength and wear resistance to handle the transmitted torque without deformation or premature failure. Depending on the specific application requirements, materials such as hardened steel, bronze, or other alloys may be chosen to ensure the durability and performance of the worm screw assembly.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of a worm screw mechanism, especially in high torque applications. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Regular maintenance, including monitoring lubricant levels and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed, is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear or failure.
Overall, worm screws can be effectively used in high torque applications, thanks to their gear reduction capabilities, load-holding properties, and efficient torque transmission. However, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as mechanical efficiency, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance to ensure that the worm screw mechanism can meet the specific requirements and demands of the high torque application.

How do you troubleshoot problems in a worm screw gear system?
Troubleshooting problems in a worm screw gear system requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve issues effectively. Here are the steps involved in troubleshooting problems in a worm screw gear system:
- Identify the Symptoms: Start by identifying the specific symptoms or issues that indicate a problem in the worm screw gear system. This can include abnormal noise, reduced performance, increased backlash, erratic motion, or any other noticeable deviations from normal operation. Gather as much information as possible about the symptoms to help narrow down the potential causes.
- Inspect and Clean: Conduct a visual inspection of the worm screw gear system to check for any obvious signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or contamination. Inspect the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel for signs of pitting, scoring, or other surface irregularities. Clean the components if necessary to remove any debris or contaminants that may be affecting the system’s performance.
- Check Lubrication: Review the lubrication of the worm screw gear system. Ensure that the system is adequately lubricated with the recommended lubricant and that the lubricant is in good condition. Insufficient or degraded lubrication can result in increased friction, wear, and inefficiencies. Replenish or replace the lubricant as needed following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Inspect Alignment: Verify the alignment of the worm screw and the worm wheel. Misalignment can cause issues such as increased friction, wear, and reduced efficiency. Check for any signs of misalignment and make adjustments as necessary to ensure proper alignment of the components. This may involve repositioning or realigning the system or addressing any underlying factors contributing to the misalignment.
- Measure Backlash: Measure the amount of backlash present in the system. Excessive backlash can lead to reduced accuracy, loss of motion control, and diminished performance. Use appropriate measuring tools, such as dial indicators, to quantify the amount of backlash. If the backlash exceeds acceptable limits, consider adjusting the system to minimize or eliminate the excessive clearance between the threads and the teeth.
- Check Load and Overloading: Evaluate the loads applied to the worm screw gear system and compare them to the system’s design limits. Overloading the system can lead to accelerated wear, tooth breakage, or component deformation. If the loads exceed the system’s capacity, consider redistributing the load, upgrading the components, or redesigning the system to handle the required loads appropriately.
- Address Specific Issues: Based on the symptoms and findings from the inspection and measurements, address any specific issues identified in the worm screw gear system. This may involve repairing or replacing worn or damaged components, adjusting clearances, realigning the system, improving lubrication, or addressing any other factors contributing to the problems observed.
- Test and Monitor: After addressing the identified issues, test the worm screw gear system to verify that the problems have been resolved. Monitor the system’s performance during operation to ensure that the symptoms have been effectively mitigated. Pay attention to any new or recurring issues that may require further investigation or adjustments.
It is important to note that troubleshooting problems in a worm screw gear system may require expertise and experience. If you encounter complex or persistent issues that you are unable to resolve, it is recommended to seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals with knowledge in mechanical power transmission systems.

How does a worm screw differ from a regular screw?
In mechanical engineering, a worm screw differs from a regular screw in several key aspects. While both types of screws have helical threads, their designs and functions are distinct. Here are the primary differences between a worm screw and a regular screw:
- Motion Transmission: The primary function of a regular screw is to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. It typically has a single-threaded or multi-threaded configuration and is used for applications such as fastening, clamping, or lifting. On the other hand, a worm screw is designed to transmit motion and power between non-parallel shafts. It converts rotary motion along its axis into rotary motion perpendicular to its axis by meshing with a worm wheel or gear.
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio of a worm screw is typically much higher compared to that of a regular screw. The helical teeth of the worm screw and the worm wheel allow for a high reduction ratio in a single gear stage. This means that a small rotation of the worm screw can result in a significant rotation of the worm wheel. In contrast, a regular screw does not have a gear ratio and is primarily used for linear motion or force multiplication.
- Orientation and Shaft Arrangement: A regular screw is typically used in applications where the input and output shafts are parallel or nearly parallel. It transfers motion and force along the same axis. In contrast, a worm screw is designed for applications where the input and output shafts are perpendicular to each other. The orientation of the worm screw and the worm wheel allows for motion transmission between non-parallel shafts.
- Self-Locking: One distinctive characteristic of a worm screw is its self-locking property. The helical teeth of the worm screw create a wedging effect that prevents the worm wheel from driving the worm screw. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads without the need for additional braking mechanisms. Regular screws, on the other hand, do not have this self-locking capability.
- Applications: Regular screws find widespread use in numerous applications, including construction, manufacturing, woodworking, and everyday objects like screws used in fastening. They are primarily employed for linear motion, clamping, or force multiplication. Worm screws, on the other hand, are commonly used in applications that require significant speed reduction, torque multiplication, or motion transmission at right angles. Typical applications include conveyor systems, winches, lifting mechanisms, and heavy machinery.
These differences in design and function make worm screws and regular screws suitable for distinct applications. Regular screws are more commonly used for linear motion and force transfer along parallel or nearly parallel shafts, while worm screws excel in transmitting motion and power between non-parallel shafts with high gear reduction ratios.


editor by CX 2024-01-24
China Single Screw Extruder Gearbox Zlyj 133 double output worm gearbox
Product Description
1) Tiny quantity
2) Big transmission torque
3) High effectiveness
4) Reduced use
Parameters :
| Type | Spec | Input Electricity (kw) |
N( enter) | N(output) | Output Torque | Permitted axial thrust of output shaft(KN) |
Screw Diameter |
Length-diameter ratio |
| (N@m) | ||||||||
| ZLYJ | 112-8 | 5.5 | 800 | a hundred | 525 | 35 | Ø35 | twenty five:01:00 |
| 133-8 | 8 | 800 | 100 | 764 | 39 | Ø50 | twenty five:01:00 | |
| 146-10 | eleven | one thousand | one hundred | 1050 | 54 | Ø55 | twenty five:01:00 | |
| 173-10 | eighteen.five | 900 | 90 | 1962 | one hundred ten | Ø65 | 25:01:00 | |
| 200-12.five | thirty | one thousand | 80 | 3581 | a hundred and fifty five | Ø75 | twenty five:01:00 | |
| 225-twelve.five | forty five | 1000 | 80 | 5371 | 180 | Ø90 | twenty five:01:00 | |
| 250-16 | 55 | 1120 | 70 | 7503 | 192 | Ø105 | twenty five:01:00 | |
| 280-16 | 75 | 960 | 60 | 7643 | 258 | Ø110 | 25:01:00 | |
| 315-16 | eighty five | 960 | 60 | 13528 | 287 | Ø120 | 25:01:00 | |
| 330-sixteen | a hundred and ten | 960 | sixty | 17507 | 360 | Ø135 | 25:01:00 | |
| 375-16 | 132 | 960 | sixty | 21008 | 390 | Ø150 | 25:01:00 | |
| 395-16 | 185 | 960 | 60 | 29442 | 400 | Ø160 | twenty five:01:00 | |
| 420-16 | 160 | 960 | 60 | 31831 | 430 | Ø160 | twenty five:01:00 | |
| 420-sixteen | 220 | 960 | sixty | 31831 | 430 | Ø170 | 25:01:00 | |
| 450-twenty | 213 | one thousand | 60 | 40640 | five hundred | Ø160/Ø170 | 25:01:00 | |
| 560-seventeen | 540 | a thousand | fifty | 84034 | 700 | Ø200 | 25:01:00 | |
| 630-10 | 540 | one thousand | fifty | 15712 | 770 | Ø250 | twenty five:01:00 |
ZLYJ gearbox sequence are transmission devices, which are specifically made for single-screw extruder with high precision, difficult equipment surface, accompany with thrust. Adopting the technical technical specs stipulated in JB/T9050.1-1999, all CZPT gearboxes are designed appropriately.
Primary Characteristics:
one. The materials of equipment is the higher toughness alloy steel, it is made by carburizing, quenching (and other heat treatment method), gringding process at very last. The equipment is in high precison ( 6 quality ) and higher hardness ( reaches HRC54-62). Apart from, it features reduced noise when running.
2. It is made up of higher bearing capability thrust, which is executed reputable and can endure larger axial thrust.
three. All the products are dealt with by pressured lubrication and cooling technique except quite few tiny specification merchandise.
4. CZPT sequence gearbox is adopted by 6-side processing box. Its normal installation is horizontal, but can also be altered to vertical set up according to customer’s requirment.
five. Performance transmission, reduced noise, prolonged operaton time.
Package deal
Packing for screw and barrel
1) Picket scenario bundle
two) Plastic movie deal
three) Appropriate to transportation
Why decide on us?
A> prolonged time experience and heritage
B> long time nitriding remedy and heating treatment method by by itself
C>advanced Fanuk series CNC personal computer-controlled milling equipment
D>depth hole drilling equipment in 8meters length, which ensure the straigtnss of barrel within.
E> CAD drawing confirmation ahead of begin generating
F> Prompt following sale service
G>Land owner and registration cash twenty five, 000, 000RMB
About us:
ZHangZhoug pinbo plastic machinery co.,ltd is located in HangZhou HangZhou city with brand of PYM(Former HangZhou yumin machine screw co.ltd since 1988). The company is specialized in making screw barrel, gearbox zlyj series, t die, filter and extruder machine. It has become one of the largest supplier of main parts in HangZhou city which
is the basement of plastic machines.
If there is any dilemma, you can speak to with us at any time, we will reply you as soon as achievable!
|
US $400-5,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Machinery, Reducer |
|---|---|
| Function: | Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Three-Ring |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Torque Arm Type |
| Step: | Stepless |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Type | Spec | Input Power (kw) |
N( enter) | N(output) | Output Torque | Permitted axial thrust of output shaft(KN) |
Screw Diameter |
Length-diameter ratio |
| (N@m) | ||||||||
| ZLYJ | 112-8 | 5.5 | 800 | 100 | 525 | 35 | Ø35 | 25:01:00 |
| 133-8 | 8 | 800 | 100 | 764 | 39 | Ø50 | 25:01:00 | |
| 146-10 | 11 | 1000 | 100 | 1050 | 54 | Ø55 | 25:01:00 | |
| 173-10 | 18.5 | 900 | 90 | 1962 | 110 | Ø65 | 25:01:00 | |
| 200-12.5 | 30 | 1000 | 80 | 3581 | 155 | Ø75 | 25:01:00 | |
| 225-12.5 | 45 | 1000 | 80 | 5371 | 180 | Ø90 | 25:01:00 | |
| 250-16 | 55 | 1120 | 70 | 7503 | 192 | Ø105 | 25:01:00 | |
| 280-16 | 75 | 960 | 60 | 7643 | 258 | Ø110 | 25:01:00 | |
| 315-16 | 85 | 960 | 60 | 13528 | 287 | Ø120 | 25:01:00 | |
| 330-16 | 110 | 960 | 60 | 17507 | 360 | Ø135 | 25:01:00 | |
| 375-16 | 132 | 960 | 60 | 21008 | 390 | Ø150 | 25:01:00 | |
| 395-16 | 185 | 960 | 60 | 29442 | 400 | Ø160 | 25:01:00 | |
| 420-16 | 160 | 960 | 60 | 31831 | 430 | Ø160 | 25:01:00 | |
| 420-16 | 220 | 960 | 60 | 31831 | 430 | Ø170 | 25:01:00 | |
| 450-20 | 213 | 1000 | 60 | 40640 | 500 | Ø160/Ø170 | 25:01:00 | |
| 560-17 | 540 | 1000 | 50 | 84034 | 700 | Ø200 | 25:01:00 | |
| 630-10 | 540 | 1000 | 50 | 103132 | 770 | Ø250 | 25:01:00 |
|
US $400-5,000 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Machinery, Reducer |
|---|---|
| Function: | Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Three-Ring |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Torque Arm Type |
| Step: | Stepless |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Type | Spec | Input Power (kw) |
N( enter) | N(output) | Output Torque | Permitted axial thrust of output shaft(KN) |
Screw Diameter |
Length-diameter ratio |
| (N@m) | ||||||||
| ZLYJ | 112-8 | 5.5 | 800 | 100 | 525 | 35 | Ø35 | 25:01:00 |
| 133-8 | 8 | 800 | 100 | 764 | 39 | Ø50 | 25:01:00 | |
| 146-10 | 11 | 1000 | 100 | 1050 | 54 | Ø55 | 25:01:00 | |
| 173-10 | 18.5 | 900 | 90 | 1962 | 110 | Ø65 | 25:01:00 | |
| 200-12.5 | 30 | 1000 | 80 | 3581 | 155 | Ø75 | 25:01:00 | |
| 225-12.5 | 45 | 1000 | 80 | 5371 | 180 | Ø90 | 25:01:00 | |
| 250-16 | 55 | 1120 | 70 | 7503 | 192 | Ø105 | 25:01:00 | |
| 280-16 | 75 | 960 | 60 | 7643 | 258 | Ø110 | 25:01:00 | |
| 315-16 | 85 | 960 | 60 | 13528 | 287 | Ø120 | 25:01:00 | |
| 330-16 | 110 | 960 | 60 | 17507 | 360 | Ø135 | 25:01:00 | |
| 375-16 | 132 | 960 | 60 | 21008 | 390 | Ø150 | 25:01:00 | |
| 395-16 | 185 | 960 | 60 | 29442 | 400 | Ø160 | 25:01:00 | |
| 420-16 | 160 | 960 | 60 | 31831 | 430 | Ø160 | 25:01:00 | |
| 420-16 | 220 | 960 | 60 | 31831 | 430 | Ø170 | 25:01:00 | |
| 450-20 | 213 | 1000 | 60 | 40640 | 500 | Ø160/Ø170 | 25:01:00 | |
| 560-17 | 540 | 1000 | 50 | 84034 | 700 | Ø200 | 25:01:00 | |
| 630-10 | 540 | 1000 | 50 | 103132 | 770 | Ø250 | 25:01:00 |
Worm Reducer
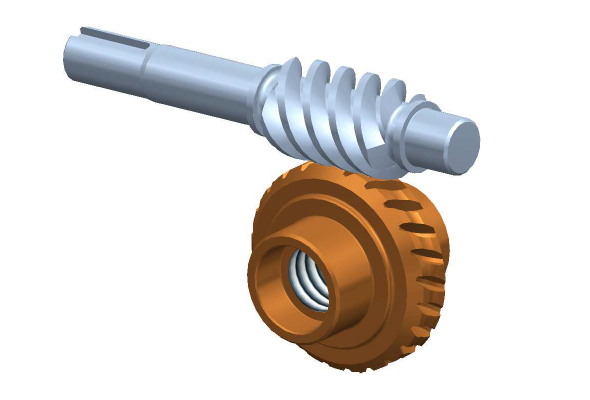
Worm reducers are commonly used to reduce the Agknx produced by a rotating shaft. They can achieve reduction ratios of five to sixty. In contrast, a single-stage hypoid gear can achieve up to a 120:1 reduction ratio. For further reduction, another type of gearing is used. So, a single stage worm reducer cannot achieve higher ratios than these.<br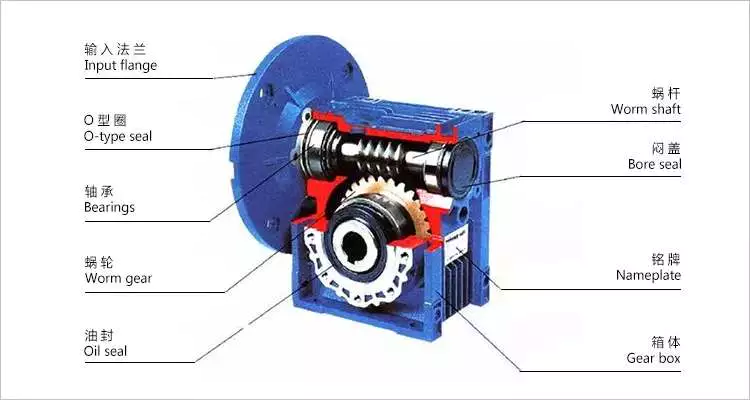
Mechanics
A worm reducer is an auxiliary mechanical device that uses worms to reduce the size of a rotating shaft. These worms have a range of tooth forms. One form is a line weave twist surface. Another is a trapezoid based on a central cross section. The trapezoid can be perpendicular to the tooth cross section, or it can be normal to the root cross section. Other forms include involute helicoids and convolute worms, which use a straight line intersecting the involute generating line.
Worm gears are lubricated with a special lubricant. Because worm gears are complex, it’s important to use the correct lubricant. Worm gear manufacturers provide approved lubricants for their gears. Using unapproved gear oil can damage your reducer’s efficiency. The right lubricant depends on several factors, including load, speed, duty cycle, and expected operating temperatures.
The efficiency of a worm gear reducer depends on several factors, including losses at gear mesh, losses in the bearings, and windage in the oil seal lip. In addition, the worm gear reducer’s efficiency varies with ambient temperature and operating temperature. The worm gear reducer’s efficiency can also vary with the ratio of the load. Moreover, worm gear reducers are subject to break-in.
Worm gear reducers are used in many different applications. They are typically used in small electric motors, but they’re also used in conveyor systems, presses, elevators, and mining applications. Worm gears are also commonly found in stringed musical instruments.
Worm gears have excellent reduction ratios and high Agknx multiplication, and they’re often used as speed reducers in low to medium-speed applications. However, the efficiency of worm gear reducers decreases with increasing ratios.
Sizes
Worm reducers come in different sizes and tooth shapes. While the tooth shape of one worm is similar to the other, different worms are designed to carry a different amount of load. For example, a circular arc worm may have a different tooth shape than one with a secondary curve. Worm gears can also be adjusted for backlash. The backlash is the difference between the advancing and receding arc.
There are two sizes of worm reducers available from Agknx Transmission. The SW-1 and SW-5 models offer ratios of 3.5:1 to 60:1 and 5:1 to 100:1 respectively. The size of the worm reducer is determined by the required gear ratio.
Worm gears have different thread counts. One is based on the central cross-section of the worm, and the other is on the right. Worm gears can have either a single or double thread. Single-threaded gears will reduce speed by 50 percent, while double-threaded gears will reduce speed by 25 percent.
Worm gear reducers are lightweight and highly reliable. They can accommodate a variety of NEMA input flanges and hollow output bore sizes. Worm reducers can be found at 6 regional warehouses, with prepaid freight. To make a purchasing decision, you should consider the horsepower and Agknx requirements of your specific application.
Applications
The Worm Reducer market is a global business that is dominated by the North American and European regions. The report provides in-depth information on the market trends, key challenges, and opportunities. It also examines the current state of the industry and projects future market growth. The report is organized into segments based on product type, major geographical regions, and application. It also presents statistics and key data about the market.
Worm gear reducers have many applications. They can be used to increase the speed of convey belts. They also help reduce noise. Worm gears have many teeth that touch the gear mesh, which makes them quieter. Moreover, the worm gears require only a single stage reducer, reducing the number of moving parts in the system.
The worm gear has long life and is suitable for different industries. It is a perfect choice for elevators and other applications that need fast stopping and braking. Its compact size and ability to hold a load make it suitable for these applications. It also prevents the load from free-falling as a result of a sudden braking. Worm gears can also be used in heavy-duty machinery such as rock crushers.
Worm gears are similar to ordinary gears except that they transfer motion at a 90-degree angle. As a result, the worm gears are extremely quiet, making them a suitable option for noise sensitive applications. They are also excellent for low-voltage applications, where the noise is critical.
Worm gears are ideal for applications with space restrictions, because they require fewer gear sets. The worm gears also allow for a smaller gearbox size. Consequently, they are the perfect choice for machines that are space-constrained, such as conveyors and packaging equipment.
Cost
The lifespan of a worm gear reducer is comparable to other gear reducers. Worm gears have a long history of innovation and use in various industries, from shipbuilding to automobile manufacturing. Today, these gear reducers are still popular with engineers. However, there are some things to keep in mind before buying one.
In the first place, a worm reducer needs to be affordable. Generally, a worm reducer costs about $120. The price varies with the brand name and features. Some products are more expensive than others, so be sure to shop around for the best price. In addition, it is important to consider the quality and design of the worm reducer before making a purchase.
Worm gear manufacturers have made significant advancements in materials, design and manufacturing. These advancements, along with the use of advanced lubricants, have resulted in significant increases in efficiency. For example, double enveloping worm gear reducers have improved efficiency by three to eight percentage points. This improvement was achieved through rigorous testing of manufacturing processes and materials. With these improvements, worm gear reducers have become more desirable in today’s market.
Worm reducers are extremely versatile and reliable, and are available in a variety of sizes. Domestic manufacturers usually stock a large selection of reducers, and are often able to ship them the same day you place your order. Most major domestic worm gear reducer manufacturers also share some critical mounting dimensions, such as the output shaft diameter, the mounting hole location, and the overall reducer housing height. Most manufacturers also offer standardized gear ratios. Some manufacturers have also improved gear design and added synthetic lubricants for better performance.
In addition, different tooth shapes of worms can increase their load carrying capacity. They can be used on secondary curves and circular arc cross sections. Moreover, the pitch point defines the boundary of the cross section. The mesh on the receding arc is smoother than that of the advancing arc. However, in the case of negative shifting, most of the mesh is on the receding arc.
Self-locking function
A worm reducer has a self-locking function. When a worm is fitted with all of its addendum teeth, the total number of teeth in the system should be greater than 40. This self-locking function is achieved through the worm’s rack and pinion mechanism. The worm’s self-locking feature can prevent the load from being dropped and is useful for many applications.
The self-locking function of a worm reducer is possible for two main reasons. First of all, a worm reducer uses two or more gears. One gear is placed at the input, and the other gear runs the output shaft. This mechanism produces a torque, which is transmitted to a spur gear.
Worm reducers can be used in a variety of industrial applications. Because of their self-locking function, they are useful for preventing back-driving. They are also helpful for lifting and holding loads. Their self-locking mechanism allows for a large gear reduction ratio without increasing the size of a gear box.
Self-locking gears can be used to prevent back-driving and inertial driving. This is useful for many industries and can prevent backdriving. However, one major disadvantage of self-locking gears is their sensitivity to operating conditions. Lubrication, vibration, and misalignment can affect their reliability.
Embodiments of the invention provide a self-locking mechanism that prevents back-driving but allows forward-driving. The self-locking mechanism may comprise first and second ratchet cams disposed about a gear member. A releasable coupling member may be interposed between the gear member and the ratchet cam. This facilitates selective coupling and decoupling.
The worm reducer has several advantages. Its compact design is ideal for many mechanical transmission systems. It also provides greater load capacity than a cross-axis helical gear mechanism.


editor by czh 2022-11-29
China supplier Factory Price Rolled Thread Double Nut Ball Screw for Precision Machine near me supplier
Product Description
Product Description
| Brand | WF |
| Material | S55C alloy steel, 50CrMo4, SCM420H |
| Diameter | 8-80mm |
| Item | SFNI/SFNU/SFH/SFY/SFS/DFS/SFV/DFV/SFI/DFI/SFU/DFU/SFM/SFK/SCI/BSH |
Details
PARAMETERS
- STRUCTURE
DATA DETAILS
MATCH
PACKING & DELIVERY
Company Introduction
HangZhou CZPT Precision Machinery Co., Ltd. established in 2, HangZhou, P.R.C
http://chromedbars
http://chromedbars
Lead Screws and Clamp Style Collars
If you have a lead screw, you’re probably interested in learning about the Acme thread on this type of shaft. You might also be interested in finding out about the Clamp style collars and Ball screw nut. But before you buy a new screw, make sure you understand what the terminology means. Here are some examples of screw shafts:
Acme thread
The standard ACME thread on a screw shaft is made of a metal that is resistant to corrosion and wear. It is used in a variety of applications. An Acme thread is available in a variety of sizes and styles. General purpose Acme threads are not designed to handle external radial loads and are supported by a shaft bearing and linear guide. Their design is intended to minimize the risk of flank wedging, which can cause friction forces and wear. The Centralizing Acme thread standard caters to applications without radial support and allows the thread to come into contact before its flanks are exposed to radial loads.
The ACME thread was first developed in 1894 for machine tools. While the acme lead screw is still the most popular screw in the US, European machines use the Trapezoidal Thread (Metric Acme). The acme thread is a stronger and more resilient alternative to square threads. It is also easier to cut than square threads and can be cut by using a single-point threading die.
Similarly to the internal threads, the metric versions of Acme are similar to their American counterparts. The only difference is that the metric threads are generally wider and are used more frequently in industrial settings. However, the metric-based screw threads are more common than their American counterparts worldwide. In addition, the Acme thread on screw shafts is used most often on external gears. But there is still a small minority of screw shafts that are made with a metric thread.
ACME screws provide a variety of advantages to users, including self-lubrication and reduced wear and tear. They are also ideal for vertical applications, where a reduced frictional force is required. In addition, ACME screws are highly resistant to back-drive and minimize the risk of backlash. Furthermore, they can be easily checked with readily available thread gauges. So, if you’re looking for a quality ACME screw for your next industrial project, look no further than ACME.
Lead screw coatings
The properties of lead screw materials affect their efficiency. These materials have high anti-corrosion, thermal resistance, and self-lubrication properties, which eliminates the need for lubrication. These coating materials include polytetrafluoroethylene (PFE), polyether ether ketone (PEK), and Vespel. Other desirable properties include high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and rigidity.
The most common materials for lead screws are carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Lead screw coatings can be PTFE-based to withstand harsh environments and remove oil and grease. In addition to preventing corrosion, lead screw coatings improve the life of polymer parts. Lead screw assembly manufacturers offer a variety of customization options for their lead screw, including custom-molded nuts, thread forms, and nut bodies.
Lead screws are typically measured in rpm, or revolutions per minute. The PV curve represents the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. This value is affected by the material used in the construction of the screw, lubrication conditions, and end fixity. The critical speed of lead screws is determined by their length and minor diameter. End fixity refers to the support for the screw and affects its rigidity and critical speed.
The primary purpose of lead screws is to enable smooth movement. To achieve this, lead screws are usually preloaded with axial load, enabling consistent contact between a screw’s filets and nuts. Lead screws are often used in linear motion control systems and feature a large area of sliding contact between male and female threads. Lead screws can be manually operated or mortised and are available in a variety of sizes and materials. The materials used for lead screws include stainless steel and bronze, which are often protected by a PTFE type coating.
These screws are made of various materials, including stainless steel, bronze, and various plastics. They are also made to meet specific requirements for environmental conditions. In addition to lead screws, they can be made of stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Surface coatings can improve the screw’s corrosion resistance, while making it more wear resistant in tough environments. A screw that is coated with PTFE will maintain its anti-corrosion properties even in tough environments.
Clamp style collars
The screw shaft clamp style collar is a basic machine component, which is attached to the shaft via multiple screws. These collars act as mechanical stops, load bearing faces, or load transfer points. Their simple design makes them easy to install. This article will discuss the pros and cons of this style of collar. Let’s look at what you need to know before choosing a screw shaft clamp style collar. Here are some things to keep in mind.
Clamp-style shaft collars are a versatile mounting option for shafts. They have a recessed screw that fully engages the thread for secure locking. Screw shaft clamp collars come in different styles and can be used in both drive and power transmission applications. Listed below are the main differences between these 2 styles of collars. They are compatible with all types of shafts and are able to handle axial loads of up to 5500 pounds.
Clamp-style shaft collars are designed to prevent the screw from accidentally damaging the shaft when tightened. They can be tightened with a set screw to counteract the initial clamping force and prevent the shaft from coming loose. However, when tightening the screw, you should use a torque wrench. Using a set screw to tighten a screw shaft collar can cause it to warp and reduce the surface area that contacts the shaft.
Another key advantage to Clamp-style shaft collars is that they are easy to install. Clamp-style collars are available in one-piece and two-piece designs. These collars lock around the shaft and are easy to remove and install. They are ideal for virtually any shaft and can be installed without removing any components. This type of collar is also recommended for those who work on machines with sensitive components. However, be aware that the higher the OD, the more difficult it is to install and remove the collar.
Screw shaft clamp style collars are usually one-piece. A two-piece collar is easier to install than a one-piece one. The two-piece collars provide a more effective clamping force, as they use the full seating torque. Two-piece collars have the added benefit of being easy to install because they require no tools to install. You can disassemble one-piece collars before installing a two-piece collar.
Ball screw nut
The proper installation of a ball screw nut requires that the nut be installed on the center of the screw shaft. The return tubes of the ball nut must be oriented upward so that the ball nut will not overtravel. The adjusting nut must be tightened against a spacer or spring washer, then the nut is placed on the screw shaft. The nut should be rotated several times in both directions to ensure that it is centered.
Ball screw nuts are typically manufactured with a wide range of preloads. Large preloads are used to increase the rigidity of a ball screw assembly and prevent backlash, the lost motion caused by a clearance between the ball and nut. Using a large amount of preload can lead to excessive heat generation. The most common preload for ball screw nuts is 1 to 3%. This is usually more than enough to prevent backlash, but a higher preload will increase torque requirements.
The diameter of a ball screw is measured from its center, called the ball circle diameter. This diameter represents the distance a ball will travel during 1 rotation of the screw shaft. A smaller diameter means that there are fewer balls to carry the load. Larger leads mean longer travels per revolution and higher speeds. However, this type of screw cannot carry a greater load capacity. Increasing the length of the ball nut is not practical, due to manufacturing constraints.
The most important component of a ball screw is a ball bearing. This prevents excessive friction between the ball and the nut, which is common in lead-screw and nut combinations. Some ball screws feature preloaded balls, which avoid “wiggle” between the nut and the ball. This is particularly desirable in applications with rapidly changing loads. When this is not possible, the ball screw will experience significant backlash.
A ball screw nut can be either single or multiple circuits. Single or multiple-circuit ball nuts can be configured with 1 or 2 independent closed paths. Multi-circuit ball nuts have 2 or more circuits, making them more suitable for heavier loads. Depending on the application, a ball screw nut can be used for small clearance assemblies and compact sizes. In some cases, end caps and deflectors may be used to feed the balls back to their original position.


China factory C7 Precision Rolled Thread Double Nut Ball Screw near me manufacturer
Product Description
Product Description
| Brand | WF |
| Material | S55C alloy steel, 50CrMo4, SCM420H |
| Diameter | 8-80mm |
| Item | SFNI/SFNU/SFH/SFY/SFS/DFS/SFV/DFV/SFI/DFI/SFU/DFU/SFM/SFK/SCI/BSH |
Details
PARAMETERS
- STRUCTURE
DATA DETAILS
MATCH
PACKING & DELIVERY
Company Introduction
HangZhou CZPT Precision Machinery Co., Ltd. established in 2, HangZhou, P.R.C
http://chromedbars
http://chromedbars
The Four Basic Components of a Screw Shaft
There are 4 basic components of a screw shaft: the Head, the Thread angle, and the Threaded shank. These components determine the length, shape, and quality of a screw. Understanding how these components work together can make purchasing screws easier. This article will cover these important factors and more. Once you know these, you can select the right type of screw for your project. If you need help choosing the correct type of screw, contact a qualified screw dealer.
Thread angle
The angle of a thread on a screw shaft is the difference between the 2 sides of the thread. Threads that are unified have a 60 degree angle. Screws have 2 parts: a major diameter, also known as the screw’s outside diameter, and a minor diameter, or the screw’s root diameter. A screw or nut has a major diameter and a minor diameter. Each has its own angle, but they all have 1 thing in common – the angle of thread is measured perpendicularly to the screw’s axis.
The pitch of a screw depends on the helix angle of the thread. In a single-start screw, the lead is equal to the pitch, and the thread angle of a multiple-start screw is based on the number of starts. Alternatively, you can use a square-threaded screw. Its square thread minimizes the contact surface between the nut and the screw, which improves efficiency and performance. A square thread requires fewer motors to transfer the same load, making it a good choice for heavy-duty applications.
A screw thread has 4 components. First, there is the pitch. This is the distance between the top and bottom surface of a nut. This is the distance the thread travels in a full revolution of the screw. Next, there is the pitch surface, which is the imaginary cylinder formed by the average of the crest and root height of each tooth. Next, there is the pitch angle, which is the angle between the pitch surface and the gear axis.
Head
There are 3 types of head for screws: flat, round, and hexagonal. They are used in industrial applications and have a flat outer face and a conical interior. Some varieties have a tamper-resistant pin in the head. These are usually used in the fabrication of bicycle parts. Some are lightweight, and can be easily carried from 1 place to another. This article will explain what each type of head is used for, and how to choose the right 1 for your screw.
The major diameter is the largest diameter of the thread. This is the distance between the crest and the root of the thread. The minor diameter is the smaller diameter and is the distance between the major and minor diameters. The minor diameter is half the major diameter. The major diameter is the upper surface of the thread. The minor diameter corresponds to the lower extreme of the thread. The thread angle is proportional to the distance between the major and minor diameters.
Lead screws are a more affordable option. They are easier to manufacture and less expensive than ball screws. They are also more efficient in vertical applications and low-speed operations. Some types of lead screws are also self-locking, and have a high coefficient of friction. Lead screws also have fewer parts. These types of screw shafts are available in various sizes and shapes. If you’re wondering which type of head of screw shaft to buy, this article is for you.
Threaded shank
Wood screws are made up of 2 parts: the head and the shank. The shank is not threaded all the way up. It is only partially threaded and contains the drive. This makes them less likely to overheat. Heads on wood screws include Oval, Round, Hex, Modified Truss, and Flat. Some of these are considered the “top” of the screw.
Screws come in many sizes and thread pitches. An M8 screw has a 1.25-mm thread pitch. The pitch indicates the distance between 2 identical threads. A pitch of 1 is greater than the other. The other is smaller and coarse. In most cases, the pitch of a screw is indicated by the letter M followed by the diameter in millimetres. Unless otherwise stated, the pitch of a screw is greater than its diameter.
Generally, the shank diameter is smaller than the head diameter. A nut with a drilled shank is commonly used. Moreover, a cotter pin nut is similar to a castle nut. Internal threads are usually created using a special tap for very hard metals. This tap must be followed by a regular tap. Slotted machine screws are usually sold packaged with nuts. Lastly, studs are often used in automotive and machine applications.
In general, screws with a metric thread are more difficult to install and remove. Fortunately, there are many different types of screw threads, which make replacing screws a breeze. In addition to these different sizes, many of these screws have safety wire holes to keep them from falling. These are just some of the differences between threaded screw and non-threaded. There are many different types of screw threads, and choosing the right 1 will depend on your needs and your budget.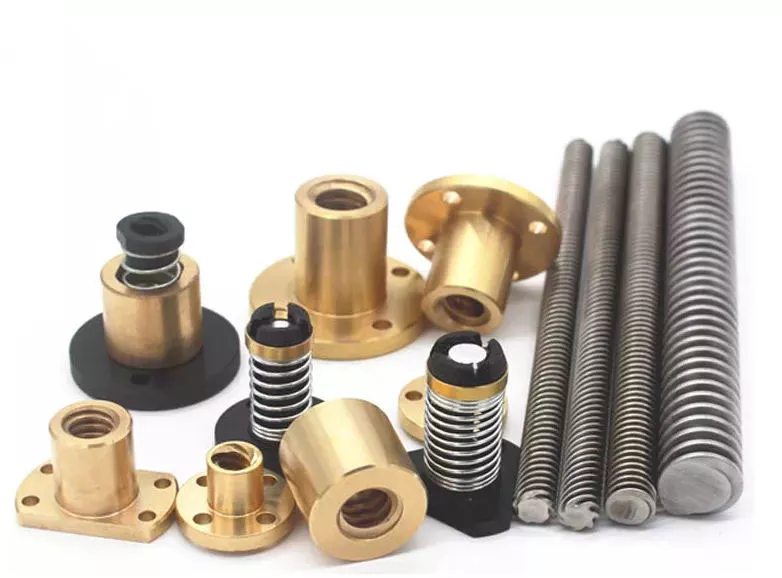
Point
There are 3 types of screw heads with points: cone, oval, and half-dog. Each point is designed for a particular application, which determines its shape and tip. For screw applications, cone, oval, and half-dog points are common. Full dog points are not common, and they are available in a limited number of sizes and lengths. According to ASTM standards, point penetration contributes as much as 15% of the total holding power of the screw, but a cone-shaped point may be more preferred in some circumstances.
There are several types of set screws, each with its own advantage. Flat-head screws reduce indentation and frequent adjustment. Dog-point screws help maintain a secure grip by securing the collar to the screw shaft. Cup-point set screws, on the other hand, provide a slip-resistant connection. The diameter of a cup-point screw is usually half of its shaft diameter. If the screw is too small, it may slack and cause the screw collar to slip.
The UNF series has a larger area for tensile stress than coarse threads and is less prone to stripping. It’s used for external threads, limited engagement, and thinner walls. When using a UNF, always use a standard tap before a specialized tap. For example, a screw with a UNF point is the same size as a type C screw but with a shorter length.
Spacer
A spacer is an insulating material that sits between 2 parts and centers the shaft of a screw or other fastener. Spacers come in different sizes and shapes. Some of them are made of Teflon, which is thin and has a low coefficient of friction. Other materials used for spacers include steel, which is durable and works well in many applications. Plastic spacers are available in various thicknesses, ranging from 4.6 to 8 mm. They’re suitable for mounting gears and other items that require less contact surface.
These devices are used for precision fastening applications and are essential fastener accessories. They create clearance gaps between the 2 joined surfaces or components and enable the screw or bolt to be torqued correctly. Here’s a quick guide to help you choose the right spacer for the job. There are many different spacers available, and you should never be without one. All you need is a little research and common sense. And once you’re satisfied with your purchase, you can make a more informed decision.
A spacer is a component that allows the components to be spaced appropriately along a screw shaft. This tool is used to keep space between 2 objects, such as the spinning wheel and an adjacent metal structure. It also helps ensure that a competition game piece doesn’t rub against an adjacent metal structure. In addition to its common use, spacers can be used in many different situations. The next time you need a spacer, remember to check that the hole in your screw is threaded.
Nut
A nut is a simple device used to secure a screw shaft. The nut is fixed on each end of the screw shaft and rotates along its length. The nut is rotated by a motor, usually a stepper motor, which uses beam coupling to accommodate misalignments in the high-speed movement of the screw. Nuts are used to secure screw shafts to machined parts, and also to mount bearings on adapter sleeves and withdrawal sleeves.
There are several types of nut for screw shafts. Some have radial anti-backlash properties, which prevent unwanted radial clearances. In addition, they are designed to compensate for thread wear. Several nut styles are available, including anti-backlash radial nuts, which have a spring that pushes down on the nut’s flexible fingers. Axial anti-backlash nuts also provide thread-locking properties.
To install a ball nut, you must first align the tangs of the ball and nut. Then, you must place the adjusting nut on the shaft and tighten it against the spacer and spring washer. Then, you need to lubricate the threads, the ball grooves, and the spring washers. Once you’ve installed the nut, you can now install the ball screw assembly.
A nut for screw shaft can be made with either a ball or a socket. These types differ from hex nuts in that they don’t need end support bearings, and are rigidly mounted at the ends. These screws can also have internal cooling mechanisms to improve rigidity. In this way, they are easier to tension than rotating screws. You can also buy hollow stationary screws for rotator nut assemblies. This type is great for applications requiring high heat and wide temperature changes, but you should be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions.


China factory Double Wire Hose Clamp Pipe Clip Screw near me factory
Product Description
Double Wire Hose Clamp Pipe Clip Screw
Hose Clamp Type:
German Type Worm Drive Hose Clamp
American Type Worm Drive Hose Clamp
British Type Worm Drive Hose Clamp
Heavy Duty Hose Clamp
Double Bolts Heavy Duty Hose Clamp
Single Ear Stepless Hose Clamp
Double Wire Hose Clamp
Product features:
Screw Type; Hexagon Head; Product Name: Hose Clamp
Screw: M5*30 to M8*80; Max Clamping Diameter: 120mm (2.5″)
Country of Manufacture: CHINA; Material: Galvanized Iron
Main Color: silver tone or copper tone
Product description:
Our hose clips are made by premium grade materials. Over the years, they are proven to be safe, durable and capable in combating extreme clamping conditions.
Attach hose to equipment fittings quickly and securely. Tighten by turning the screw with a screwdriver or hex head wrench. Spring steel double wire maintains pressure and holds hose securely in place. The Double-Loop design has tighter grip on hose.
– Unique Clamp housing ensures maximum thrust when tightening
– Release or tighten the bolt to adjust the band diameter range
– Exceeds BSI standards in all areas, providing excellent reliability
– Lightweight, low profile, compact design allows ease of installation in restricted applications
Specifications:
| Size | Wire Diameter | Screw |
| mm | ||
| 11-14 | 1.5 | M5*30 |
| 13-16 | ||
| 15-18 | ||
| 17-20 | 1.8 | |
| 19-22 | ||
| 20-24 | ||
| 22-26 | ||
| 24-28 | ||
| 26-30 | 2.2 | M6*40 |
| 28-32 | ||
| 31-35 | ||
| 34-38 | ||
| 35-40 | ||
| 37-42 | ||
| 40-45 | ||
| 43-48 | M6*50 | |
| 45-50 | ||
| 47-52 | ||
| 50-55 | ||
| 53-58 | ||
| 55-60 | M6*60 | |
| 54-62 | ||
| 60-65 | ||
| 63-68 | ||
| 65-70 | M6*70 | |
| 70-75 | ||
| 75-80 | ||
| 80-85 | 2.5 | |
| 84-90 | ||
| 89-95 | ||
| 94-100 | M8*80 | |
| 98-105 | ||
| 103-110 | ||
| 108-115 | ||
| 113-120 |
Screw Shaft Types
If you’re looking for a screw shaft, but aren’t sure which type to buy, you’re in luck. In this article, we’ll talk about the different types, including Threaded shank, Round head, and Machined. Once you’ve read it, you’ll know which type to buy. Then, you can decide whether you want a ball screw nut or a threaded shank.
Machined screw shafts
Besides the standard stainless steel shaft, manufacturers also provide a variety of other materials, such as titanium, bronze, and brass. In addition to stainless steel, manufacturers also provide a variety of top-coating options, including zinc, brass, and chromium. Aluminum screws are not particularly durable and are easily affected by weather. Most screw shafts feature self-locking mechanisms. They are especially useful in C-clamps, vises, and screw-top container lids.
For applications where accuracy is vital, a ball screw shaft needs to be annealed. A heat treatment can be performed on the ball screw shaft to ensure that both ends are heated evenly. In this process, the shaft will be more durable, while maintaining its high-precision properties. These screw shafts are a key component in computer-controlled motion-control systems, wire bonding, and other industries that require high-precision and high-quality performance.
Depending on the material used, screw shafts can be made of stainless steel or titanium. High-precision CNC machines and lathes are typically used to manufacture screw shafts. Various shapes and sizes are available, each with a specific application. Whether you need a small or large screw, you can find 1 to fit your needs. And since each size requires a different material, your choice of material is important as well.
In general, the materials used for machining screw shafts are steel, stainless steel, titanium, brass, bronze, and aluminum. Metals that resist corrosion are also commonly used. Other materials for screw shafts are Teflon, nylon, and nylon. You can also find threaded screw shafts in materials such as porcelain, glass, and ceramic. If you want to use your screws in a unique material, consider purchasing a customized one.
Ball screw nuts
If you have a screw shaft, the last thing you want to worry about is the ball nut slipping off. To prevent this, you can place a temporary stop in the shaft’s grooves to ensure that the ball nut does not slide off. When you remove the stop, you can then install the ball screw nut. But, before you can install the ball screw nut, you have to make sure that you have a good grip on the shaft.
When selecting ball screw nuts, it’s important to consider how much preload you need to apply to avoid excessive backlash. Preloading eliminates this problem by making the ball nut compact. It also prevents backlash, which is lost motion caused by clearance between the ball and nut. Backlash disrupts repeatability and accuracy. This is where spacer preloading comes in. You can insert a spacer between the 2 ball nuts to transmit the force to the nut. However, you should keep in mind that this method reduces the load capacity of the ball screw.
The critical speed of a screw is the maximum rotating speed before it whips. This critical speed is influenced by several factors, including the diameter of the screw shaft, the number of support elements, and the material. By adjusting these factors, you can reduce the number of components used and the amount of time it takes to assemble the screw shaft. In addition, you can also reduce the number of components and avoid stacking tolerances. However, the critical speed of plastic nuts is limited due to sliding friction.
The ball screw nut has several characteristics that make it unique. Its most prominent feature is the presence of ball bearings. These balls help reduce friction between the screw nut and the shaft. Without ball bearings, the friction would be too high to function properly. Another important characteristic is the groove profile of the nut and ball. These 2 features ensure that the ball and the nut meet at 2 points. You’ll be amazed by the results of the work of these ball screw nuts.
Threaded shank
Wood screws are usually not fully threaded because the shank has an unthreaded portion at the top. This shoulder part forces the screw to compress 2 pieces of wood, which prevents the screw from overheating and compromising the materials strength. As the screw is threaded partially up, it is not as difficult to remove as a fully threaded screw. However, it is important to note that a wood screw will not hold as tightly as 1 with a fully threaded shank.
In addition to being universal, screw threads can be of different sizes. For example, a M8 screw has a thread pitch of 1.25 mm. To avoid confusion, screw thread pitches are commonly given with a multiplication sign. For example, M8x1 means that the screw is 8 mm in diameter but has a thread pitch of 1 mm per 360-degree rotation. Those who are not familiar with these dimensions may find it confusing.
The OD of the threaded portion of a bolt is generally smaller than the OD of the nut. If the shank is too deep for the nut to fit, the threads may bottom out. This is why it’s important to use a thread-cutting bit with a small thread diameter. You can use a micrometer or caliper to measure the thread diameter. This tool will also allow you to easily identify which screw size fits where and how well.
The metric system is the most widely used. Fasteners with DIN numbers are generally metric in size. This makes them very useful for industrial settings. You can find metric-sized screws anywhere, as long as you buy them from a reputable manufacturer. These fasteners also come with a dog point, which is used for safety wire. If the screw needs to be replaced, the shank can be drilled with a hole for a safety wire or for a dog-point.
Round head
A round head screw is the most common type used for machine screws. Other common types include truss head, flat head, and hexed head. Each has a different profile and are used for different purposes. A round head screw is typically wider than a flat or a hexed head, and has a slightly rounded surface. These screws are useful for projects involving sheet metal or sheet-metal parts. Round heads are usually slightly wider than a hex head screw, and they may also be used as a substitute for washers in certain applications. However, truss heads are not necessary for every project.
A wood screw has a smooth shank that protrudes above the surface of the material it is attaching. A metal screw has a threaded shaft that is fully threaded from head to point, and a fully threaded shaft provides more bite. Two common head styles are round head and pan head. If the task requires the screw to be flush or countersunk, the round head will be the best choice.
Another type is the Reed & Prince screw drive. These are similar to Phillips screws but have a 75-degree V shape. They are commonly used in marine hardware and are also known as BNAE NFL22-070. This type is also used for steel plate hangers. In addition to round head and pan head screws, there are a variety of other screw types. You can even get a head with a slotted head if you know where to look.
Screw diameters are specified according to the ISO 261 or ISO 262 standards. An M8 screw has a diameter of 8.25 mm. The M8 screw has a pitch of 1.25 mm, which is equivalent to 1 mm per 360 degrees. There are several other standard screw sizes and thread diameters available. You can find them all by consulting the relevant standards. But remember, the metric system is the most popular.
Self-locking mechanism
A self-locking mechanism for a screw shaft is a device that secures the screw to its supporting member in a failure position. The locking mechanism provides a positive connection between the screw shaft and the control surface during normal operation, and locks the screw to its supporting member when the screw fails. Previous attempts to solve this problem have typically used secondary nuts with free play on the screw, which were intentionally designed to jam when loaded. However, such a device can be unreliable, which is why the present invention offers a more robust and reliable locking mechanism.
The self-locking function of a screw depends on several factors, including its pitch angle and the coefficient of friction of the threads. The angle of friction must be less than the tangent of the material pairing to prevent untightening of the screw. Screws with self-locking mechanisms have an efficiency e lower than 50%, which is less than half. Self-locking screws also have the benefit of being less efficient than a standard screw.
Unlike a normal screw, a self-locking screw can be turned in either direction. The nut 22 rotates with the screw shaft, and the member 23 is translated in an axial direction. Regardless of the direction of the rotation of the screw, this axial translation will result in the opposite moment to that input moment. While screw self-locking mechanisms are typically less expensive, they are more reliable and durable.
Another important feature of self-locking screws is that they are not susceptible to independent loosening. The screw cannot rotate without a certain amount of torque. In addition, a self-locking screw shaft must have a small wedge with a smaller half-angle than the arctangent of the static friction. This means that the torque applied by the driver must be greater than the torque needed to overcome the friction.

