Product Description
Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Type: | Round Head |
| Groove: | Cross |
| Connection: | Hinged Bolts |
| Head Style: | Square |
| Standard: | DIN, GB, ANSI, BSW, JIS, GOST |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can worm screws be used for high torque applications?
Yes, worm screws can be used for high torque applications. The design of a worm screw mechanism allows for efficient torque transmission and multiplication, making it suitable for applications that require high torque output. Here are some key points to consider regarding the use of worm screws in high torque applications:
- Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio, which results in a lower output speed and higher output torque. This gear reduction capability allows worm screws to generate and transmit substantial torque, making them well-suited for high torque applications.
- Efficiency: While worm screws can provide high torque output, it’s important to consider the mechanical efficiency of the system. The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. It’s crucial to ensure that the efficiency of the worm screw mechanism meets the requirements of the specific high torque application.
- Load Holding: Another advantage of worm screws is their self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel, which provides resistance against backward rotation. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads in a fixed position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. In high torque applications where load holding is required, worm screws can provide reliable and secure positioning.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the worm screw and worm wheel should be carefully selected to withstand high torque loads. Both components should have sufficient strength and wear resistance to handle the transmitted torque without deformation or premature failure. Depending on the specific application requirements, materials such as hardened steel, bronze, or other alloys may be chosen to ensure the durability and performance of the worm screw assembly.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of a worm screw mechanism, especially in high torque applications. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Regular maintenance, including monitoring lubricant levels and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed, is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear or failure.
Overall, worm screws can be effectively used in high torque applications, thanks to their gear reduction capabilities, load-holding properties, and efficient torque transmission. However, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as mechanical efficiency, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance to ensure that the worm screw mechanism can meet the specific requirements and demands of the high torque application.
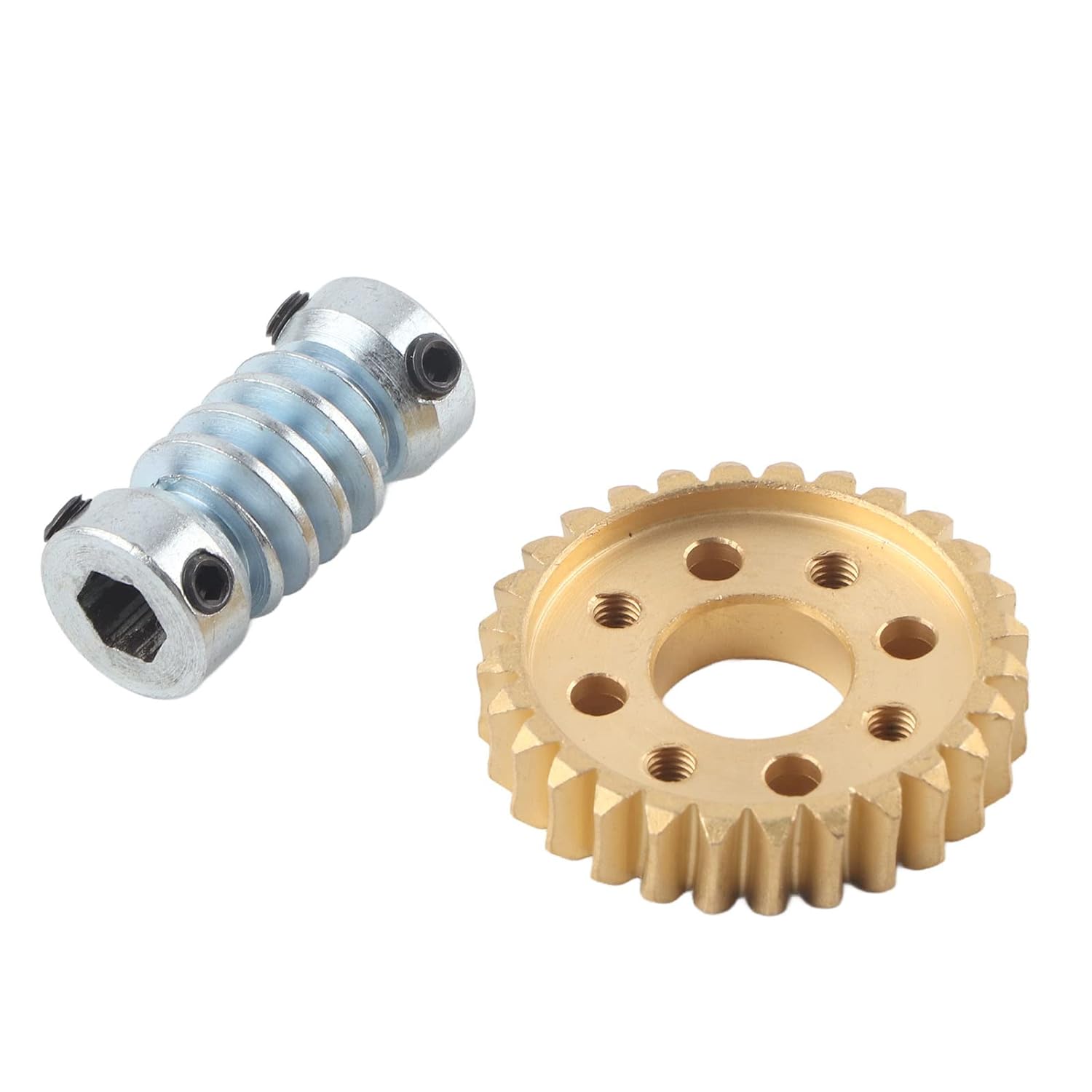

How do environmental factors affect the lifespan and performance of worm screws?
Environmental factors can have a significant impact on the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Here are some ways in which different environmental conditions can affect worm screw operation:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the material properties of worm screws. High temperatures can cause thermal expansion, leading to increased clearances and reduced efficiency. It can also accelerate wear and degradation of lubricants, leading to increased friction and potential damage. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can make lubricants less effective and increase the risk of brittle fracture or reduced flexibility in materials.
- Humidity and Moisture: Exposure to high humidity or moisture can lead to corrosion and rusting of worm screws, especially when they are made of materials that are not resistant to moisture. Corrosion can cause surface pitting, reduced strength, and accelerated wear, ultimately compromising the performance and lifespan of the worm screw.
- Dust and Contaminants: Dust, dirt, and other contaminants present in the environment can enter the worm gear system and cause abrasive wear on the worm screw. These particles can act as abrasives, accelerating the wear of the contacting surfaces and potentially leading to premature failure or reduced performance. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to mitigate the effects of dust and contaminants.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to chemicals, such as acids, solvents, or corrosive substances, can have a detrimental effect on worm screws. Chemicals can corrode the surfaces, degrade lubricants, and affect the material properties, leading to reduced lifespan and compromised performance. Choosing materials and coatings that are resistant to specific chemicals present in the environment is crucial for long-term performance.
- Load and Overloading: Environmental conditions, such as heavy loads or overloading, can significantly impact the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Excessive loads can lead to increased stress levels, deformation, and accelerated wear on the worm screw. It is important to operate worm gear systems within their specified load capacities and avoid overloading to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Operating Speed: The operating speed of the worm screw can also be influenced by environmental factors. High-speed applications may generate more heat due to friction, necessitating effective cooling mechanisms. On the other hand, low-speed applications may exhibit reduced lubrication effectiveness, requiring specific lubricants or maintenance practices to ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear.
To mitigate the effects of environmental factors, proper maintenance, regular inspection, and suitable protective measures are essential. This includes using appropriate lubricants, implementing effective sealing mechanisms, applying protective coatings, and considering environmental factors during the design and material selection process. By considering and addressing environmental factors, the lifespan and performance of worm screws can be optimized, ensuring reliable operation in various operating conditions.

How does a worm screw mechanism work?
A worm screw mechanism, also known as a worm gear mechanism, is a type of power transmission system that consists of a worm screw and a worm wheel. It is designed to transmit motion and power between non-parallel shafts. The mechanism works based on the interaction between the helical threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a worm screw mechanism works:
- Structure: The worm screw is a cylindrical shaft with a helical thread wrapped around it, resembling a screw. The worm wheel, also known as a worm gear, is a gear with teeth that mesh with the threads of the worm screw. The orientation of the worm screw and the worm wheel is such that the axes of rotation are perpendicular to each other.
- Motion Transmission: When the worm screw is rotated, its helical threads engage with the teeth of the worm wheel. As the worm screw rotates, it drives the worm wheel to rotate as well. The helical shape of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel allow for motion transmission perpendicular to the axis of the worm screw.
- Gear Reduction: One of the key characteristics of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio in a single gear stage. This means that a small rotation of the worm screw can result in a substantial rotation of the worm wheel. The gear reduction enables the worm screw mechanism to generate high torque output at the worm wheel.
- Self-Locking: A notable feature of the worm screw mechanism is its self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel. This means that the worm wheel cannot easily rotate the worm screw. Instead, the worm screw tends to hold its position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. The self-locking feature makes the worm screw mechanism suitable for applications that require holding loads in a fixed position.
- Efficiency and Backlash: The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. Additionally, worm screw mechanisms may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which refers to the slight play or clearance between the threads and teeth. Backlash can affect precision and introduce a small amount of lost motion in the system.
- Applications: Worm screw mechanisms find applications in various industries and machinery where motion transmission at right angles and high gear reduction ratios are required. Common applications include conveyor systems, lifting mechanisms, winches, automotive steering systems, robotics, and machine tools.
The worm screw mechanism offers a unique combination of motion transmission, gear reduction, and self-locking capabilities, making it suitable for specific applications where precise control, high torque output, and the ability to hold loads are essential.


editor by CX 2024-01-17
China wholesaler Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
Product Description
Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Type: | Round Head |
| Groove: | Cross |
| Connection: | Hinged Bolts |
| Head Style: | Square |
| Standard: | DIN, GB, ANSI, BSW, JIS, GOST |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can worm screws be used for high torque applications?
Yes, worm screws can be used for high torque applications. The design of a worm screw mechanism allows for efficient torque transmission and multiplication, making it suitable for applications that require high torque output. Here are some key points to consider regarding the use of worm screws in high torque applications:
- Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio, which results in a lower output speed and higher output torque. This gear reduction capability allows worm screws to generate and transmit substantial torque, making them well-suited for high torque applications.
- Efficiency: While worm screws can provide high torque output, it’s important to consider the mechanical efficiency of the system. The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. It’s crucial to ensure that the efficiency of the worm screw mechanism meets the requirements of the specific high torque application.
- Load Holding: Another advantage of worm screws is their self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel, which provides resistance against backward rotation. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads in a fixed position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. In high torque applications where load holding is required, worm screws can provide reliable and secure positioning.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the worm screw and worm wheel should be carefully selected to withstand high torque loads. Both components should have sufficient strength and wear resistance to handle the transmitted torque without deformation or premature failure. Depending on the specific application requirements, materials such as hardened steel, bronze, or other alloys may be chosen to ensure the durability and performance of the worm screw assembly.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of a worm screw mechanism, especially in high torque applications. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Regular maintenance, including monitoring lubricant levels and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed, is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear or failure.
Overall, worm screws can be effectively used in high torque applications, thanks to their gear reduction capabilities, load-holding properties, and efficient torque transmission. However, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as mechanical efficiency, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance to ensure that the worm screw mechanism can meet the specific requirements and demands of the high torque application.
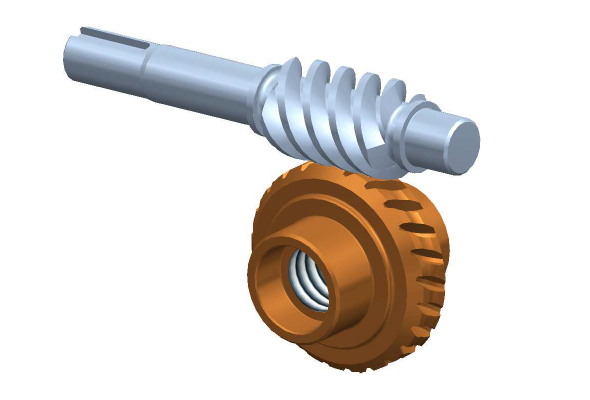
How does the pitch of a worm screw affect its performance?
The pitch of a worm screw plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics and capabilities. The pitch refers to the axial distance between consecutive threads on the worm screw. Here’s how the pitch of a worm screw affects its performance:
- Speed and Efficiency: The pitch of a worm screw directly influences the speed and efficiency of the worm gear system. A smaller pitch, which means a finer thread, results in a higher gear ratio and slower output speed. Conversely, a larger pitch, or coarser thread, leads to a lower gear ratio and faster output speed. This relationship between pitch and speed allows for speed reduction or multiplication in mechanical power transmission systems.
- Load Capacity: The pitch of a worm screw also affects its load-carrying capacity. A finer pitch tends to distribute the load over more threads, resulting in a larger contact area between the worm screw and the worm wheel. This increased contact area improves load distribution and allows for higher load capacity. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may have a reduced contact area, which can limit the load-carrying capability of the worm gear system.
- Backlash: Backlash is the clearance or play between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. The pitch of a worm screw influences the amount of backlash present in the system. A finer pitch generally results in lower backlash due to the smaller clearance between the threads and the teeth. In contrast, coarser pitches may have increased backlash, which can negatively impact the system’s accuracy, precision, and responsiveness.
- Efficiency and Heat Generation: The pitch of a worm screw affects the overall efficiency of the worm gear system. Finer pitches tend to have higher efficiency due to reduced sliding friction between the threads and the teeth. This reduced friction results in less heat generation, contributing to higher overall system efficiency. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may exhibit increased sliding friction, leading to higher energy losses and heat generation.
- Manufacturing and Design Considerations: The pitch of a worm screw also influences the manufacturing process and design considerations. Finer pitches generally require more precise machining or grinding processes to achieve the desired thread geometry. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may offer advantages in terms of ease of manufacturing and reduced sensitivity to manufacturing tolerances. The selection of the optimal pitch depends on factors such as the desired gear ratio, load requirements, desired efficiency, and manufacturing capabilities.
It’s important to note that the pitch of a worm screw is typically specified by the manufacturer and should be chosen carefully based on the specific application requirements. Consulting with experts or engineers familiar with worm gear systems can help in selecting the appropriate pitch to achieve the desired performance and functionality.

How do you calculate the gear ratio for a worm screw and gear setup?
In a worm screw and gear setup, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the worm wheel (gear) and the number of threads on the worm screw. The gear ratio represents the relationship between the rotational speed of the worm screw and the resulting rotational speed of the worm wheel. The formula to calculate the gear ratio is as follows:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Worm Wheel / Number of Threads on Worm Screw
Here’s a step-by-step process to calculate the gear ratio:
- Count the number of teeth on the worm wheel. This can be done by visually inspecting the gear or referring to its specifications.
- Count the number of threads on the worm screw. The threads refer to the number of complete turns or helical grooves wrapped around the cylindrical body of the worm screw.
- Divide the number of teeth on the worm wheel by the number of threads on the worm screw.
- The result of the division is the gear ratio. It represents the number of revolutions of the worm screw required to complete one revolution of the worm wheel.
For example, let’s say the worm wheel has 40 teeth, and the worm screw has 2 threads. Using the formula, we can calculate the gear ratio as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 teeth / 2 threads = 20
In this case, for every full revolution of the worm screw, the worm wheel will rotate 1/20th of a revolution. This indicates a significant speed reduction, resulting in high torque output at the worm wheel.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio calculated using this formula assumes an ideal scenario without considering factors like friction, efficiency losses, or the pitch diameter of the gears. In practical applications, these factors may affect the actual gear ratio and performance of the worm screw and gear setup.


editor by CX 2023-12-04
China OEM Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand with Free Design Custom
Product Description
adjustable bevel gear worm screw jack with motor high quality China factory brand
What Are Screw Shaft Threads?
A screw shaft is a threaded part used to fasten other components. The threads on a screw shaft are often described by their Coefficient of Friction, which describes how much friction is present between the mating surfaces. This article discusses these characteristics as well as the Material and Helix angle. You’ll have a better understanding of your screw shaft’s threads after reading this article. Here are some examples. Once you understand these details, you’ll be able to select the best screw nut for your needs.
Coefficient of friction between the mating surfaces of a nut and a screw shaft
There are 2 types of friction coefficients. Dynamic friction and static friction. The latter refers to the amount of friction a nut has to resist an opposing motion. In addition to the material strength, a higher coefficient of friction can cause stick-slip. This can lead to intermittent running behavior and loud squeaking. Stick-slip may lead to a malfunctioning plain bearing. Rough shafts can be used to improve this condition.
The 2 types of friction coefficients are related to the applied force. When applying force, the applied force must equal the nut’s pitch diameter. When the screw shaft is tightened, the force may be removed. In the case of a loosening clamp, the applied force is smaller than the bolt’s pitch diameter. Therefore, the higher the property class of the bolt, the lower the coefficient of friction.
In most cases, the screwface coefficient of friction is lower than the nut face. This is because of zinc plating on the joint surface. Moreover, power screws are commonly used in the aerospace industry. Whether or not they are power screws, they are typically made of carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel. They are often used in conjunction with bronze or plastic nuts, which are preferred in higher-duty applications. These screws often require no holding brakes and are extremely easy to use in many applications.
The coefficient of friction between the mating surfaces of t-screws is highly dependent on the material of the screw and the nut. For example, screws with internal lubricated plastic nuts use bearing-grade bronze nuts. These nuts are usually used on carbon steel screws, but can be used with stainless steel screws. In addition to this, they are easy to clean.
Helix angle
In most applications, the helix angle of a screw shaft is an important factor for torque calculation. There are 2 types of helix angle: right and left hand. The right hand screw is usually smaller than the left hand one. The left hand screw is larger than the right hand screw. However, there are some exceptions to the rule. A left hand screw may have a greater helix angle than a right hand screw.
A screw’s helix angle is the angle formed by the helix and the axial line. Although the helix angle is not usually changed, it can have a significant effect on the processing of the screw and the amount of material conveyed. These changes are more common in 2 stage and special mixing screws, and metering screws. These measurements are crucial for determining the helix angle. In most cases, the lead angle is the correct angle when the screw shaft has the right helix angle.
High helix screws have large leads, sometimes up to 6 times the screw diameter. These screws reduce the screw diameter, mass, and inertia, allowing for higher speed and precision. High helix screws are also low-rotation, so they minimize vibrations and audible noises. But the right helix angle is important in any application. You must carefully choose the right type of screw for the job at hand.
If you choose a screw gear that has a helix angle other than parallel, you should select a thrust bearing with a correspondingly large center distance. In the case of a screw gear, a 45-degree helix angle is most common. A helix angle greater than zero degrees is also acceptable. Mixing up helix angles is beneficial because it allows for a variety of center distances and unique applications.
Thread angle
The thread angle of a screw shaft is measured from the base of the head of the screw to the top of the screw’s thread. In America, the standard screw thread angle is 60 degrees. The standard thread angle was not widely adopted until the early twentieth century. A committee was established by the Franklin Institute in 1864 to study screw threads. The committee recommended the Sellers thread, which was modified into the United States Standard Thread. The standardized thread was adopted by the United States Navy in 1868 and was recommended for construction by the Master Car Builders’ Association in 1871.
Generally speaking, the major diameter of a screw’s threads is the outside diameter. The major diameter of a nut is not directly measured, but can be determined with go/no-go gauges. It is necessary to understand the major and minor diameters in relation to each other in order to determine a screw’s thread angle. Once this is known, the next step is to determine how much of a pitch is necessary to ensure a screw’s proper function.
Helix angle and thread angle are 2 different types of angles that affect screw efficiency. For a lead screw, the helix angle is the angle between the helix of the thread and the line perpendicular to the axis of rotation. A lead screw has a greater helix angle than a helical one, but has higher frictional losses. A high-quality lead screw requires a higher torque to rotate. Thread angle and lead angle are complementary angles, but each screw has its own specific advantages.
Screw pitch and TPI have little to do with tolerances, craftsmanship, quality, or cost, but rather the size of a screw’s thread relative to its diameter. Compared to a standard screw, the fine and coarse threads are easier to tighten. The coarser thread is deeper, which results in lower torques. If a screw fails because of torsional shear, it is likely to be a result of a small minor diameter.
Material
Screws have a variety of different sizes, shapes, and materials. They are typically machined on CNC machines and lathes. Each type is used for different purposes. The size and material of a screw shaft are influenced by how it will be used. The following sections give an overview of the main types of screw shafts. Each 1 is designed to perform a specific function. If you have questions about a specific type, contact your local machine shop.
Lead screws are cheaper than ball screws and are used in light-duty, intermittent applications. Lead screws, however, have poor efficiency and are not recommended for continuous power transmission. But, they are effective in vertical applications and are more compact. Lead screws are typically used as a kinematic pair with a ball screw. Some types of lead screws also have self-locking properties. Because they have a low coefficient of friction, they have a compact design and very few parts.
Screws are made of a variety of metals and alloys. Steel is an economical and durable material, but there are also alloy steel and stainless steel types. Bronze nuts are the most common and are often used in higher-duty applications. Plastic nuts provide low-friction, which helps reduce the drive torques. Stainless steel screws are also used in high-performance applications, and may be made of titanium. The materials used to create screw shafts vary, but they all have their specific functions.
Screws are used in a wide range of applications, from industrial and consumer products to transportation equipment. They are used in many different industries, and the materials they’re made of can determine their life. The life of a screw depends on the load that it bears, the design of its internal structure, lubrication, and machining processes. When choosing screw assemblies, look for a screw made from the highest quality steels possible. Usually, the materials are very clean, so they’re a great choice for a screw. However, the presence of imperfections may cause a normal fatigue failure.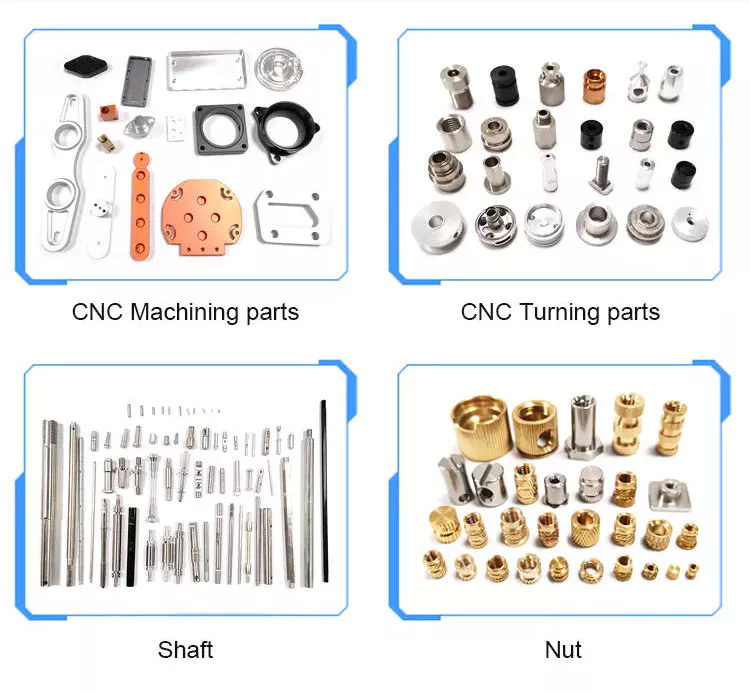
Self-locking features
Screws are known to be self-locking by nature. The mechanism for this feature is based on several factors, such as the pitch angle of the threads, material pairing, lubrication, and heating. This feature is only possible if the shaft is subjected to conditions that are not likely to cause the threads to loosen on their own. The self-locking ability of a screw depends on several factors, including the pitch angle of the thread flank and the coefficient of sliding friction between the 2 materials.
One of the most common uses of screws is in a screw top container lid, corkscrew, threaded pipe joint, vise, C-clamp, and screw jack. Other applications of screw shafts include transferring power, but these are often intermittent and low-power operations. Screws are also used to move material in Archimedes’ screw, auger earth drill, screw conveyor, and micrometer.
A common self-locking feature for a screw is the presence of a lead screw. A screw with a low PV value is safe to operate, but a screw with high PV will need a lower rotation speed. Another example is a self-locking screw that does not require lubrication. The PV value is also dependent on the material of the screw’s construction, as well as its lubrication conditions. Finally, a screw’s end fixity – the way the screw is supported – affects the performance and efficiency of a screw.
Lead screws are less expensive and easier to manufacture. They are a good choice for light-weight and intermittent applications. These screws also have self-locking capabilities. They can be self-tightened and require less torque for driving than other types. The advantage of lead screws is their small size and minimal number of parts. They are highly efficient in vertical and intermittent applications. They are not as accurate as lead screws and often have backlash, which is caused by insufficient threads.


China Professional Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand near me shop
Product Description
Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
Screws and Screw Shafts
A screw is a mechanical device that holds objects together. Screws are usually forged or machined. They are also used in screw jacks and press-fitted vises. Their self-locking properties make them a popular choice in many different industries. Here are some of the benefits of screws and how they work. Also read about their self-locking properties. The following information will help you choose the right screw for your application.
Machined screw shaft
A machined screw shaft can be made of various materials, depending on the application. Screw shafts can be made from stainless steel, brass, bronze, titanium, or iron. Most manufacturers use high-precision CNC machines or lathes to manufacture these products. These products come in many sizes and shapes, and they have varying applications. Different materials are used for different sizes and shapes. Here are some examples of what you can use these screws for:
Screws are widely used in many applications. One of the most common uses is in holding objects together. This type of fastener is used in screw jacks, vises, and screw presses. The thread pitch of a screw can vary. Generally, a smaller pitch results in greater mechanical advantage. Hence, a machined screw shaft should be sized appropriately. This ensures that your product will last for a long time.
A machined screw shaft should be compatible with various threading systems. In general, the ASME system is used for threaded parts. The threaded hole occupies most of the shaft. The thread of the bolt occupy either part of the shaft, or the entire one. There are also alternatives to bolts, including riveting, rolling pins, and pinned shafts. These alternatives are not widely used today, but they are useful for certain niche applications.
If you are using a ball screw, you can choose to anneal the screw shaft. To anneal the screw shaft, use a water-soaked rag as a heat barrier. You can choose from 2 different options, depending on your application. One option is to cover the screw shaft with a dust-proof enclosure. Alternatively, you can install a protective heat barrier over the screw shaft. You can also choose to cover the screw shaft with a dust-proof machine.
If you need a smaller size, you can choose a smaller screw. It may be smaller than a quarter of an inch, but it may still be compatible with another part. The smaller ones, however, will often have a corresponding mating part. These parts are typically denominated by their ANSI numerical size designation, which does not indicate threads-per-inch. There is an industry standard for screw sizes that is a little easier to understand.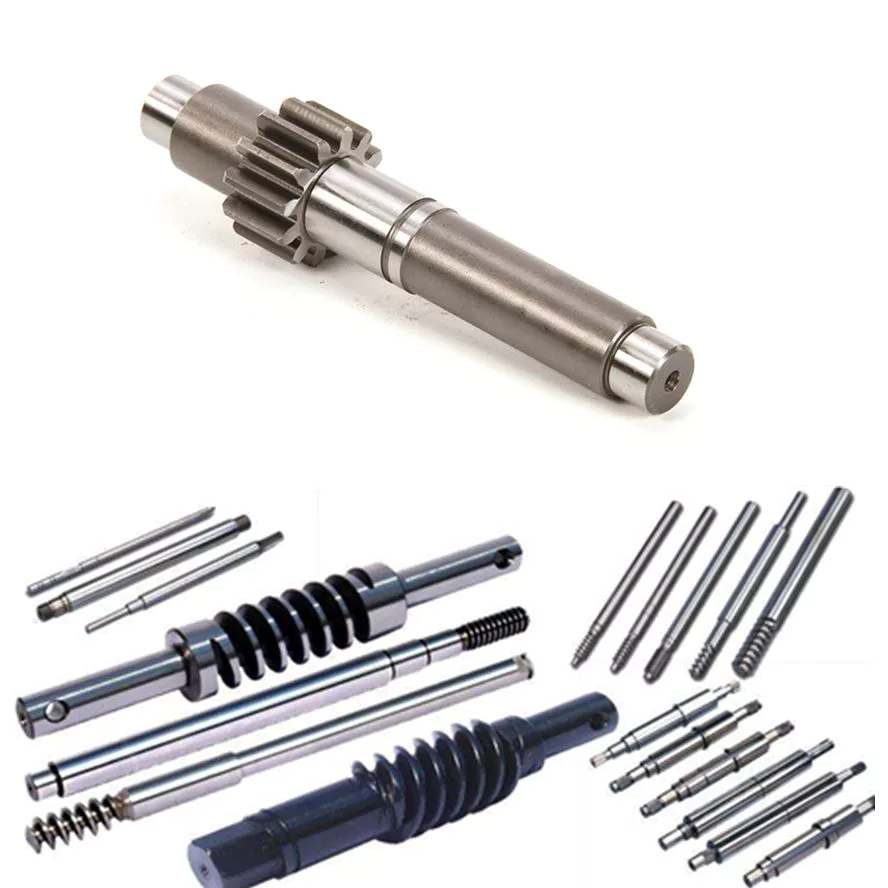
Ball screw nut
When choosing a Ball screw nut for a screw shaft, it is important to consider the critical speed of the machine. This value excites the natural frequency of a screw and determines how fast it can be turned. In other words, it varies with the screw diameter and unsupported length. It also depends on the screw shaft’s diameter and end fixity. Depending on the application, the nut can be run at a maximum speed of about 80% of its theoretical critical speed.
The inner return of a ball nut is a cross-over deflector that forces the balls to climb over the crest of the screw. In 1 revolution of the screw, a ball will cross over the nut crest to return to the screw. Similarly, the outer circuit is a circular shape. Both flanges have 1 contact point on the ball shaft, and the nut is connected to the screw shaft by a screw.
The accuracy of ball screws depends on several factors, including the manufacturing precision of the ball grooves, the compactness of the assembly, and the set-up precision of the nut. Depending on the application, the lead accuracy of a ball screw nut may vary significantly. To improve lead accuracy, preloading, and lubrication are important. Ewellix ball screw assembly specialists can help you determine the best option for your application.
A ball screw nut should be preloaded prior to installation in order to achieve the expected service life. The smallest amount of preload required can reduce a ball screw’s calculated life by as much as 90 percent. Using a lubricant of a standard grade is recommended. Some lubricants contain additives. Using grease or oil in place of oil can prolong the life of the screw.
A ball screw nut is a type of threaded nut that is used in a number of different applications. It works similar to a ball bearing in that it contains hardened steel balls that move along a series of inclined races. When choosing a ball screw nut, engineers should consider the following factors: speed, life span, mounting, and lubrication. In addition, there are other considerations, such as the environment in which the screw is used.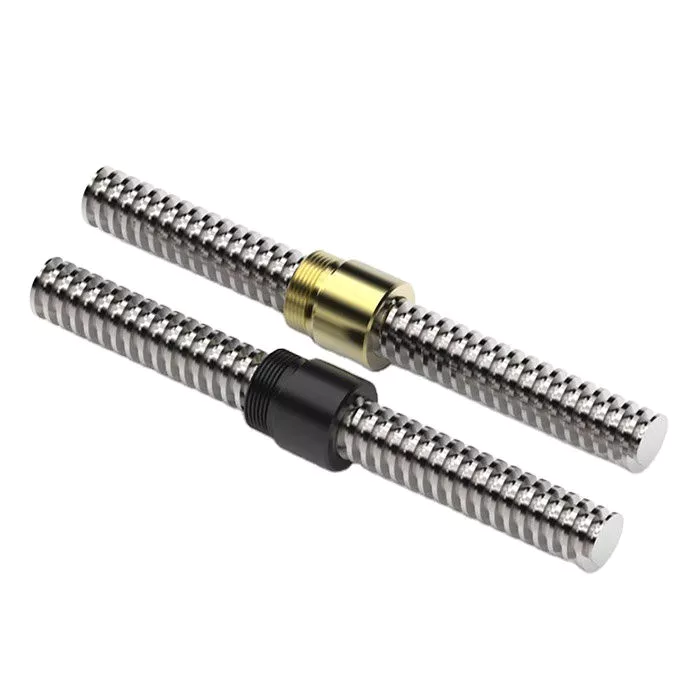
Self-locking property of screw shaft
A self-locking screw is 1 that is capable of rotating without the use of a lock washer or bolt. This property is dependent on a number of factors, but 1 of them is the pitch angle of the thread. A screw with a small pitch angle is less likely to self-lock, while a large pitch angle is more likely to spontaneously rotate. The limiting angle of a self-locking thread can be calculated by calculating the torque Mkdw at which the screw is first released.
The pitch angle of the screw’s threads and its coefficient of friction determine the self-locking function of the screw. Other factors that affect its self-locking function include environmental conditions, high or low temperature, and vibration. Self-locking screws are often used in single-line applications and are limited by the size of their pitch. Therefore, the self-locking property of the screw shaft depends on the specific application.
The self-locking feature of a screw is an important factor. If a screw is not in a state of motion, it can be a dangerous or unusable machine. The self-locking property of a screw is critical in many applications, from corkscrews to threaded pipe joints. Screws are also used as power linkages, although their use is rarely necessary for high-power operations. In the archimedes’ screw, for example, the blades of the screw rotate around an axis. A screw conveyor uses a rotating helical chamber to move materials. A micrometer uses a precision-calibrated screw to measure length.
Self-locking screws are commonly used in lead screw technology. Their pitch and coefficient of friction are important factors in determining the self-locking property of screws. This property is advantageous in many applications because it eliminates the need for a costly brake. Its self-locking property means that the screw will be secure without requiring a special kind of force or torque. There are many other factors that contribute to the self-locking property of a screw, but this is the most common factor.
Screws with right-hand threads have threads that angle up to the right. The opposite is true for left-hand screws. While turning a screw counter-clockwise will loosen it, a right-handed person will use a right-handed thumb-up to turn it. Similarly, a left-handed person will use their thumb to turn a screw counter-clockwise. And vice versa.
Materials used to manufacture screw shaft
Many materials are commonly used to manufacture screw shafts. The most common are steel, stainless steel, brass, bronze, and titanium. These materials have advantages and disadvantages that make them good candidates for screw production. Some screw types are also made of copper to fight corrosion and ensure durability over time. Other materials include nylon, Teflon, and aluminum. Brass screws are lightweight and have aesthetic appeal. The choice of material for a screw shaft depends on the use it will be made for.
Shafts are typically produced using 3 steps. Screws are manufactured from large coils, wire, or round bar stock. After these are produced, the blanks are cut to the appropriate length and cold headed. This cold working process pressudes features into the screw head. More complicated screw shapes may require 2 heading processes to achieve the desired shape. The process is very precise and accurate, so it is an ideal choice for screw manufacturing.
The type of material used to manufacture a screw shaft is crucial for the function it will serve. The type of material chosen will depend on where the screw is being used. If the screw is for an indoor project, you can opt for a cheaper, low-tech screw. But if the screw is for an outdoor project, you’ll need to use a specific type of screw. This is because outdoor screws will be exposed to humidity and temperature changes. Some screws may even be coated with a protective coating to protect them from the elements.
Screws can also be self-threading and self-tapping. The self-threading or self-tapping screw creates a complementary helix within the material. Other screws are made with a thread which cuts into the material it fastens. Other types of screws create a helical groove on softer material to provide compression. The most common uses of a screw include holding 2 components together.
There are many types of bolts available. Some are more expensive than others, but they are generally more resistant to corrosion. They can also be made from stainless steel or aluminum. But they require high-strength materials. If you’re wondering what screws are, consider this article. There are tons of options available for screw shaft manufacturing. You’ll be surprised how versatile they can be! The choice is yours, and you can be confident that you’ll find the screw shaft that will best fit your application.

