Product Description
HangZhou CHINAMFG Actuators Manufacture Co.,Ltd is a verified manufacturing and trading company , has been specialized in the electric damper actuators for the CHINAMFG system, and the customized processing services since 1989.
1. Machining service:
Custom gears, shafts etc transmission parts,
Custom all kinds of the machinery parts, Stamping, CNC lathe, milling machine, grinder, machining center, laser etc process all available.
2. Electric damper actuator:
spring return, modulating, reverse, on/off etc,function is analogy to brand drive
| TYPE | GEAR TRANSMISSION PARTS |
| MATERIAL | Stainless steel,Steel(Iron,)Brass,Copper |
| TOLERANCE | ±0.001mm |
| QC SYSTEM | 100% inspection before shipment |
| PAYMENT TERMS | T/T at sight, Paypal, Western Union,etc. |
| SAMPLE TIME | 3-7working days FOR SAMPLES |
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machinery Accessory |
|---|---|
| Standard: | GB, EN, API650, China GB Code, JIS Code, TEMA, ASME |
| Surface Treatment: | Anodizing |
| Production Type: | Mass Production |
| Machining Method: | CNC Machining |
| Material: | Nylon, Steel, Plastic, Brass, Alloy, Copper, Aluminum, Iron |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do you select the right worm screw for a specific application?
Selecting the right worm screw for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Here are the key steps to guide you in selecting the appropriate worm screw:
- Identify Application Requirements: Begin by understanding the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors such as torque, speed, direction of rotation, load capacity, precision, and environmental conditions. Determine the desired gear ratio and any additional features or specifications needed for the worm screw to meet the application’s objectives.
- Consider Design Parameters: Evaluate the design parameters of the worm screw, including the number of starts, lead angle, pitch diameter, and thread profile. These parameters directly influence the gear ratio, mechanical efficiency, and load-carrying capacity of the worm screw. Choose the design parameters that align with the application requirements, considering factors like torque transmission, speed regulation, and size constraints.
- Material Selection: Selecting the right material for the worm screw is crucial for its durability and performance. Consider factors such as strength, wear resistance, and compatibility with other mating components. Common materials for worm screws include hardened steel, stainless steel, bronze, or other alloys. Consult material specifications and consider the anticipated operating conditions to ensure the selected material can withstand the loads and environmental factors present in the application.
- Lubrication Requirements: Determine the lubrication requirements for the specific application. Some worm screws may require lubrication to reduce friction and wear, while others may have self-lubricating properties. Consider the type of lubricant (oil or grease), the frequency of lubrication, and the accessibility for lubrication maintenance. Ensure that the selected worm screw is compatible with the required lubrication method and can meet the lubrication demands of the application.
- Consider Mounting and Installation: Evaluate the mounting and installation requirements of the worm screw. Assess factors such as space limitations, alignment considerations, coupling options, and connection methods. Ensure that the selected worm screw can be easily integrated into the mechanical system and meets the specific installation requirements without compromising overall performance.
- Consult Manufacturer Resources: Utilize manufacturer resources, such as catalogs, technical specifications, and application guidelines, to gather information about available worm screw options. Manufacturers often provide recommendations and selection guides based on different application scenarios and performance criteria. Their expertise can help ensure that you choose the most suitable worm screw for your specific application.
- Review Cost and Availability: Consider the cost and availability of the worm screw. Evaluate the pricing, lead times, and availability from different suppliers or manufacturers. Balance the desired performance and quality with the budget constraints of the project, ensuring that the selected worm screw offers a cost-effective solution without compromising reliability or performance.
By following these steps and considering the application requirements, design parameters, material selection, lubrication needs, mounting considerations, manufacturer resources, and cost factors, you can select the right worm screw that meets the specific demands of your application. It’s important to consult with experts or seek assistance from manufacturers if you require further guidance or have unique requirements.

What are the latest innovations in worm screw design and materials?
In recent years, there have been several notable innovations in worm screw design and materials that aim to improve performance, efficiency, durability, and overall functionality. Here are some of the latest advancements in this field:
- Advanced Materials: One of the significant trends in worm screw design is the use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring materials with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and fatigue properties. For example, advanced alloys and composite materials are being employed to improve load capacity, reduce weight, and increase the longevity of worm screws. Additionally, advancements in material science and engineering are leading to the development of self-lubricating materials, which can minimize friction and improve efficiency by reducing the need for external lubrication.
- Improved Thread Geometries: Innovations in thread geometries have focused on optimizing load distribution, reducing friction, and improving efficiency. Researchers and engineers are developing novel thread profiles and forms that enhance contact between the worm screw and the worm wheel. These designs help minimize backlash, increase load-carrying capacity, and improve overall system performance. Additionally, advancements in computer simulations and modeling techniques enable more accurate analysis and optimization of thread geometries for specific applications.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Surface treatments and coatings are being applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. For instance, advanced coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings or specialized lubricious coatings help reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and minimize the need for external lubrication. Surface treatments like nitriding or carburizing can improve hardness and provide resistance against abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of worm screws.
- Precision Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing processes and technologies have enabled the production of worm screws with higher precision and tighter tolerances. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC grinding and high-precision gear hobbing, allow for the creation of worm screws with superior dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and better tooth profile control. These manufacturing advancements contribute to enhanced performance, reduced backlash, and increased overall system efficiency.
- Computer-Aided Design and Simulation: The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools has revolutionized worm screw design and optimization. Engineers can now create virtual models, simulate the behavior of worm gear systems, and analyze various design parameters to optimize performance before physical prototypes are manufactured. This iterative design process helps reduce development time, minimize costs, and improve the final design and performance of worm screws.
- Integration with Digitalization and Automation: The integration of worm gear systems with digitalization and automation technologies is another area of innovation. Worm screws are being designed to work seamlessly with sensor technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load. This data can be utilized for predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and optimization of the overall system performance.
It’s important to note that the field of worm screw design and materials is continuously evolving, and new innovations are being introduced regularly. Keeping up with the latest research, advancements, and industry developments is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in worm gear system applications.

How does a worm screw mechanism work?
A worm screw mechanism, also known as a worm gear mechanism, is a type of power transmission system that consists of a worm screw and a worm wheel. It is designed to transmit motion and power between non-parallel shafts. The mechanism works based on the interaction between the helical threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a worm screw mechanism works:
- Structure: The worm screw is a cylindrical shaft with a helical thread wrapped around it, resembling a screw. The worm wheel, also known as a worm gear, is a gear with teeth that mesh with the threads of the worm screw. The orientation of the worm screw and the worm wheel is such that the axes of rotation are perpendicular to each other.
- Motion Transmission: When the worm screw is rotated, its helical threads engage with the teeth of the worm wheel. As the worm screw rotates, it drives the worm wheel to rotate as well. The helical shape of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel allow for motion transmission perpendicular to the axis of the worm screw.
- Gear Reduction: One of the key characteristics of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio in a single gear stage. This means that a small rotation of the worm screw can result in a substantial rotation of the worm wheel. The gear reduction enables the worm screw mechanism to generate high torque output at the worm wheel.
- Self-Locking: A notable feature of the worm screw mechanism is its self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel. This means that the worm wheel cannot easily rotate the worm screw. Instead, the worm screw tends to hold its position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. The self-locking feature makes the worm screw mechanism suitable for applications that require holding loads in a fixed position.
- Efficiency and Backlash: The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. Additionally, worm screw mechanisms may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which refers to the slight play or clearance between the threads and teeth. Backlash can affect precision and introduce a small amount of lost motion in the system.
- Applications: Worm screw mechanisms find applications in various industries and machinery where motion transmission at right angles and high gear reduction ratios are required. Common applications include conveyor systems, lifting mechanisms, winches, automotive steering systems, robotics, and machine tools.
The worm screw mechanism offers a unique combination of motion transmission, gear reduction, and self-locking capabilities, making it suitable for specific applications where precise control, high torque output, and the ability to hold loads are essential.


editor by CX 2024-01-15
China Standard Hot Selling Manufacturers Custom Galvanized Worm Gear Brass Gear Worm Gear Shaft Screw
Product Description
|
Material |
Low carbon steel( 1214, 1215, Y20, Y35), medium carbon steel( S45C, 4140, 4340) / Stainless steeL, 303, 304, 316 / Aluminum 6061, 6063, 7075 / Brass / Bronze / Copper / Titanium / Plastic (POM, PEEK, Nylon, Acrylic, PMMA, PVC, Derlin, ABS, HDEP) And Customized raw material,ect. |
|
Color |
According to customer’s requests |
|
Standard |
ROHS, HE, ISO9000-2008, IGS, TS16949 etc. |
|
Surface treatment |
Heat treatment, polishing electropolishing, plating, electrophresis, black oxide, galvanizing, cold galvanizing, powder coating, paint coating, sand blasting, shot blasting, anodize,passivasion etching,PAD printing, laster carving,dacromet, nickel plating,ect. |
|
Process |
Purchasing raw material / do Inspection on raw material (IQC) / make samples / Inspection samples(QC and engineer) / Sample approvel by customer / Mass production(LQC,PQC) / Surface finish (IQC) / Packing (FQC) / Make Delivery(FQC). |
|
Capabilities |
cnc turning/milling/machining stamping/bending/welding tapping/knurling/Thread hobbing/heading/chamfering Solidworks, STEP, IGS, AutoCAD |
|
Used |
electronics, electrical appliances, furniture, construction, toys, automotive /motorcycle, machinery, kitchen home appliances and other fields |
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Surface Finishing: | Zinc Plated |
| Grade: | Custom Service |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you select the right worm screw for a specific application?
Selecting the right worm screw for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Here are the key steps to guide you in selecting the appropriate worm screw:
- Identify Application Requirements: Begin by understanding the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors such as torque, speed, direction of rotation, load capacity, precision, and environmental conditions. Determine the desired gear ratio and any additional features or specifications needed for the worm screw to meet the application’s objectives.
- Consider Design Parameters: Evaluate the design parameters of the worm screw, including the number of starts, lead angle, pitch diameter, and thread profile. These parameters directly influence the gear ratio, mechanical efficiency, and load-carrying capacity of the worm screw. Choose the design parameters that align with the application requirements, considering factors like torque transmission, speed regulation, and size constraints.
- Material Selection: Selecting the right material for the worm screw is crucial for its durability and performance. Consider factors such as strength, wear resistance, and compatibility with other mating components. Common materials for worm screws include hardened steel, stainless steel, bronze, or other alloys. Consult material specifications and consider the anticipated operating conditions to ensure the selected material can withstand the loads and environmental factors present in the application.
- Lubrication Requirements: Determine the lubrication requirements for the specific application. Some worm screws may require lubrication to reduce friction and wear, while others may have self-lubricating properties. Consider the type of lubricant (oil or grease), the frequency of lubrication, and the accessibility for lubrication maintenance. Ensure that the selected worm screw is compatible with the required lubrication method and can meet the lubrication demands of the application.
- Consider Mounting and Installation: Evaluate the mounting and installation requirements of the worm screw. Assess factors such as space limitations, alignment considerations, coupling options, and connection methods. Ensure that the selected worm screw can be easily integrated into the mechanical system and meets the specific installation requirements without compromising overall performance.
- Consult Manufacturer Resources: Utilize manufacturer resources, such as catalogs, technical specifications, and application guidelines, to gather information about available worm screw options. Manufacturers often provide recommendations and selection guides based on different application scenarios and performance criteria. Their expertise can help ensure that you choose the most suitable worm screw for your specific application.
- Review Cost and Availability: Consider the cost and availability of the worm screw. Evaluate the pricing, lead times, and availability from different suppliers or manufacturers. Balance the desired performance and quality with the budget constraints of the project, ensuring that the selected worm screw offers a cost-effective solution without compromising reliability or performance.
By following these steps and considering the application requirements, design parameters, material selection, lubrication needs, mounting considerations, manufacturer resources, and cost factors, you can select the right worm screw that meets the specific demands of your application. It’s important to consult with experts or seek assistance from manufacturers if you require further guidance or have unique requirements.

What are the latest innovations in worm screw design and materials?
In recent years, there have been several notable innovations in worm screw design and materials that aim to improve performance, efficiency, durability, and overall functionality. Here are some of the latest advancements in this field:
- Advanced Materials: One of the significant trends in worm screw design is the use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring materials with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and fatigue properties. For example, advanced alloys and composite materials are being employed to improve load capacity, reduce weight, and increase the longevity of worm screws. Additionally, advancements in material science and engineering are leading to the development of self-lubricating materials, which can minimize friction and improve efficiency by reducing the need for external lubrication.
- Improved Thread Geometries: Innovations in thread geometries have focused on optimizing load distribution, reducing friction, and improving efficiency. Researchers and engineers are developing novel thread profiles and forms that enhance contact between the worm screw and the worm wheel. These designs help minimize backlash, increase load-carrying capacity, and improve overall system performance. Additionally, advancements in computer simulations and modeling techniques enable more accurate analysis and optimization of thread geometries for specific applications.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Surface treatments and coatings are being applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. For instance, advanced coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings or specialized lubricious coatings help reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and minimize the need for external lubrication. Surface treatments like nitriding or carburizing can improve hardness and provide resistance against abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of worm screws.
- Precision Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing processes and technologies have enabled the production of worm screws with higher precision and tighter tolerances. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC grinding and high-precision gear hobbing, allow for the creation of worm screws with superior dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and better tooth profile control. These manufacturing advancements contribute to enhanced performance, reduced backlash, and increased overall system efficiency.
- Computer-Aided Design and Simulation: The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools has revolutionized worm screw design and optimization. Engineers can now create virtual models, simulate the behavior of worm gear systems, and analyze various design parameters to optimize performance before physical prototypes are manufactured. This iterative design process helps reduce development time, minimize costs, and improve the final design and performance of worm screws.
- Integration with Digitalization and Automation: The integration of worm gear systems with digitalization and automation technologies is another area of innovation. Worm screws are being designed to work seamlessly with sensor technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load. This data can be utilized for predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and optimization of the overall system performance.
It’s important to note that the field of worm screw design and materials is continuously evolving, and new innovations are being introduced regularly. Keeping up with the latest research, advancements, and industry developments is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in worm gear system applications.

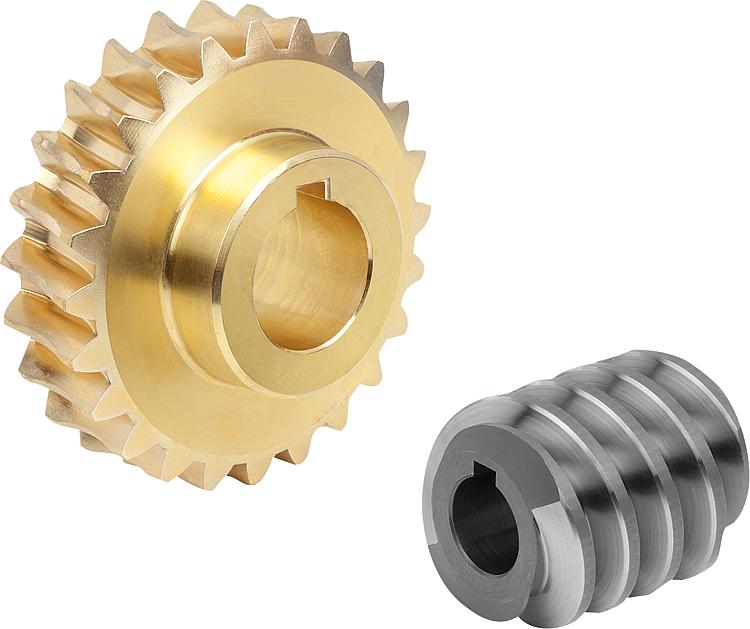
What is a worm screw in mechanical engineering?
In mechanical engineering, a worm screw, also known as a worm gear screw or worm gear, is a type of gear mechanism used to transmit motion and power between non-parallel shafts. It consists of a spiral-shaped screw, called the worm, and a gear wheel, called the worm wheel or worm gear. The worm screw and worm wheel have helical teeth that mesh together to transfer rotational motion.
The worm screw typically has a single thread or multiple threads wrapped around its cylindrical body. The worm wheel, on the other hand, has teeth that are specially shaped to mesh with the worm screw. The orientation of the worm screw and worm wheel is such that the axes of rotation are perpendicular to each other. This configuration allows the worm screw to convert rotational motion along its axis into rotary motion perpendicular to its axis.
One of the defining characteristics of a worm screw is its high gear ratio. Due to the helical nature of the teeth, a worm screw can achieve a high reduction ratio in a single gear stage. This means that a small rotation of the worm screw can result in a substantial rotation of the worm wheel. The ratio of the number of teeth on the worm wheel to the number of threads on the worm screw determines the reduction ratio.
Worm screws have several advantages and applications in mechanical engineering:
- High Reduction Ratio: As mentioned earlier, worm screws offer high gear ratios, making them suitable for applications that require significant speed reduction and torque multiplication. They are commonly used in applications where large gear reductions are needed, such as in conveyor systems, winches, and lifting equipment.
- Self-Locking: A unique characteristic of worm screws is their self-locking property. The angle of the helical teeth creates a wedging effect that prevents the worm wheel from driving the worm screw. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads without the need for additional braking mechanisms, making them suitable for applications where holding positions or preventing back-driving is crucial, such as in elevators or lifting mechanisms.
- Smooth and Quiet Operation: The helical teeth of the worm screw and worm wheel facilitate smooth and quiet operation. The gradual engagement and disengagement of the teeth minimize noise, vibration, and backlash, resulting in a more efficient and reliable gear mechanism.
- Compact Design: Worm screws offer a compact design compared to other gear mechanisms. The perpendicular arrangement of the worm screw and worm wheel allows for a compact and space-saving installation, making them suitable for applications where size constraints are a consideration.
- Reduction of Input Speed: Worm screws are commonly used to reduce the speed of the input shaft while increasing torque. This is advantageous in applications where slower, controlled motion is required, such as in industrial machinery, conveyors, and robotics.
It should be noted that worm screws also have some limitations, including lower efficiency compared to other gear mechanisms, higher friction due to sliding motion, and limited reverse operation capabilities. Therefore, careful consideration of the specific application requirements is necessary when deciding whether to use a worm screw in a mechanical system.


editor by CX 2024-01-09
China manufacturer Manufacturer Customized Precision CNC Turning Part Worm Gears Head Brass Screw
Product Description
Product Description
| Thickness | 0.15MM-20MM |
| Material | Spring steel(SWC), Music wire(SWP),Stainless steeK(SUS),Mild-carbon steel, |
| Phosphor copper, Beryllium copper, Brass, Aluminum 60Si2Mn,55CrSi, Alloy steel etc. | |
| -Stainless steel 17-7-PH(631SUS), Inconel X750,Bezinal Wire etc | |
| Finish | Zinc ! Nickel / Chrome / Tin / Silver / Copper I Gold / Dacromet plating,Blacking, |
| E-coating,Powder coating, PvC dipped etc | |
| Appliction | Auto,Micro,Hardware,Furniture,Bicycle,Industrial,ect. |
| Sample | 3-5work days |
| Delievery | 7-15days |
| Payment Terms | T/T,DIA,D/P,L/C,MoneyGram,Paypal payments. |
| Package | 1.PE bag inside, carton outside/Pallet. |
| 2.Other packages: Wooden box, individual packaging, tray packaging,tape & reelpackaging etc. | |
| 3.Per our customer’s need. |
Company Information
CHINAMFG is a manufacturer who established in 2004, located in HangZhou city. Our plant cover more than 3,000 square CHINAMFG and 100 employees around. We specialize in spring and stamping part, such as compression spring, torsion spring, wire forming, battery contact etc,North America, Europe, Southeast Aisa are our niche markets. Until now we have exported to over 40 countries.
Custom Feedback
FAQ
1. Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
HangZhou CHINAMFG is an OEM manufacturer of spring and stamping part with 17years.
2. Do you offer custom service?
Yes, it’s our job, send us your specification or drawings, and we will make you perfect products. Or tell us your idea for
getting a design from us.
3. Could I ask for samples before the bulk production?
Why not, we all concern the quality, and it’s the way to get rid of getting poor quality.
4. Which methods of payment do you accept?
T/T, L/C, Western Union, Trade Assurance.
5.What is your lead time?
3-7days for samples, 10-15days for mass production.
6.How do you make our business long-term ?
We provide professional service, keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit.
7.How many color we can choose?
Pantone colors, we can custom make any colors you like.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1years |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1years |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Can worm screws be used for high torque applications?
Yes, worm screws can be used for high torque applications. The design of a worm screw mechanism allows for efficient torque transmission and multiplication, making it suitable for applications that require high torque output. Here are some key points to consider regarding the use of worm screws in high torque applications:
- Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio, which results in a lower output speed and higher output torque. This gear reduction capability allows worm screws to generate and transmit substantial torque, making them well-suited for high torque applications.
- Efficiency: While worm screws can provide high torque output, it’s important to consider the mechanical efficiency of the system. The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. It’s crucial to ensure that the efficiency of the worm screw mechanism meets the requirements of the specific high torque application.
- Load Holding: Another advantage of worm screws is their self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel, which provides resistance against backward rotation. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads in a fixed position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. In high torque applications where load holding is required, worm screws can provide reliable and secure positioning.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the worm screw and worm wheel should be carefully selected to withstand high torque loads. Both components should have sufficient strength and wear resistance to handle the transmitted torque without deformation or premature failure. Depending on the specific application requirements, materials such as hardened steel, bronze, or other alloys may be chosen to ensure the durability and performance of the worm screw assembly.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of a worm screw mechanism, especially in high torque applications. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Regular maintenance, including monitoring lubricant levels and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed, is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear or failure.
Overall, worm screws can be effectively used in high torque applications, thanks to their gear reduction capabilities, load-holding properties, and efficient torque transmission. However, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as mechanical efficiency, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance to ensure that the worm screw mechanism can meet the specific requirements and demands of the high torque application.

Can worm screws be customized for specific engineering needs?
Yes, worm screws can be customized to meet specific engineering needs and application requirements. Customization allows for tailoring the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the worm screw to optimize its performance and functionality. Here are some aspects of worm screws that can be customized:
- Thread Geometry: The thread geometry of a worm screw can be customized to suit specific requirements. This includes the shape, profile, lead angle, and thread form. Custom thread geometries can be designed to optimize load distribution, minimize friction, reduce backlash, improve efficiency, or achieve specific performance characteristics.
- Pitch and Lead: The pitch and lead of a worm screw can be tailored to meet the desired gear ratio, output speed, load capacity, and other performance criteria. Customizing the pitch and lead allows for precise control over the speed reduction or multiplication capabilities of the worm gear system.
- Materials: Worm screws can be customized to be made from different materials based on the specific application requirements. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, bronze, and various alloys. The choice of material depends on factors such as load capacity, durability, corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and other environmental considerations.
- Diameter and Length: The diameter and length of a worm screw can be customized to suit the mechanical constraints and dimensional requirements of the application. Custom sizing ensures proper fit, alignment, and integration within the overall system design.
- Coatings and Surface Treatments: Custom coatings or surface treatments can be applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. These can include treatments such as hardening, heat treatment, plating, or specialized coatings to improve wear resistance, reduce friction, or provide corrosion protection.
- Special Features: Worm screws can be customized to incorporate special features or modifications based on specific engineering needs. This may include the addition of keyways, flanges, shaft extensions, or other components to facilitate integration with other system elements or to accommodate unique mechanical requirements.
Customization of worm screws requires collaboration between engineers, designers, and manufacturers with expertise in worm gear systems. It is important to define the specific engineering needs, performance requirements, and operational conditions to ensure that the customized worm screw meets the desired objectives effectively.

What are the advantages of using a worm screw in gear systems?
Using a worm screw in gear systems offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in certain applications. Here are some of the advantages of using a worm screw:
- High Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw is its ability to provide a high gear reduction ratio in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a significant reduction in rotational speed. This allows for efficient torque multiplication, enabling the transmission of high torque output from the worm screw to the worm wheel. The high gear reduction is beneficial in applications that require slow and powerful movements, such as lifting heavy loads or controlling conveyor systems.
- Compact Design: Worm screw mechanisms are known for their compact design. Compared to other gear systems, such as spur gears or helical gears, a worm screw setup can achieve a similar gear reduction with fewer components. This makes it a space-saving solution, especially in applications where limited space is available or where a compact design is desired.
- Self-Locking: The self-locking property of a worm screw is a significant advantage in many applications. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a natural tendency to hold its position and prevent backward rotation of the worm wheel. This self-locking feature eliminates the need for additional braking mechanisms or external locking devices, simplifying the overall system design and improving safety and stability in applications that require load holding or position locking.
- Right-Angle Transmission: Worm screw mechanisms provide motion transmission at a right angle, allowing for the transfer of motion between non-parallel shafts. This makes them suitable for applications where the input and output shafts are oriented perpendicular to each other. Examples include automotive steering systems, where the rotational motion from the steering wheel needs to be converted into lateral motion for steering the vehicle.
- Quiet Operation: Worm screw gear systems tend to operate quietly compared to other gear configurations. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation. This can be advantageous in applications where noise reduction is desirable, such as in office equipment, appliances, or environments where low noise levels are required.
It’s important to note that while worm screw mechanisms offer these advantages, there are also some considerations to keep in mind. For instance, worm screws can have lower mechanical efficiency compared to other gear systems due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth, leading to energy losses. Additionally, they may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which can affect precision and introduce a small amount of lost motion in the system. Nevertheless, the unique characteristics of worm screws make them a valuable choice in various applications where high gear reduction, self-locking, compactness, and right-angle transmission are essential.


editor by CX 2024-01-05
China factory Hot Selling Manufacturers Custom Galvanized Worm Gear Brass Gear Worm Gear Shaft Screw
Product Description
|
Material |
Low carbon steel( 1214, 1215, Y20, Y35), medium carbon steel( S45C, 4140, 4340) / Stainless steeL, 303, 304, 316 / Aluminum 6061, 6063, 7075 / Brass / Bronze / Copper / Titanium / Plastic (POM, PEEK, Nylon, Acrylic, PMMA, PVC, Derlin, ABS, HDEP) And Customized raw material,ect. |
|
Color |
According to customer’s requests |
|
Standard |
ROHS, HE, ISO9000-2008, IGS, TS16949 etc. |
|
Surface treatment |
Heat treatment, polishing electropolishing, plating, electrophresis, black oxide, galvanizing, cold galvanizing, powder coating, paint coating, sand blasting, shot blasting, anodize,passivasion etching,PAD printing, laster carving,dacromet, nickel plating,ect. |
|
Process |
Purchasing raw material / do Inspection on raw material (IQC) / make samples / Inspection samples(QC and engineer) / Sample approvel by customer / Mass production(LQC,PQC) / Surface finish (IQC) / Packing (FQC) / Make Delivery(FQC). |
|
Capabilities |
cnc turning/milling/machining stamping/bending/welding tapping/knurling/Thread hobbing/heading/chamfering Solidworks, STEP, IGS, AutoCAD |
|
Used |
electronics, electrical appliances, furniture, construction, toys, automotive /motorcycle, machinery, kitchen home appliances and other fields |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Surface Finishing: | Zinc Plated |
| Grade: | Custom Service |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you select the right worm screw for a specific application?
Selecting the right worm screw for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Here are the key steps to guide you in selecting the appropriate worm screw:
- Identify Application Requirements: Begin by understanding the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors such as torque, speed, direction of rotation, load capacity, precision, and environmental conditions. Determine the desired gear ratio and any additional features or specifications needed for the worm screw to meet the application’s objectives.
- Consider Design Parameters: Evaluate the design parameters of the worm screw, including the number of starts, lead angle, pitch diameter, and thread profile. These parameters directly influence the gear ratio, mechanical efficiency, and load-carrying capacity of the worm screw. Choose the design parameters that align with the application requirements, considering factors like torque transmission, speed regulation, and size constraints.
- Material Selection: Selecting the right material for the worm screw is crucial for its durability and performance. Consider factors such as strength, wear resistance, and compatibility with other mating components. Common materials for worm screws include hardened steel, stainless steel, bronze, or other alloys. Consult material specifications and consider the anticipated operating conditions to ensure the selected material can withstand the loads and environmental factors present in the application.
- Lubrication Requirements: Determine the lubrication requirements for the specific application. Some worm screws may require lubrication to reduce friction and wear, while others may have self-lubricating properties. Consider the type of lubricant (oil or grease), the frequency of lubrication, and the accessibility for lubrication maintenance. Ensure that the selected worm screw is compatible with the required lubrication method and can meet the lubrication demands of the application.
- Consider Mounting and Installation: Evaluate the mounting and installation requirements of the worm screw. Assess factors such as space limitations, alignment considerations, coupling options, and connection methods. Ensure that the selected worm screw can be easily integrated into the mechanical system and meets the specific installation requirements without compromising overall performance.
- Consult Manufacturer Resources: Utilize manufacturer resources, such as catalogs, technical specifications, and application guidelines, to gather information about available worm screw options. Manufacturers often provide recommendations and selection guides based on different application scenarios and performance criteria. Their expertise can help ensure that you choose the most suitable worm screw for your specific application.
- Review Cost and Availability: Consider the cost and availability of the worm screw. Evaluate the pricing, lead times, and availability from different suppliers or manufacturers. Balance the desired performance and quality with the budget constraints of the project, ensuring that the selected worm screw offers a cost-effective solution without compromising reliability or performance.
By following these steps and considering the application requirements, design parameters, material selection, lubrication needs, mounting considerations, manufacturer resources, and cost factors, you can select the right worm screw that meets the specific demands of your application. It’s important to consult with experts or seek assistance from manufacturers if you require further guidance or have unique requirements.
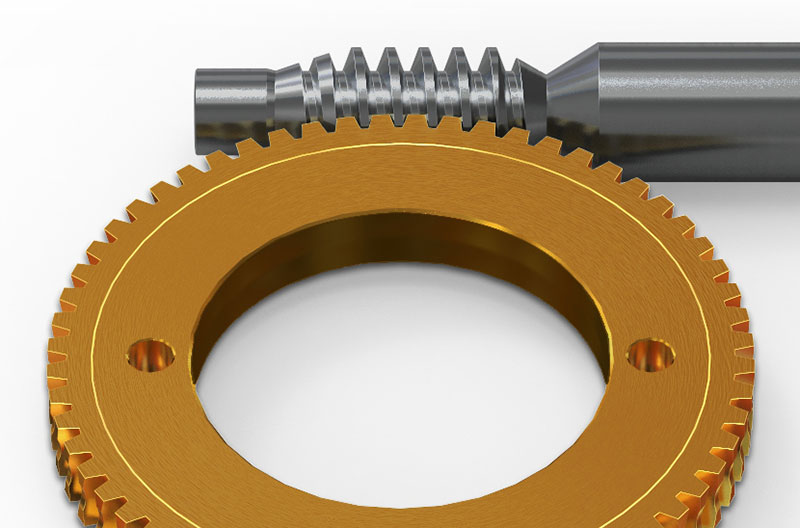
Are there different types of worm screws available?
Yes, there are different types of worm screws available to suit various applications and requirements. The design and characteristics of a worm screw can vary based on factors such as the material used, the thread geometry, the type of worm wheel, and the intended application. Here are some common types of worm screws:
- Standard Worm Screws: Standard worm screws are the most commonly used type and are available in a wide range of sizes and materials. They typically have a single-start thread and are made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, or bronze. Standard worm screws are suitable for general-purpose applications where moderate precision and load capacity are required.
- Double-Enveloping Worm Screws: Double-enveloping worm screws, also known as hourglass worm screws, have a unique thread profile that improves contact and load distribution between the worm screw and the worm wheel. This design offers enhanced torque transmission, higher efficiency, and increased load-carrying capacity compared to standard worm screws. Double-enveloping worm screws are often used in heavy-duty applications, such as gearboxes and high-load power transmission systems.
- Low-Lead Worm Screws: Low-lead worm screws have a smaller thread lead angle compared to standard worm screws. This design reduces the amount of sliding contact between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel, resulting in lower friction and improved efficiency. Low-lead worm screws are commonly used in applications where high efficiency and reduced heat generation are critical, such as in precision machinery and high-speed gear systems.
- Self-Locking Worm Screws: Self-locking worm screws are designed to have a high friction angle between the threads, making them capable of preventing reverse motion or backdriving. This self-locking feature eliminates the need for additional braking mechanisms or external locking devices in certain applications. Self-locking worm screws are commonly used in vertical lift systems, hoists, and other applications where holding the load position is essential.
- High-Precision Worm Screws: High-precision worm screws are manufactured to tighter tolerances and have improved accuracy compared to standard worm screws. They are designed to provide precise positioning and motion control in applications where high accuracy and repeatability are required. High-precision worm screws are often used in CNC machines, robotics, and other precision equipment.
- Customized Worm Screws: In addition to the standard types mentioned above, worm screws can also be customized to meet specific application requirements. Customized worm screws may involve variations in thread geometry, pitch, diameter, materials, or other parameters to suit unique applications or performance specifications.
The selection of the appropriate type of worm screw depends on factors such as the desired load capacity, efficiency requirements, backlash tolerance, positional accuracy, and environmental conditions. It is important to consult with manufacturers, engineers, or experts familiar with worm screw applications to determine the most suitable type for a specific application.

What are the advantages of using a worm screw in gear systems?
Using a worm screw in gear systems offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in certain applications. Here are some of the advantages of using a worm screw:
- High Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw is its ability to provide a high gear reduction ratio in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a significant reduction in rotational speed. This allows for efficient torque multiplication, enabling the transmission of high torque output from the worm screw to the worm wheel. The high gear reduction is beneficial in applications that require slow and powerful movements, such as lifting heavy loads or controlling conveyor systems.
- Compact Design: Worm screw mechanisms are known for their compact design. Compared to other gear systems, such as spur gears or helical gears, a worm screw setup can achieve a similar gear reduction with fewer components. This makes it a space-saving solution, especially in applications where limited space is available or where a compact design is desired.
- Self-Locking: The self-locking property of a worm screw is a significant advantage in many applications. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a natural tendency to hold its position and prevent backward rotation of the worm wheel. This self-locking feature eliminates the need for additional braking mechanisms or external locking devices, simplifying the overall system design and improving safety and stability in applications that require load holding or position locking.
- Right-Angle Transmission: Worm screw mechanisms provide motion transmission at a right angle, allowing for the transfer of motion between non-parallel shafts. This makes them suitable for applications where the input and output shafts are oriented perpendicular to each other. Examples include automotive steering systems, where the rotational motion from the steering wheel needs to be converted into lateral motion for steering the vehicle.
- Quiet Operation: Worm screw gear systems tend to operate quietly compared to other gear configurations. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation. This can be advantageous in applications where noise reduction is desirable, such as in office equipment, appliances, or environments where low noise levels are required.
It’s important to note that while worm screw mechanisms offer these advantages, there are also some considerations to keep in mind. For instance, worm screws can have lower mechanical efficiency compared to other gear systems due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth, leading to energy losses. Additionally, they may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which can affect precision and introduce a small amount of lost motion in the system. Nevertheless, the unique characteristics of worm screws make them a valuable choice in various applications where high gear reduction, self-locking, compactness, and right-angle transmission are essential.


editor by CX 2023-12-01
China Hot selling Manufacturer Customized Precision CNC Turning Part Worm Gears Head Brass Screw
Product Description
Product Description
| Thickness | 0.15MM-20MM |
| Material | Spring steel(SWC), Music wire(SWP),Stainless steeK(SUS),Mild-carbon steel, |
| Phosphor copper, Beryllium copper, Brass, Aluminum 60Si2Mn,55CrSi, Alloy steel etc. | |
| -Stainless steel 17-7-PH(631SUS), Inconel X750,Bezinal Wire etc | |
| Finish | Zinc ! Nickel / Chrome / Tin / Silver / Copper I Gold / Dacromet plating,Blacking, |
| E-coating,Powder coating, PvC dipped etc | |
| Appliction | Auto,Micro,Hardware,Furniture,Bicycle,Industrial,ect. |
| Sample | 3-5work days |
| Delievery | 7-15days |
| Payment Terms | T/T,DIA,D/P,L/C,MoneyGram,Paypal payments. |
| Package | 1.PE bag inside, carton outside/Pallet. |
| 2.Other packages: Wooden box, individual packaging, tray packaging,tape & reelpackaging etc. | |
| 3.Per our customer’s need. |
Company Information
Hongsheng is a manufacturer who established in 2004, located in HangZhou city. Our plant cover more than 3,000 square CHINAMFG and 100 employees around. We specialize in spring and stamping part, such as compression spring, torsion spring, wire forming, battery contact etc,North America, Europe, Southeast Aisa are our niche markets. Until now we have exported to over 40 countries.
Custom Feedback
FAQ
1. Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
HangZhou CHINAMFG is an OEM manufacturer of spring and stamping part with 17years.
2. Do you offer custom service?
Yes, it’s our job, send us your specification or drawings, and we will make you perfect products. Or tell us your idea for
getting a design from us.
3. Could I ask for samples before the bulk production?
Why not, we all concern the quality, and it’s the way to get rid of getting poor quality.
4. Which methods of payment do you accept?
T/T, L/C, Western Union, Trade Assurance.
5.What is your lead time?
3-7days for samples, 10-15days for mass production.
6.How do you make our business long-term ?
We provide professional service, keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit.
7.How many color we can choose?
Pantone colors, we can custom make any colors you like.
| After-sales Service: | 1years |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1years |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What are the common issues or failures associated with worm screws?
Worm screws, like any mechanical component, can experience certain issues or failures over time. Understanding these common problems is important for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Here are some common issues or failures associated with worm screws:
- Wear and Surface Damage: Due to the sliding contact between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel, wear can occur over time. This wear can lead to surface damage, such as pitting, scoring, or galling. Excessive wear and surface damage can affect the performance and efficiency of the worm screw gear system, resulting in increased backlash, decreased torque transmission, and potential failure.
- Lubrication Problems: Inadequate or improper lubrication is a common cause of issues in worm screw systems. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and accelerated wear. On the other hand, over-lubrication can cause excessive drag and fluid churn, leading to inefficient power transmission. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals, types of lubricants, and proper lubrication techniques to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the worm screw system.
- Backlash and Inaccuracy: Backlash refers to the play or clearance between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. Excessive backlash can result in reduced accuracy, loss of motion control, and diminished overall system performance. Backlash can be caused by factors such as wear, misalignment, or improper assembly. Regular inspection and adjustment of backlash are necessary to maintain the desired precision and minimize the effects of backlash-related issues.
- Misalignment: Misalignment between the worm screw and the worm wheel can result in increased friction, wear, and inefficiencies. Misalignment can occur due to factors such as improper installation, component deformation, or external forces. It is essential to ensure proper alignment during installation and periodically check for misalignment during routine maintenance. Adjustments should be made as necessary to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
- Overloading: Subjecting the worm screw gear system to excessive loads beyond its design limits can lead to failure. Overloading can result in accelerated wear, tooth breakage, or component deformation. It is important to operate the system within the specified load limits and consider factors such as shock loads, dynamic loads, and variations in operating conditions. If higher loads are required, it may be necessary to select a worm screw system with a higher load capacity or redesign the system accordingly.
- Corrosion and Contamination: Corrosion and contamination can negatively impact the performance and lifespan of worm screw systems. Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles can lead to corrosion, rusting, or damage to the surfaces of the worm screw and worm wheel. Contamination can interfere with smooth operation and cause accelerated wear. Proper environmental protection, regular cleaning, and appropriate sealing measures can help mitigate the effects of corrosion and contamination.
- Insufficient Stiffness: Worm screws rely on proper support and stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and prevent deflection. Inadequate stiffness in the supporting structure or mounting arrangement can result in excessive deflection, misalignment, and decreased performance. It is crucial to ensure that the worm screw system is properly supported and mounted to maintain the required rigidity and stiffness for optimal operation.
It’s important to note that the specific issues or failures associated with worm screws can vary depending on factors such as the application, operating conditions, maintenance practices, and the quality of the components. Regular inspection, proper lubrication, alignment checks, load monitoring, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for minimizing the occurrence of these issues and ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of worm screw systems.
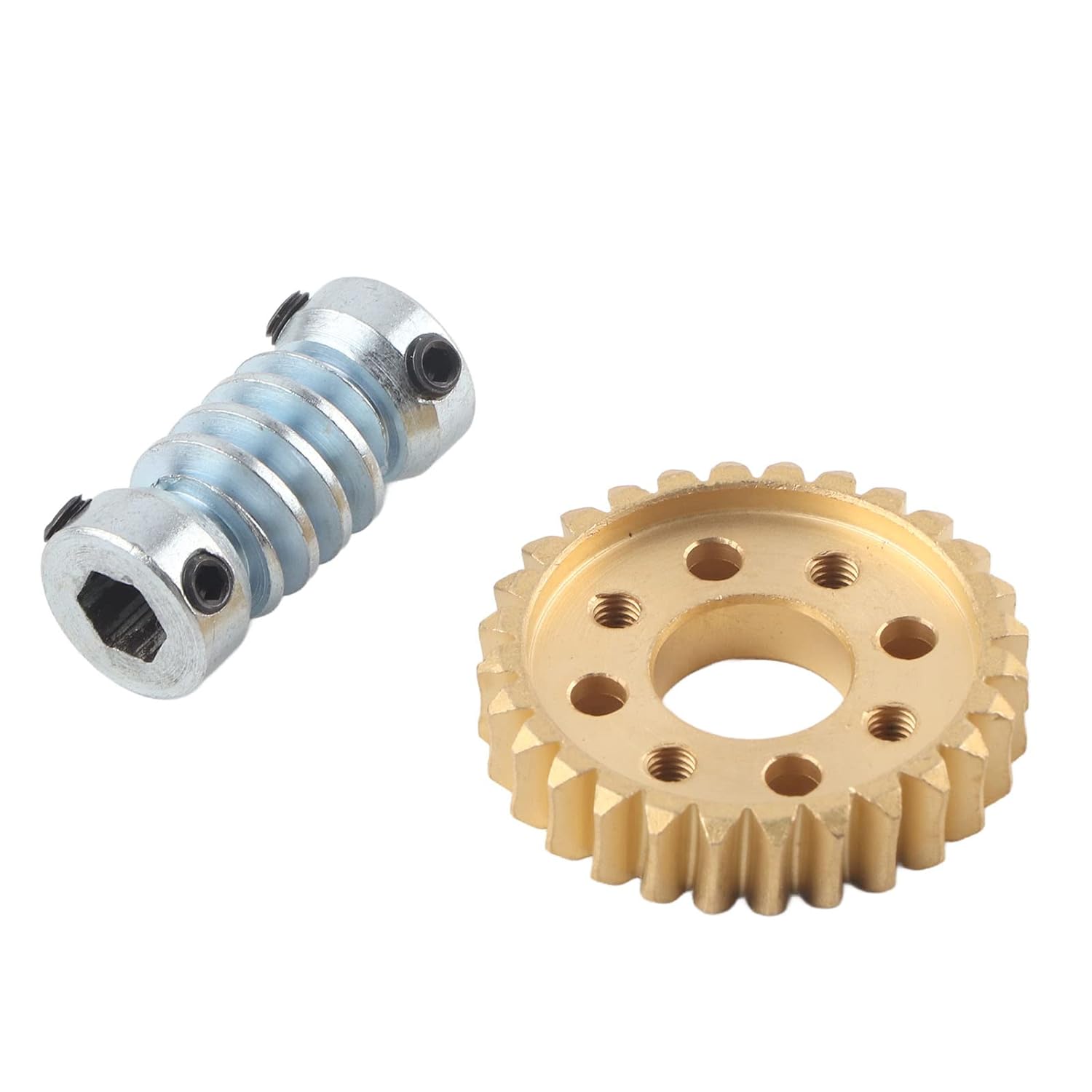

How do environmental factors affect the lifespan and performance of worm screws?
Environmental factors can have a significant impact on the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Here are some ways in which different environmental conditions can affect worm screw operation:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the material properties of worm screws. High temperatures can cause thermal expansion, leading to increased clearances and reduced efficiency. It can also accelerate wear and degradation of lubricants, leading to increased friction and potential damage. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can make lubricants less effective and increase the risk of brittle fracture or reduced flexibility in materials.
- Humidity and Moisture: Exposure to high humidity or moisture can lead to corrosion and rusting of worm screws, especially when they are made of materials that are not resistant to moisture. Corrosion can cause surface pitting, reduced strength, and accelerated wear, ultimately compromising the performance and lifespan of the worm screw.
- Dust and Contaminants: Dust, dirt, and other contaminants present in the environment can enter the worm gear system and cause abrasive wear on the worm screw. These particles can act as abrasives, accelerating the wear of the contacting surfaces and potentially leading to premature failure or reduced performance. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to mitigate the effects of dust and contaminants.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to chemicals, such as acids, solvents, or corrosive substances, can have a detrimental effect on worm screws. Chemicals can corrode the surfaces, degrade lubricants, and affect the material properties, leading to reduced lifespan and compromised performance. Choosing materials and coatings that are resistant to specific chemicals present in the environment is crucial for long-term performance.
- Load and Overloading: Environmental conditions, such as heavy loads or overloading, can significantly impact the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Excessive loads can lead to increased stress levels, deformation, and accelerated wear on the worm screw. It is important to operate worm gear systems within their specified load capacities and avoid overloading to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Operating Speed: The operating speed of the worm screw can also be influenced by environmental factors. High-speed applications may generate more heat due to friction, necessitating effective cooling mechanisms. On the other hand, low-speed applications may exhibit reduced lubrication effectiveness, requiring specific lubricants or maintenance practices to ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear.
To mitigate the effects of environmental factors, proper maintenance, regular inspection, and suitable protective measures are essential. This includes using appropriate lubricants, implementing effective sealing mechanisms, applying protective coatings, and considering environmental factors during the design and material selection process. By considering and addressing environmental factors, the lifespan and performance of worm screws can be optimized, ensuring reliable operation in various operating conditions.

What are the typical applications of worm screws in machinery?
Worm screws, also known as worm gears or worm gear screws, have a wide range of applications in machinery where motion transmission and torque multiplication are required. Their unique characteristics make them suitable for various industries and applications. Here are some typical applications of worm screws in machinery:
- Conveyor Systems: Worm screws are commonly used in conveyor systems to control the movement of materials. They provide precise speed reduction and torque multiplication, allowing for efficient transportation of goods in industries such as manufacturing, packaging, and logistics.
- Lifting Mechanisms: Worm screws are extensively used in lifting mechanisms, such as screw jacks or worm gear lifts. They provide reliable and controlled vertical motion for lifting heavy loads in applications like automotive service garages, construction sites, and material handling equipment.
- Winches and Hoists: Worm screws are employed in winches and hoists to provide high torque and controlled lifting or pulling operations. They are commonly used in applications such as cranes, marine equipment, elevators, and stage rigging.
- Rotary Actuators: Worm screws are utilized in rotary actuators to convert the input rotary motion into a controlled rotary output motion. This makes them suitable for applications like valve actuators, positioning systems, and robotic joints.
- Automotive Applications: Worm screws find use in automotive applications, particularly in steering systems. They are employed in steering gearboxes to convert the rotary motion from the steering wheel into the lateral motion required for steering the vehicle.
- Machine Tools: Worm screws are used in machine tools, such as milling machines, lathes, and drill presses, to control various linear and rotary movements. They provide precise positioning and motion control for cutting, shaping, and drilling operations.
- Printing and Packaging Machinery: Worm screws are employed in printing and packaging machinery to control the movement of printing heads, cutting blades, and packaging components. They ensure accurate and synchronized motion for high-quality printing and packaging processes.
- Robotics: Worm screws are utilized in robotics for precise and controlled motion in robotic arms, grippers, and other robotic mechanisms. They enable accurate positioning and smooth motion control in industrial automation and robotic applications.
These are just a few examples of the typical applications of worm screws in machinery. Their ability to provide high gear reduction ratios, precise motion control, and self-locking characteristics make them suitable for a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, construction, automotive, robotics, and many others where efficient power transmission and controlled motion are essential.


editor by CX 2023-11-27
China OEM Hot Selling Manufacturers Custom Galvanized Worm Gear Brass Gear Worm Gear Shaft Screw near me manufacturer
Product Description
|
Material |
Low carbon steel( 1214, 1215, Y20, Y35), medium carbon steel( S45C, 4140, 4340) / Stainless steeL, 303, 304, 316 / Aluminum 6061, 6063, 7075 / Brass / Bronze / Copper / Titanium / Plastic (POM, PEEK, Nylon, Acrylic, PMMA, PVC, Derlin, ABS, HDEP) And Customized raw material,ect. |
|
Color |
According to customer’s requests |
|
Standard |
ROHS, HE, ISO9000-2008, IGS, TS16949 etc. |
|
Surface treatment |
Heat treatment, polishing electropolishing, plating, electrophresis, black oxide, galvanizing, cold galvanizing, powder coating, paint coating, sand blasting, shot blasting, anodize,passivasion etching,PAD printing, laster carving,dacromet, nickel plating,ect. |
|
Process |
Purchasing raw material / do Inspection on raw material (IQC) / make samples / Inspection samples(QC and engineer) / Sample approvel by customer / Mass production(LQC,PQC) / Surface finish (IQC) / Packing (FQC) / Make Delivery(FQC). |
|
Capabilities |
cnc turning/milling/machining stamping/bending/welding tapping/knurling/Thread hobbing/heading/chamfering Solidworks, STEP, IGS, AutoCAD |
|
Used |
electronics, electrical appliances, furniture, construction, toys, automotive /motorcycle, machinery, kitchen home appliances and other fields |
Screw Shaft Types
A screw shaft is a cylindrical part that turns. Depending on its size, it is able to drive many different types of devices. The following information outlines the different types of screws, including their sizes, material, function, and applications. To help you select the right screw shaft, consider the following factors:
Size
A screw can come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from a quarter to a quarter-inch in diameter. A screw is a cylindrical shaft with an inclined plane wrapped around it, and its main function is to fasten objects together by translating torque into a linear force. This article will discuss the dimensions of screws and how to determine the size of a screw. It is important to note that screw sizes can be large and small depending on the purpose.
The diameter of a screw is the diameter of its shaft, and it must match the inner diameter of its nuts and washers. Screws of a certain diameter are also called machine screws, and they can be larger or smaller. Screw diameters are measured on the shaft underneath the screw head. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standardized screw diameters in 3/50-inch to 16 (3/8-inch) inches, and more recently, sizes were added in U.S. fractions of an inch. While shaft and head diameters are standardized, screw length may vary from job to job.
In the case of the 2.3-mm screw group, the construct strength was not improved by the 1.2-mm group. The smaller screw size did not increase the strength of the construct. Further, ABS material did not improve the construct strength. Thus, the size of screw shaft is an important consideration in model design. And remember that the more complex your model is, the larger it will be. A screw of a given size will have a similar failure rate as a screw of a different diameter.
Although different screw sizes are widely used, the differences in screw size were not statistically significant. Although there are some limitations, screws of different sizes are generally sufficient for fixation of a metacarpal shaft fracture. However, further clinical studies are needed to compare screw sizes for fracture union rates. So, if you are unsure of what size of screw shaft you need for your case, make sure to check the metric chart and ensure you use the right one.
Material
The material of a screw shaft plays an important role in the overall performance of a screw. Axial and central forces act to apply torque to the screw, while external forces, such as friction, exert a bending moment. The torsional moments are reflected in the torque, and this causes the screw to rotate at a higher rate than necessary. To ensure the longevity of the screw, the material of the screw shaft should be able to handle the bending moment, while the diameter of the shaft should be small enough to avoid causing damage.
Screws are made from different metals, such as steel, brass, titanium, and bronze. Manufacturers often apply a top coating of chromium, brass, or zinc to improve corrosion resistance. Screws made of aluminum are not durable and are prone to rusting due to exposure to weather conditions. The majority of screw shafts are self-locking. They are suited for many applications, including threaded fasteners, C-clamps, and vises.
Screws that are fabricated with conical sections typically feature reduced open cross-sectional areas at the discharge point. This is a key design parameter of conical screw shafts. In fact, reductions of up to 72% are common across a variety of applications. If the screw is designed to have a hard-iron hanger bearing, it must be hardened. If the screw shaft is not hardened, it will require an additional lubricant.
Another consideration is the threads. Screw shafts are typically made of high-precision threads and ridges. These are manufactured on lathes and CNC machines. Different shapes require different materials. Materials for the screw shaft vary. There are many different sizes and shapes available, and each 1 has its own application. In addition to helical and conical screw shafts, different materials are also available. When choosing material, the best 1 depends on the application.
The life of the screw depends on its size, load, and design. In general, the material of the screw shaft, nut body, and balls and rollers determine its fatigue life. This affects the overall life of the screw. To determine whether a specific screw has a longer or shorter life, the manufacturer must consider these factors, as well as the application requirements. The material should be clean and free of imperfections. It should be smooth and free of cracks or flaking, which may result in premature failure.
Function
The function of a screw shaft is to facilitate the rotation of a screw. Screws have several thread forms, including single-start, double-start and multi-start. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article we’ll explore each of them in detail. The function of a screw shaft can vary based on its design, but the following are common types. Here are some examples of screw shaft types and their purposes.
The screw’s torque enables it to lift objects. It can be used in conjunction with a bolt and nut to lift a load. Screws are also used to secure objects together. You can use them in screw presses, vises, and screw jacks. But their primary function is to hold objects together. Listed below are some of their main functions. When used to lift heavy loads, they can provide the required force to secure an object.
Screws can be classified into 2 types: square and round. Square threads are more efficient than round ones because they apply 0deg of angle to the nut. Square threads are also stronger than round threads and are often used in high-load applications. They’re generally cheaper to manufacture and are more difficult to break. And unlike square threads, which have a 0deg thread angle, these threads can’t be broken easily with a screwdriver.
A screw’s head is made of a series of spiral-like structures that extend from a cylindrical part to a tip. This portion of the screw is called the shank and is made of the smallest area. The shank is the portion that applies more force to the object. As the shaft extends from the head, it becomes thinner and narrow, forming a pointed tip. The head is the most important part of the screw, so it needs to be strong to perform its function.
The diameter of the screw shaft is measured in millimeters. The M8 screw has a thread pitch of 1.25 mm. Generally, the size of the screw shaft is indicated by the major and minor diameter. These dimensions are appended with a multiplication sign (M8x1).
Applications
The design of screws, including their size and shape, determines their critical rotating speeds. These speeds depend on the threaded part of the screw, the helix angle, and the geometry of the contact surfaces. When applied to a screw, these limits are referred to as “permissible speed limits.” These maximum speeds are meant for short periods of time and optimized running conditions. Continuous operation at these speeds can reduce the calculated life of a nut mechanism.
The main materials used to manufacture screws and screw shafts include steel, stainless steel, titanium, bronze, and brass. Screws may be coated for corrosion resistance, or they may be made of aluminium. Some materials can be threaded, including Teflon and nylon. Screw threads can even be molded into glass or porcelain. For the most part, steel and stainless steel are the most common materials for screw shafts. Depending on the purpose, a screw will be made of a material that is suitable for the application.
In addition to being used in fasteners, screw shafts are used in micrometers, drillers, conveyor belts, and helicopter blades. There are numerous applications of screw shafts, from weighing scales to measuring lengths. If you’re in the market for a screw, make sure to check out these applications. You’ll be happy you did! They can help you get the job done faster. So, don’t delay your next project.
If you’re interested in learning about screw sizing, then it’s important to know the axial and moment loads that your screws will experience. By following the laws of mechanics and knowing the load you can calculate the nominal life of your screw. You can also consider the effect of misalignment, uneven loading, and shocks on your screw. These will all affect the life of your screw. Then, you can select the right screw.


China manufacturer Spare Parts Brass Worm Gear and Worm Screw Drive with Good quality
Product Description
Star Win is a verified manufacturing and trading comb company in alibaba website, specialized in the electric damper actuators for the CZPT system, and the custom machining service. Since 1989, now have form the product list as following:
1. Machining service:
Custom gears, shafts etc transmission parts,
Custom all kinds of the machinery parts, Stamping, CNC lathe, milling machine, grinder, machining center, laser etc process all available.
2. Electric damper actuator:
spring return, modulating, reverse, on/off etc,function is analogy to brand drive
Our team of experienced engineers can give advice on materials and other factors that go into developing a quality product.
We utilize full CAD/CAM systems.
At Star Win, our mission is to provide quality products and services on time and at a reasonable cost
Screw Shaft Features Explained
When choosing the screw shaft for your application, you should consider the features of the screws: threads, lead, pitch, helix angle, and more. You may be wondering what these features mean and how they affect the screw’s performance. This article explains the differences between these factors. The following are the features that affect the performance of screws and their properties. You can use these to make an informed decision and purchase the right screw. You can learn more about these features by reading the following articles.
Threads
The major diameter of a screw thread is the larger of the 2 extreme diameters. The major diameter of a screw is also known as the outside diameter. This dimension can’t be directly measured, but can be determined by measuring the distance between adjacent sides of the thread. In addition, the mean area of a screw thread is known as the pitch. The diameter of the thread and pitch line are directly proportional to the overall size of the screw.
The threads are classified by the diameter and pitch. The major diameter of a screw shaft has the largest number of threads; the smaller diameter is called the minor diameter. The thread angle, also known as the helix angle, is measured perpendicular to the axis of the screw. The major diameter is the largest part of the screw; the minor diameter is the lower end of the screw. The thread angle is the half distance between the major and minor diameters. The minor diameter is the outer surface of the screw, while the top surface corresponds to the major diameter.
The pitch is measured at the crest of a thread. In other words, a 16-pitch thread has a diameter of 1 sixteenth of the screw shaft’s diameter. The actual diameter is 0.03125 inches. Moreover, a large number of manufacturers use this measurement to determine the thread pitch. The pitch diameter is a critical factor in successful mating of male and female threads. So, when determining the pitch diameter, you need to check the thread pitch plate of a screw.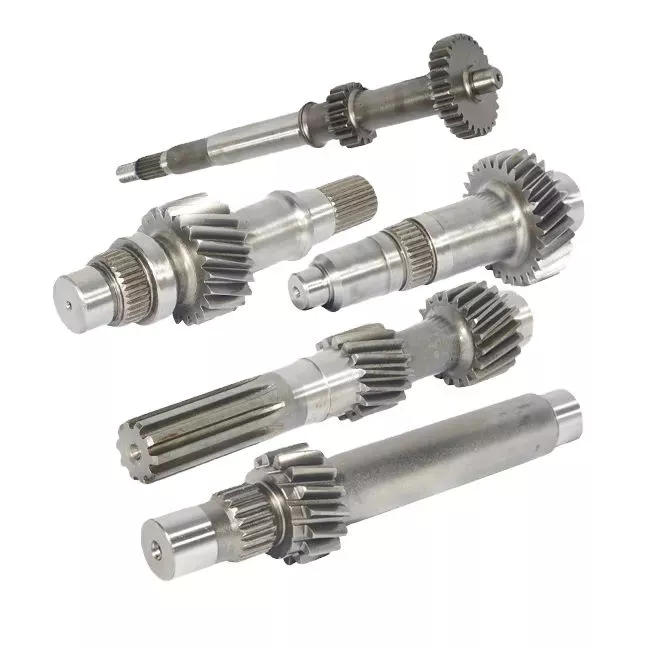
Lead
In screw shaft applications, a solid, corrosion-resistant material is an important requirement. Lead screws are a robust choice, which ensure shaft direction accuracy. This material is widely used in lathes and measuring instruments. They have black oxide coatings and are suited for environments where rusting is not acceptable. These screws are also relatively inexpensive. Here are some advantages of lead screws. They are highly durable, cost-effective, and offer high reliability.
A lead screw system may have multiple starts, or threads that run parallel to each other. The lead is the distance the nut travels along the shaft during a single revolution. The smaller the lead, the tighter the thread. The lead can also be expressed as the pitch, which is the distance between adjacent thread crests or troughs. A lead screw has a smaller pitch than a nut, and the smaller the lead, the greater its linear speed.
When choosing lead screws, the critical speed is the maximum number of revolutions per minute. This is determined by the minor diameter of the shaft and its length. The critical speed should never be exceeded or the lead will become distorted or cracked. The recommended operational speed is around 80 percent of the evaluated critical speed. Moreover, the lead screw must be properly aligned to avoid excessive vibrations. In addition, the screw pitch must be within the design tolerance of the shaft.
Pitch
The pitch of a screw shaft can be viewed as the distance between the crest of a thread and the surface where the threads meet. In mathematics, the pitch is equivalent to the length of 1 wavelength. The pitch of a screw shaft also relates to the diameter of the threads. In the following, the pitch of a screw is explained. It is important to note that the pitch of a screw is not a metric measurement. In the following, we will define the 2 terms and discuss how they relate to 1 another.
A screw’s pitch is not the same in all countries. The United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States have standardized screw threads according to the UN system. Therefore, there is a need to specify the pitch of a screw shaft when a screw is being manufactured. The standardization of pitch and diameter has also reduced the cost of screw manufacturing. Nevertheless, screw threads are still expensive. The United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States have introduced a system for the calculation of screw pitch.
The pitch of a lead screw is the same as that of a lead screw. The diameter is 0.25 inches and the circumference is 0.79 inches. When calculating the mechanical advantage of a screw, divide the diameter by its pitch. The larger the pitch, the more threads the screw has, increasing its critical speed and stiffness. The pitch of a screw shaft is also proportional to the number of starts in the shaft.
Helix angle
The helix angle of a screw shaft is the angle formed between the circumference of the cylinder and its helix. Both of these angles must be equal to 90 degrees. The larger the lead angle, the smaller the helix angle. Some reference materials refer to angle B as the helix angle. However, the actual angle is derived from calculating the screw geometry. Read on for more information. Listed below are some of the differences between helix angles and lead angles.
High helix screws have a long lead. This length reduces the number of effective turns of the screw. Because of this, fine pitch screws are usually used for small movements. A typical example is a 16-mm x 5-inch screw. Another example of a fine pitch screw is a 12x2mm screw. It is used for small moves. This type of screw has a lower lead angle than a high-helix screw.
A screw’s helix angle refers to the relative angle of the flight of the helix to the plane of the screw axis. While screw helix angles are not often altered from the standard square pitch, they can have an effect on processing. Changing the helix angle is more common in two-stage screws, special mixing screws, and metering screws. When a screw is designed for this function, it should be able to handle the materials it is made of.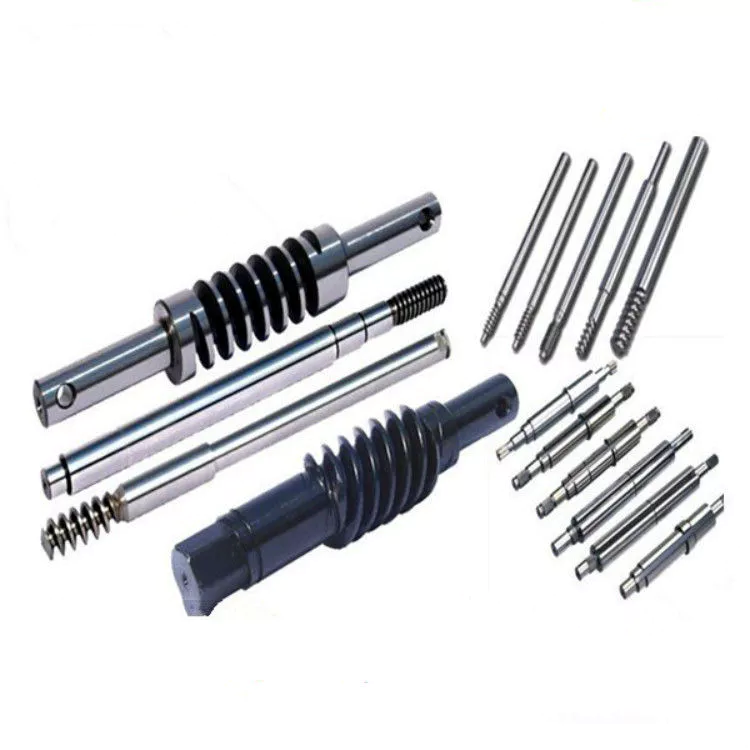
Size
The diameter of a screw is its diameter, measured from the head to the shaft. Screw diameters are standardized by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. The diameters of screws range from 3/50 inches to 16 inches, and more recently, fractions of an inch have been added. However, shaft diameters may vary depending on the job, so it is important to know the right size for the job. The size chart below shows the common sizes for screws.
Screws are generally referred to by their gauge, which is the major diameter. Screws with a major diameter less than a quarter of an inch are usually labeled as #0 to #14 and larger screws are labeled as sizes in fractions of an inch. There are also decimal equivalents of each screw size. These measurements will help you choose the correct size for your project. The screws with the smaller diameters were not tested.
In the previous section, we described the different shaft sizes and their specifications. These screw sizes are usually indicated by fractions of an inch, followed by a number of threads per inch. For example, a ten-inch screw has a shaft size of 2” with a thread pitch of 1/4″, and it has a diameter of 2 inches. This screw is welded to a two-inch Sch. 40 pipe. Alternatively, it can be welded to a 9-inch O.A.L. pipe.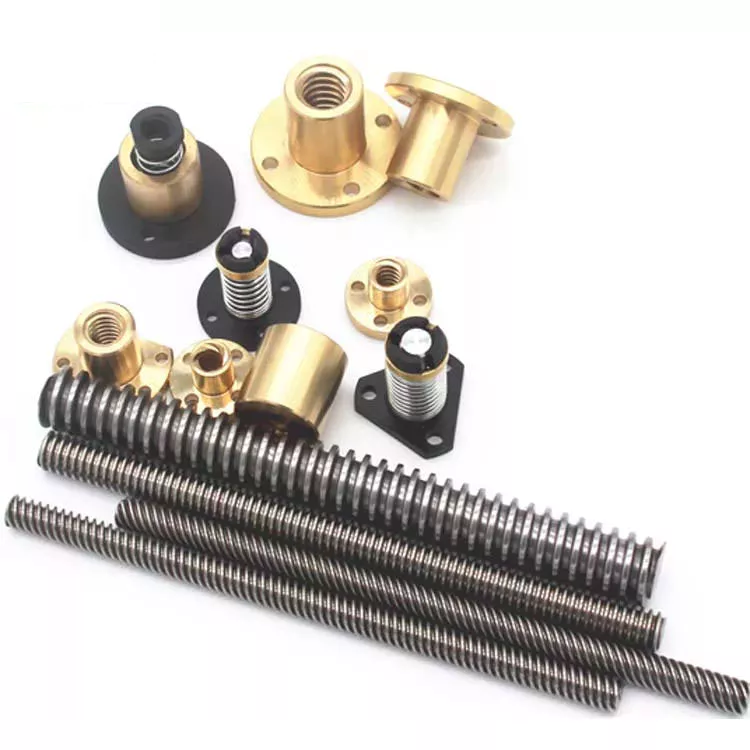
Shape
Screws come in a wide variety of sizes and shapes, from the size of a quarter to the diameter of a U.S. quarter. Screws’ main function is to hold objects together and to translate torque into linear force. The shape of a screw shaft, if it is round, is the primary characteristic used to define its use. The following chart shows how the screw shaft differs from a quarter:
The shape of a screw shaft is determined by 2 features: its major diameter, or distance from the outer edge of the thread on 1 side to the inner smooth surface of the shaft. These are generally 2 to 16 millimeters in diameter. Screw shafts can have either a fully threaded shank or a half-threaded shank, with the latter providing better stability. Regardless of whether the screw shaft is round or domed, it is important to understand the different characteristics of a screw before attempting to install it into a project.
The screw shaft’s diameter is also important to its application. The ball circle diameter refers to the distance between the center of 2 opposite balls in contact with the grooves. The root diameter, on the other hand, refers to the distance between the bottommost grooves of the screw shaft. These are the 2 main measurements that define the screw’s overall size. Pitch and nominal diameter are important measurements for a screw’s performance in a particular application.
Lubrication
In most cases, lubrication of a screw shaft is accomplished with grease. Grease is made up of mineral or synthetic oil, thickening agent, and additives. The thickening agent can be a variety of different substances, including lithium, bentonite, aluminum, and barium complexes. A common classification for lubricating grease is NLGI Grade. While this may not be necessary when specifying the type of grease to use for a particular application, it is a useful qualitative measure.
When selecting a lubricant for a screw shaft, the operating temperature and the speed of the shaft determine the type of oil to use. Too much oil can result in heat buildup, while too little can lead to excessive wear and friction. The proper lubrication of a screw shaft directly affects the temperature rise of a ball screw, and the life of the assembly. To ensure the proper lubrication, follow the guidelines below.
Ideally, a low lubrication level is appropriate for medium-sized feed stuff factories. High lubrication level is appropriate for larger feed stuff factories. However, in low-speed applications, the lubrication level should be sufficiently high to ensure that the screws run freely. This is the only way to reduce friction and ensure the longest life possible. Lubrication of screw shafts is an important consideration for any screw.

