Product Description
TXR Series Sleeve Type Single Nut Ball Screw (C5/Ct7/Ct10)
| Table of Shaft dia. and Lead combination for Rolled Ball Screw | ||||||||||||||||
| Lead (mm) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 30 | ||
| Shaft dia (mm) | 4 | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 5 | / | |||||||||||||||
| 6 | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 8 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||
| 10 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||
| 12 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 14 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||
Accuracy Class & Axial Clearance
Accuracy grade of TXR series(sleeve type single nut ball screw)are based on C5,Ct7 and Ct10(JIS B 1192-3). According to accuracy grade, Axial play 0.005(Preload :C5),0.02(Ct7) and 0.05mm or less(Ct10).
Material & Surface Hardness
TXR series (sleeve type single nut ball screw) of screw shaft screw material S55C (induction hardening), nut material SCM415H (carburizing and hardening), the surface hardness of the ball screw part is HRC58 or higher.
Shaft End Shape
The shape of the shaft end of the TXR series (sleeve type single nut ball screws) has been standardized.
Application:
1. Medical industry
2.Lithium battery industry
3.Solar photovoltaic industry
4. Semi conductor Industry
5. General industry machinery
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment
9. 3C industry etc
Technical Drawing
Specification List
FACTORY DETAILED PROCESSING PHOTOS
HIGH QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
FAQ
1. Why choose CHINAMFG China?
Over the past 14 years, CHINAMFG has always insisted that “products and services” start from Japanese industry standards,taking ZheJiang standards as the bottom line, actively invest in the development of new transmission components and self-experiment and test. With the service tenet of “exceeding customer expectations”, establish a “trusted” partnership.
2. What is your main products ?
We are a leading manufacturer and distributor of linear motion components in China. Especially miniature size of Ball Screws and Linear Actuators and linear motion guideways. Our brand “KGG” stands for ” Know-how,” ” Great Quality,” and ” Good value” and our factory is located in the most advanced city in China: ZheJiang with the best equipment and sophisticated technology, completely strict quality control system. Our aim is to supply world leader class linear motion components but with most reasonable price in the world.
3. How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
4. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
5. How can I get a sample to check the quality?
After confirmation of our quoted price, you can place the sample order. The sample will be started after you CHINAMFG back our detailed technical file.
6. What’s your payment terms?
Our payment terms is 30% deposit,balance 70% before shipment. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C7 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 10mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 3-Row |
| Nut Type: | Sleeve Type Single Nut |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

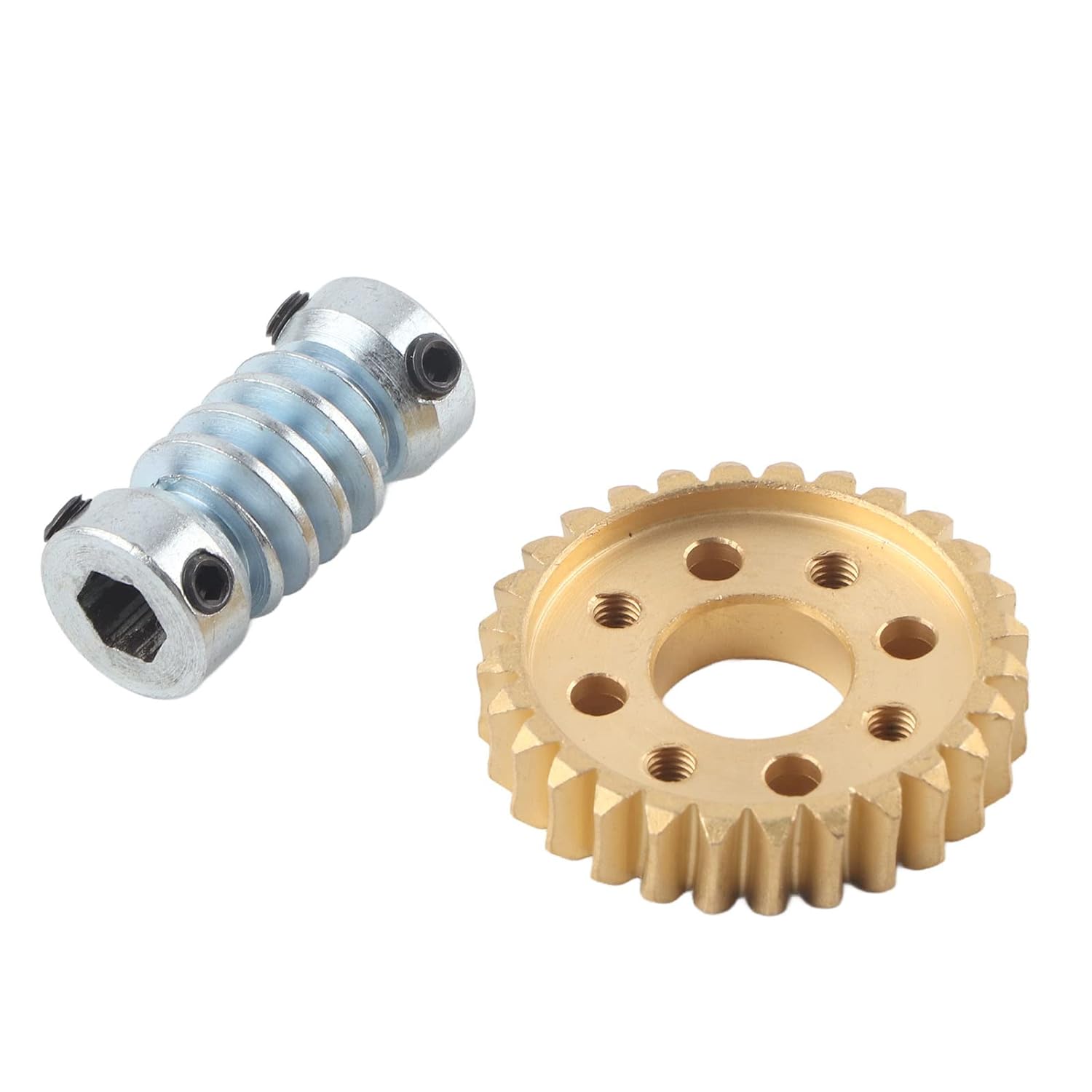
What are the limitations of using worm screws in mechanical designs?
While worm screws offer several advantages in mechanical designs, they also have some limitations that should be considered. Here are the key limitations of using worm screws:
- Lower Mechanical Efficiency: Worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower mechanical efficiency compared to other gear systems. This is primarily due to the sliding contact between the worm screw threads and the worm wheel teeth, which results in higher friction and energy losses. The lower mechanical efficiency can lead to heat generation, reduced power transmission, and decreased overall system efficiency. It’s important to consider the trade-off between the desired gear reduction and the mechanical efficiency requirements of the specific application.
- Limited High-Speed Applications: Worm screws are not well-suited for high-speed applications. The sliding contact and meshing action between the threads and teeth can generate heat and cause wear at high rotational speeds. Additionally, the higher friction and lower mechanical efficiency mentioned earlier can limit the maximum achievable speed of the system. If high-speed operation is a requirement, alternative gear systems, such as spur gears or helical gears, may be more suitable.
- Backlash: Worm screw mechanisms can exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which is the lost motion or clearance between the threads and teeth when changing direction. Backlash can negatively impact precision and positioning accuracy in applications that require tight tolerances. It’s important to consider backlash and implement measures to minimize its effects, such as using anti-backlash mechanisms or incorporating backlash compensation techniques.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials for worm screws is crucial to ensure their durability and performance. Worm screws typically require harder materials to withstand the sliding contact and high contact pressures between the threads and teeth. The selection of suitable materials may increase the manufacturing complexity and cost of the worm screw assembly. Additionally, the choice of materials should consider factors such as compatibility, wear resistance, and the specific operating conditions of the application.
- Load Distribution: In worm screw mechanisms, the load is distributed over a limited number of teeth on the worm wheel. This concentrated load distribution can result in higher stresses and wear on the contacting surfaces. It’s important to consider the load capacity and contact area of the worm wheel teeth to ensure that the assembly can handle the anticipated loads without premature failure or excessive wear.
- Required Lubrication: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of worm screw mechanisms. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces. However, the need for lubrication adds complexity to the design and maintenance of the system. It requires regular monitoring of lubricant levels and periodic lubricant replenishment or replacement. Failure to maintain proper lubrication can result in increased friction, wear, and potential system failure.
Despite these limitations, worm screws continue to be widely used in various mechanical designs due to their unique characteristics and advantages. It’s essential to carefully evaluate the specific requirements and constraints of the application and consider alternative gear systems if the limitations of worm screws pose significant challenges to the desired performance and efficiency.

How do environmental factors affect the lifespan and performance of worm screws?
Environmental factors can have a significant impact on the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Here are some ways in which different environmental conditions can affect worm screw operation:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the material properties of worm screws. High temperatures can cause thermal expansion, leading to increased clearances and reduced efficiency. It can also accelerate wear and degradation of lubricants, leading to increased friction and potential damage. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can make lubricants less effective and increase the risk of brittle fracture or reduced flexibility in materials.
- Humidity and Moisture: Exposure to high humidity or moisture can lead to corrosion and rusting of worm screws, especially when they are made of materials that are not resistant to moisture. Corrosion can cause surface pitting, reduced strength, and accelerated wear, ultimately compromising the performance and lifespan of the worm screw.
- Dust and Contaminants: Dust, dirt, and other contaminants present in the environment can enter the worm gear system and cause abrasive wear on the worm screw. These particles can act as abrasives, accelerating the wear of the contacting surfaces and potentially leading to premature failure or reduced performance. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to mitigate the effects of dust and contaminants.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to chemicals, such as acids, solvents, or corrosive substances, can have a detrimental effect on worm screws. Chemicals can corrode the surfaces, degrade lubricants, and affect the material properties, leading to reduced lifespan and compromised performance. Choosing materials and coatings that are resistant to specific chemicals present in the environment is crucial for long-term performance.
- Load and Overloading: Environmental conditions, such as heavy loads or overloading, can significantly impact the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Excessive loads can lead to increased stress levels, deformation, and accelerated wear on the worm screw. It is important to operate worm gear systems within their specified load capacities and avoid overloading to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Operating Speed: The operating speed of the worm screw can also be influenced by environmental factors. High-speed applications may generate more heat due to friction, necessitating effective cooling mechanisms. On the other hand, low-speed applications may exhibit reduced lubrication effectiveness, requiring specific lubricants or maintenance practices to ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear.
To mitigate the effects of environmental factors, proper maintenance, regular inspection, and suitable protective measures are essential. This includes using appropriate lubricants, implementing effective sealing mechanisms, applying protective coatings, and considering environmental factors during the design and material selection process. By considering and addressing environmental factors, the lifespan and performance of worm screws can be optimized, ensuring reliable operation in various operating conditions.

How does a worm screw differ from a regular screw?
In mechanical engineering, a worm screw differs from a regular screw in several key aspects. While both types of screws have helical threads, their designs and functions are distinct. Here are the primary differences between a worm screw and a regular screw:
- Motion Transmission: The primary function of a regular screw is to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. It typically has a single-threaded or multi-threaded configuration and is used for applications such as fastening, clamping, or lifting. On the other hand, a worm screw is designed to transmit motion and power between non-parallel shafts. It converts rotary motion along its axis into rotary motion perpendicular to its axis by meshing with a worm wheel or gear.
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio of a worm screw is typically much higher compared to that of a regular screw. The helical teeth of the worm screw and the worm wheel allow for a high reduction ratio in a single gear stage. This means that a small rotation of the worm screw can result in a significant rotation of the worm wheel. In contrast, a regular screw does not have a gear ratio and is primarily used for linear motion or force multiplication.
- Orientation and Shaft Arrangement: A regular screw is typically used in applications where the input and output shafts are parallel or nearly parallel. It transfers motion and force along the same axis. In contrast, a worm screw is designed for applications where the input and output shafts are perpendicular to each other. The orientation of the worm screw and the worm wheel allows for motion transmission between non-parallel shafts.
- Self-Locking: One distinctive characteristic of a worm screw is its self-locking property. The helical teeth of the worm screw create a wedging effect that prevents the worm wheel from driving the worm screw. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads without the need for additional braking mechanisms. Regular screws, on the other hand, do not have this self-locking capability.
- Applications: Regular screws find widespread use in numerous applications, including construction, manufacturing, woodworking, and everyday objects like screws used in fastening. They are primarily employed for linear motion, clamping, or force multiplication. Worm screws, on the other hand, are commonly used in applications that require significant speed reduction, torque multiplication, or motion transmission at right angles. Typical applications include conveyor systems, winches, lifting mechanisms, and heavy machinery.
These differences in design and function make worm screws and regular screws suitable for distinct applications. Regular screws are more commonly used for linear motion and force transfer along parallel or nearly parallel shafts, while worm screws excel in transmitting motion and power between non-parallel shafts with high gear reduction ratios.


editor by CX 2024-03-15
China high quality Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
Product Description
Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Type: | Round Head |
| Groove: | Cross |
| Connection: | Hinged Bolts |
| Head Style: | Square |
| Standard: | DIN, GB, ANSI, BSW, JIS, GOST |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can worm screws be used for high torque applications?
Yes, worm screws can be used for high torque applications. The design of a worm screw mechanism allows for efficient torque transmission and multiplication, making it suitable for applications that require high torque output. Here are some key points to consider regarding the use of worm screws in high torque applications:
- Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio, which results in a lower output speed and higher output torque. This gear reduction capability allows worm screws to generate and transmit substantial torque, making them well-suited for high torque applications.
- Efficiency: While worm screws can provide high torque output, it’s important to consider the mechanical efficiency of the system. The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. It’s crucial to ensure that the efficiency of the worm screw mechanism meets the requirements of the specific high torque application.
- Load Holding: Another advantage of worm screws is their self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel, which provides resistance against backward rotation. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads in a fixed position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. In high torque applications where load holding is required, worm screws can provide reliable and secure positioning.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the worm screw and worm wheel should be carefully selected to withstand high torque loads. Both components should have sufficient strength and wear resistance to handle the transmitted torque without deformation or premature failure. Depending on the specific application requirements, materials such as hardened steel, bronze, or other alloys may be chosen to ensure the durability and performance of the worm screw assembly.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of a worm screw mechanism, especially in high torque applications. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Regular maintenance, including monitoring lubricant levels and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed, is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear or failure.
Overall, worm screws can be effectively used in high torque applications, thanks to their gear reduction capabilities, load-holding properties, and efficient torque transmission. However, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as mechanical efficiency, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance to ensure that the worm screw mechanism can meet the specific requirements and demands of the high torque application.

How do environmental factors affect the lifespan and performance of worm screws?
Environmental factors can have a significant impact on the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Here are some ways in which different environmental conditions can affect worm screw operation:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the material properties of worm screws. High temperatures can cause thermal expansion, leading to increased clearances and reduced efficiency. It can also accelerate wear and degradation of lubricants, leading to increased friction and potential damage. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can make lubricants less effective and increase the risk of brittle fracture or reduced flexibility in materials.
- Humidity and Moisture: Exposure to high humidity or moisture can lead to corrosion and rusting of worm screws, especially when they are made of materials that are not resistant to moisture. Corrosion can cause surface pitting, reduced strength, and accelerated wear, ultimately compromising the performance and lifespan of the worm screw.
- Dust and Contaminants: Dust, dirt, and other contaminants present in the environment can enter the worm gear system and cause abrasive wear on the worm screw. These particles can act as abrasives, accelerating the wear of the contacting surfaces and potentially leading to premature failure or reduced performance. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to mitigate the effects of dust and contaminants.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to chemicals, such as acids, solvents, or corrosive substances, can have a detrimental effect on worm screws. Chemicals can corrode the surfaces, degrade lubricants, and affect the material properties, leading to reduced lifespan and compromised performance. Choosing materials and coatings that are resistant to specific chemicals present in the environment is crucial for long-term performance.
- Load and Overloading: Environmental conditions, such as heavy loads or overloading, can significantly impact the lifespan and performance of worm screws. Excessive loads can lead to increased stress levels, deformation, and accelerated wear on the worm screw. It is important to operate worm gear systems within their specified load capacities and avoid overloading to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Operating Speed: The operating speed of the worm screw can also be influenced by environmental factors. High-speed applications may generate more heat due to friction, necessitating effective cooling mechanisms. On the other hand, low-speed applications may exhibit reduced lubrication effectiveness, requiring specific lubricants or maintenance practices to ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear.
To mitigate the effects of environmental factors, proper maintenance, regular inspection, and suitable protective measures are essential. This includes using appropriate lubricants, implementing effective sealing mechanisms, applying protective coatings, and considering environmental factors during the design and material selection process. By considering and addressing environmental factors, the lifespan and performance of worm screws can be optimized, ensuring reliable operation in various operating conditions.

How does a worm screw mechanism work?
A worm screw mechanism, also known as a worm gear mechanism, is a type of power transmission system that consists of a worm screw and a worm wheel. It is designed to transmit motion and power between non-parallel shafts. The mechanism works based on the interaction between the helical threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a worm screw mechanism works:
- Structure: The worm screw is a cylindrical shaft with a helical thread wrapped around it, resembling a screw. The worm wheel, also known as a worm gear, is a gear with teeth that mesh with the threads of the worm screw. The orientation of the worm screw and the worm wheel is such that the axes of rotation are perpendicular to each other.
- Motion Transmission: When the worm screw is rotated, its helical threads engage with the teeth of the worm wheel. As the worm screw rotates, it drives the worm wheel to rotate as well. The helical shape of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel allow for motion transmission perpendicular to the axis of the worm screw.
- Gear Reduction: One of the key characteristics of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio in a single gear stage. This means that a small rotation of the worm screw can result in a substantial rotation of the worm wheel. The gear reduction enables the worm screw mechanism to generate high torque output at the worm wheel.
- Self-Locking: A notable feature of the worm screw mechanism is its self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel. This means that the worm wheel cannot easily rotate the worm screw. Instead, the worm screw tends to hold its position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. The self-locking feature makes the worm screw mechanism suitable for applications that require holding loads in a fixed position.
- Efficiency and Backlash: The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. Additionally, worm screw mechanisms may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which refers to the slight play or clearance between the threads and teeth. Backlash can affect precision and introduce a small amount of lost motion in the system.
- Applications: Worm screw mechanisms find applications in various industries and machinery where motion transmission at right angles and high gear reduction ratios are required. Common applications include conveyor systems, lifting mechanisms, winches, automotive steering systems, robotics, and machine tools.
The worm screw mechanism offers a unique combination of motion transmission, gear reduction, and self-locking capabilities, making it suitable for specific applications where precise control, high torque output, and the ability to hold loads are essential.


editor by CX 2024-01-17
China Best Sales Straight Carbon Steel Shaft Worm Spline Screw Machinery Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Knurling/Polishing High Precision with Quenching for Power Tools Motor Rotor
Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings, joints……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, and drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ12(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.015mm |
| Roundness | 0.01mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.2-0.6 |
| Straightness | 0.01mm |
| Hardness | Customized |
| Length | 153mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial orders are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

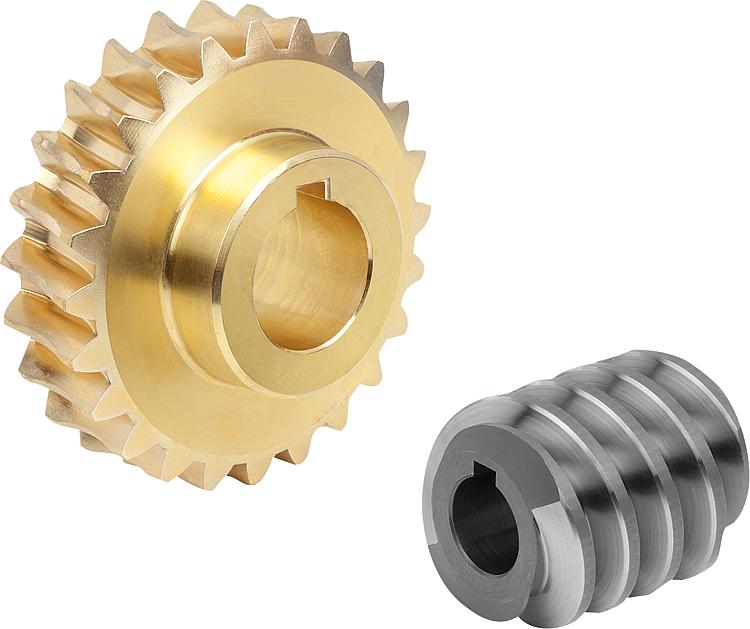
How do you properly lubricate a worm screw and gear assembly?
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of a worm screw and gear assembly. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, thereby extending the lifespan of the components. Here are the steps to properly lubricate a worm screw and gear assembly:
- Clean the Assembly: Before applying lubrication, ensure that the worm screw and gear assembly is free from dirt, debris, and old lubricant residues. Clean the surfaces using an appropriate cleaning agent or solvent, followed by a thorough drying process.
- Select the Right Lubricant: Choose a lubricant specifically designed for gear systems or worm screw applications. Consider factors such as viscosity, temperature range, load capacity, and compatibility with the materials used in the assembly. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or lubrication guidelines for the specific assembly to determine the suitable lubricant type and grade.
- Apply the Lubricant: Apply the lubricant to the contacting surfaces of the worm screw and gear assembly. Use an appropriate applicator, such as a brush, oil can, or grease gun, depending on the lubricant form (oil or grease) and the accessibility of the components. Ensure complete coverage of the gear teeth, worm screw threads, and other relevant surfaces. Pay attention to areas where the most significant friction and wear occur.
- Monitor the Lubricant Level: Check the lubricant level regularly to ensure an adequate supply. Depending on the application and operating conditions, lubricant consumption or degradation may occur over time. It is important to maintain the lubricant level within the recommended range to ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear or overheating.
- Periodic Lubrication Maintenance: Establish a lubrication maintenance schedule based on the operating conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect the assembly for signs of lubricant degradation, contamination, or insufficient lubrication. Replace the lubricant as needed and follow the recommended intervals for lubricant replenishment or reapplication.
- Consideration for Grease Lubrication: If using grease as the lubricant, it is important to choose a high-quality grease suitable for worm screw applications. Grease provides better adhesion to surfaces and tends to stay in place, offering longer-lasting lubrication compared to oil. However, excessive grease accumulation or over-greasing should be avoided, as it can lead to increased friction and inefficiency.
It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for lubrication specific to the worm screw and gear assembly. Different assemblies may have unique lubrication requirements based on their design, load capacity, operating conditions, and materials used. By properly lubricating the worm screw and gear assembly, you can ensure optimal performance, reduce wear, and extend the operational life of the components.

What are the latest innovations in worm screw design and materials?
In recent years, there have been several notable innovations in worm screw design and materials that aim to improve performance, efficiency, durability, and overall functionality. Here are some of the latest advancements in this field:
- Advanced Materials: One of the significant trends in worm screw design is the use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring materials with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and fatigue properties. For example, advanced alloys and composite materials are being employed to improve load capacity, reduce weight, and increase the longevity of worm screws. Additionally, advancements in material science and engineering are leading to the development of self-lubricating materials, which can minimize friction and improve efficiency by reducing the need for external lubrication.
- Improved Thread Geometries: Innovations in thread geometries have focused on optimizing load distribution, reducing friction, and improving efficiency. Researchers and engineers are developing novel thread profiles and forms that enhance contact between the worm screw and the worm wheel. These designs help minimize backlash, increase load-carrying capacity, and improve overall system performance. Additionally, advancements in computer simulations and modeling techniques enable more accurate analysis and optimization of thread geometries for specific applications.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Surface treatments and coatings are being applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. For instance, advanced coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings or specialized lubricious coatings help reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and minimize the need for external lubrication. Surface treatments like nitriding or carburizing can improve hardness and provide resistance against abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of worm screws.
- Precision Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing processes and technologies have enabled the production of worm screws with higher precision and tighter tolerances. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC grinding and high-precision gear hobbing, allow for the creation of worm screws with superior dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and better tooth profile control. These manufacturing advancements contribute to enhanced performance, reduced backlash, and increased overall system efficiency.
- Computer-Aided Design and Simulation: The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools has revolutionized worm screw design and optimization. Engineers can now create virtual models, simulate the behavior of worm gear systems, and analyze various design parameters to optimize performance before physical prototypes are manufactured. This iterative design process helps reduce development time, minimize costs, and improve the final design and performance of worm screws.
- Integration with Digitalization and Automation: The integration of worm gear systems with digitalization and automation technologies is another area of innovation. Worm screws are being designed to work seamlessly with sensor technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load. This data can be utilized for predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and optimization of the overall system performance.
It’s important to note that the field of worm screw design and materials is continuously evolving, and new innovations are being introduced regularly. Keeping up with the latest research, advancements, and industry developments is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in worm gear system applications.
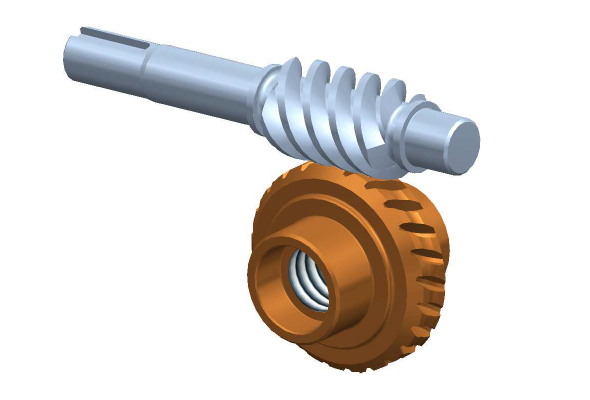
How do you calculate the gear ratio for a worm screw and gear setup?
In a worm screw and gear setup, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the worm wheel (gear) and the number of threads on the worm screw. The gear ratio represents the relationship between the rotational speed of the worm screw and the resulting rotational speed of the worm wheel. The formula to calculate the gear ratio is as follows:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Worm Wheel / Number of Threads on Worm Screw
Here’s a step-by-step process to calculate the gear ratio:
- Count the number of teeth on the worm wheel. This can be done by visually inspecting the gear or referring to its specifications.
- Count the number of threads on the worm screw. The threads refer to the number of complete turns or helical grooves wrapped around the cylindrical body of the worm screw.
- Divide the number of teeth on the worm wheel by the number of threads on the worm screw.
- The result of the division is the gear ratio. It represents the number of revolutions of the worm screw required to complete one revolution of the worm wheel.
For example, let’s say the worm wheel has 40 teeth, and the worm screw has 2 threads. Using the formula, we can calculate the gear ratio as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 teeth / 2 threads = 20
In this case, for every full revolution of the worm screw, the worm wheel will rotate 1/20th of a revolution. This indicates a significant speed reduction, resulting in high torque output at the worm wheel.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio calculated using this formula assumes an ideal scenario without considering factors like friction, efficiency losses, or the pitch diameter of the gears. In practical applications, these factors may affect the actual gear ratio and performance of the worm screw and gear setup.


editor by CX 2024-01-11
China wholesaler Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
Product Description
Adjustable Bevel Gear Worm Screw Jack with Motor High Quality China Factory Brand
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|
| Type: | Round Head |
| Groove: | Cross |
| Connection: | Hinged Bolts |
| Head Style: | Square |
| Standard: | DIN, GB, ANSI, BSW, JIS, GOST |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Can worm screws be used for high torque applications?
Yes, worm screws can be used for high torque applications. The design of a worm screw mechanism allows for efficient torque transmission and multiplication, making it suitable for applications that require high torque output. Here are some key points to consider regarding the use of worm screws in high torque applications:
- Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio, which results in a lower output speed and higher output torque. This gear reduction capability allows worm screws to generate and transmit substantial torque, making them well-suited for high torque applications.
- Efficiency: While worm screws can provide high torque output, it’s important to consider the mechanical efficiency of the system. The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. It’s crucial to ensure that the efficiency of the worm screw mechanism meets the requirements of the specific high torque application.
- Load Holding: Another advantage of worm screws is their self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel, which provides resistance against backward rotation. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads in a fixed position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. In high torque applications where load holding is required, worm screws can provide reliable and secure positioning.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the worm screw and worm wheel should be carefully selected to withstand high torque loads. Both components should have sufficient strength and wear resistance to handle the transmitted torque without deformation or premature failure. Depending on the specific application requirements, materials such as hardened steel, bronze, or other alloys may be chosen to ensure the durability and performance of the worm screw assembly.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of a worm screw mechanism, especially in high torque applications. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Regular maintenance, including monitoring lubricant levels and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed, is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear or failure.
Overall, worm screws can be effectively used in high torque applications, thanks to their gear reduction capabilities, load-holding properties, and efficient torque transmission. However, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as mechanical efficiency, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance to ensure that the worm screw mechanism can meet the specific requirements and demands of the high torque application.

How does the pitch of a worm screw affect its performance?
The pitch of a worm screw plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics and capabilities. The pitch refers to the axial distance between consecutive threads on the worm screw. Here’s how the pitch of a worm screw affects its performance:
- Speed and Efficiency: The pitch of a worm screw directly influences the speed and efficiency of the worm gear system. A smaller pitch, which means a finer thread, results in a higher gear ratio and slower output speed. Conversely, a larger pitch, or coarser thread, leads to a lower gear ratio and faster output speed. This relationship between pitch and speed allows for speed reduction or multiplication in mechanical power transmission systems.
- Load Capacity: The pitch of a worm screw also affects its load-carrying capacity. A finer pitch tends to distribute the load over more threads, resulting in a larger contact area between the worm screw and the worm wheel. This increased contact area improves load distribution and allows for higher load capacity. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may have a reduced contact area, which can limit the load-carrying capability of the worm gear system.
- Backlash: Backlash is the clearance or play between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. The pitch of a worm screw influences the amount of backlash present in the system. A finer pitch generally results in lower backlash due to the smaller clearance between the threads and the teeth. In contrast, coarser pitches may have increased backlash, which can negatively impact the system’s accuracy, precision, and responsiveness.
- Efficiency and Heat Generation: The pitch of a worm screw affects the overall efficiency of the worm gear system. Finer pitches tend to have higher efficiency due to reduced sliding friction between the threads and the teeth. This reduced friction results in less heat generation, contributing to higher overall system efficiency. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may exhibit increased sliding friction, leading to higher energy losses and heat generation.
- Manufacturing and Design Considerations: The pitch of a worm screw also influences the manufacturing process and design considerations. Finer pitches generally require more precise machining or grinding processes to achieve the desired thread geometry. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may offer advantages in terms of ease of manufacturing and reduced sensitivity to manufacturing tolerances. The selection of the optimal pitch depends on factors such as the desired gear ratio, load requirements, desired efficiency, and manufacturing capabilities.
It’s important to note that the pitch of a worm screw is typically specified by the manufacturer and should be chosen carefully based on the specific application requirements. Consulting with experts or engineers familiar with worm gear systems can help in selecting the appropriate pitch to achieve the desired performance and functionality.

How do you calculate the gear ratio for a worm screw and gear setup?
In a worm screw and gear setup, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the worm wheel (gear) and the number of threads on the worm screw. The gear ratio represents the relationship between the rotational speed of the worm screw and the resulting rotational speed of the worm wheel. The formula to calculate the gear ratio is as follows:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Worm Wheel / Number of Threads on Worm Screw
Here’s a step-by-step process to calculate the gear ratio:
- Count the number of teeth on the worm wheel. This can be done by visually inspecting the gear or referring to its specifications.
- Count the number of threads on the worm screw. The threads refer to the number of complete turns or helical grooves wrapped around the cylindrical body of the worm screw.
- Divide the number of teeth on the worm wheel by the number of threads on the worm screw.
- The result of the division is the gear ratio. It represents the number of revolutions of the worm screw required to complete one revolution of the worm wheel.
For example, let’s say the worm wheel has 40 teeth, and the worm screw has 2 threads. Using the formula, we can calculate the gear ratio as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 teeth / 2 threads = 20
In this case, for every full revolution of the worm screw, the worm wheel will rotate 1/20th of a revolution. This indicates a significant speed reduction, resulting in high torque output at the worm wheel.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio calculated using this formula assumes an ideal scenario without considering factors like friction, efficiency losses, or the pitch diameter of the gears. In practical applications, these factors may affect the actual gear ratio and performance of the worm screw and gear setup.


editor by CX 2023-12-04
China Best price 1240 1400 rpm 1 hp speed reduce gearbox worm gear motor for screw conveyor worm gearbox china
2023-05-06
China Standard Customized High Quality Long Shaft Screw Thread Shaft for Dual Shaft Worm Gear Motor Factory wholesaler
Product Description
Product Description
| Part name | Customized High Quality Long Shaft Screw Thread Shaft for Dual Shaft Worm Gear Motor Factory |
| Material | Iron,Stainless Steel,Brass,Al,Copper,etc. |
| Thickness | 0.1-8UM |
| Surface treatment | Zinc, Nickel, Chrome, Tin,Silver,Gold,etc. |
| Process | CNC and Automatic Lathing |
| Place of Origin | HangZhou |
| Application Area | Auto Industry ; Medical Equipment Industry ; Electric Heating Industry ; Thermostat Industry ; Household Appliance Industry ; Solar Energy ; Radar ; Etc |
| Type | High-Precision nonstandard parts(OEM Service) |
| Certificate | IATF16949 2016;I SO9001 2015; ISO14001:2015;RoHS;REACH;ISO 13485 |
| Company History | Since 2001 |
About Customized High Quality Long Shaft Screw Thread Shaft for Dual Shaft Worm Gear Motor Factory:
1:From Socket Shoulder Bolts and Hex Tap Bolts to Large Diameter Bolts,FULIMEI Fastener the custom Bolt that you need.
2:Material: Iron,Stainless Steel,Brass,Al,Copper,etc. you can choose according your detail requirement too.
3:OEM Service Offered, Design Service Offered.
4:Fast delivery and 100% checking before shipment. Now we’re exporting to worldwide with competitive prices, good quality and excellent services.
Detailed Photos
Contact FULIMEI discuss your project requirements. Our team will work closely with you to find a solution to suit your application.
After Sales Service
Certifications
FULIMEI strictly comply with ISO9001 quality management system to control the production and quality of products,
and through SGS certification.
Company Profile
Production Equipment
Please have a look at the production site.We have enough machines and technicians to ensure your delivery date,
as shown in the figure below:
Testing instrument
Inspection process: Raw material inspection (IQC) – first article confirmation (IPQC) – site inspection (IPQC) – final inspection (FQC) – delivery inspection (QA)
The testing instruments used by our quality department include:Raw material chemical composition spectrograph, X-ray coating thickness tester, sclerometer, salt spray tester, Micrometer,Callipers,Thread ring gauge,Dialgauge,Manometer,Angle gauge,Full Automatic Vision Tester.
Packaging & Shipping
-
BY SEA & BY AIR
-
Port : HangZhou & HONGKONG
-
Carton size : As the clients’ requirement.
-
Packing : Inner plastic bags+ outer carton+wooden case, or according to the demand of the customers.
How do you know FULIMEI rivets perform good? Consider the fact that our rivets are used by these mission-critical applications:
Critical safety equipment makers: our rivets perform when livelihoods are at risk.
Automotive components: on road or track, high and low speeds, our rivets deliver.
Electrical applications: when precision and accuracy count, FULIMEI wins.
We mainly manufacture accessories suitable for “temperature controller industry, switch industry, medical equipment
hardware industry, home appliances industry, electric heating tube industry ect” and so on.
FAQ
Who we are?
A professional fastener manufacturer specialized in rivet,screws, bolts and nuts which used for electrical equipment with over 20 years of rich experience.
What can we do for you?
1. 100% local manufacturer 2. Best material selection 3. Best lead time and stable production 4. Rich experience on export business 5. Professional services 6. Quality control
Why do you choose us?
Responsibility, Efficiency, Loyalty, Win-Win, Punctuality, Cost effectiveness.
When could we cooperate?
Whenever you want.
Where are we from?
We located at HangZhou,convenient transportation.
How can customize products?
Attach your drawings with details(Suface treatment,material,quantity and special requirements etc).
How long can I get the quaotation?
We will give you the quotation within 8 hours(Considering the time difference).
How can I get a sample for testing?
We will provide free or charged samples depends on the products.
How long will produce the parts?
Normally within 10 working days ,we will arrange the produce schedule depends on the quantity and the delivery.
What’s your payment terms?
We accept Paypal for small account, big amount, T/T is preferred.
How about the transportation?
Samples by air (if not too heavy),otherwise by sea or air.
What if the products we received are not good?
contact us without hesitation,our special after-sales service will take the responsibility
Screw Shaft Types
A screw shaft is a cylindrical part that turns. Depending on its size, it is able to drive many different types of devices. The following information outlines the different types of screws, including their sizes, material, function, and applications. To help you select the right screw shaft, consider the following factors:
Size
A screw can come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from a quarter to a quarter-inch in diameter. A screw is a cylindrical shaft with an inclined plane wrapped around it, and its main function is to fasten objects together by translating torque into a linear force. This article will discuss the dimensions of screws and how to determine the size of a screw. It is important to note that screw sizes can be large and small depending on the purpose.
The diameter of a screw is the diameter of its shaft, and it must match the inner diameter of its nuts and washers. Screws of a certain diameter are also called machine screws, and they can be larger or smaller. Screw diameters are measured on the shaft underneath the screw head. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standardized screw diameters in 3/50-inch to 16 (3/8-inch) inches, and more recently, sizes were added in U.S. fractions of an inch. While shaft and head diameters are standardized, screw length may vary from job to job.
In the case of the 2.3-mm screw group, the construct strength was not improved by the 1.2-mm group. The smaller screw size did not increase the strength of the construct. Further, ABS material did not improve the construct strength. Thus, the size of screw shaft is an important consideration in model design. And remember that the more complex your model is, the larger it will be. A screw of a given size will have a similar failure rate as a screw of a different diameter.
Although different screw sizes are widely used, the differences in screw size were not statistically significant. Although there are some limitations, screws of different sizes are generally sufficient for fixation of a metacarpal shaft fracture. However, further clinical studies are needed to compare screw sizes for fracture union rates. So, if you are unsure of what size of screw shaft you need for your case, make sure to check the metric chart and ensure you use the right one.
Material
The material of a screw shaft plays an important role in the overall performance of a screw. Axial and central forces act to apply torque to the screw, while external forces, such as friction, exert a bending moment. The torsional moments are reflected in the torque, and this causes the screw to rotate at a higher rate than necessary. To ensure the longevity of the screw, the material of the screw shaft should be able to handle the bending moment, while the diameter of the shaft should be small enough to avoid causing damage.
Screws are made from different metals, such as steel, brass, titanium, and bronze. Manufacturers often apply a top coating of chromium, brass, or zinc to improve corrosion resistance. Screws made of aluminum are not durable and are prone to rusting due to exposure to weather conditions. The majority of screw shafts are self-locking. They are suited for many applications, including threaded fasteners, C-clamps, and vises.
Screws that are fabricated with conical sections typically feature reduced open cross-sectional areas at the discharge point. This is a key design parameter of conical screw shafts. In fact, reductions of up to 72% are common across a variety of applications. If the screw is designed to have a hard-iron hanger bearing, it must be hardened. If the screw shaft is not hardened, it will require an additional lubricant.
Another consideration is the threads. Screw shafts are typically made of high-precision threads and ridges. These are manufactured on lathes and CNC machines. Different shapes require different materials. Materials for the screw shaft vary. There are many different sizes and shapes available, and each 1 has its own application. In addition to helical and conical screw shafts, different materials are also available. When choosing material, the best 1 depends on the application.
The life of the screw depends on its size, load, and design. In general, the material of the screw shaft, nut body, and balls and rollers determine its fatigue life. This affects the overall life of the screw. To determine whether a specific screw has a longer or shorter life, the manufacturer must consider these factors, as well as the application requirements. The material should be clean and free of imperfections. It should be smooth and free of cracks or flaking, which may result in premature failure.
Function
The function of a screw shaft is to facilitate the rotation of a screw. Screws have several thread forms, including single-start, double-start and multi-start. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article we’ll explore each of them in detail. The function of a screw shaft can vary based on its design, but the following are common types. Here are some examples of screw shaft types and their purposes.
The screw’s torque enables it to lift objects. It can be used in conjunction with a bolt and nut to lift a load. Screws are also used to secure objects together. You can use them in screw presses, vises, and screw jacks. But their primary function is to hold objects together. Listed below are some of their main functions. When used to lift heavy loads, they can provide the required force to secure an object.
Screws can be classified into 2 types: square and round. Square threads are more efficient than round ones because they apply 0deg of angle to the nut. Square threads are also stronger than round threads and are often used in high-load applications. They’re generally cheaper to manufacture and are more difficult to break. And unlike square threads, which have a 0deg thread angle, these threads can’t be broken easily with a screwdriver.
A screw’s head is made of a series of spiral-like structures that extend from a cylindrical part to a tip. This portion of the screw is called the shank and is made of the smallest area. The shank is the portion that applies more force to the object. As the shaft extends from the head, it becomes thinner and narrow, forming a pointed tip. The head is the most important part of the screw, so it needs to be strong to perform its function.
The diameter of the screw shaft is measured in millimeters. The M8 screw has a thread pitch of 1.25 mm. Generally, the size of the screw shaft is indicated by the major and minor diameter. These dimensions are appended with a multiplication sign (M8x1).
Applications
The design of screws, including their size and shape, determines their critical rotating speeds. These speeds depend on the threaded part of the screw, the helix angle, and the geometry of the contact surfaces. When applied to a screw, these limits are referred to as “permissible speed limits.” These maximum speeds are meant for short periods of time and optimized running conditions. Continuous operation at these speeds can reduce the calculated life of a nut mechanism.
The main materials used to manufacture screws and screw shafts include steel, stainless steel, titanium, bronze, and brass. Screws may be coated for corrosion resistance, or they may be made of aluminium. Some materials can be threaded, including Teflon and nylon. Screw threads can even be molded into glass or porcelain. For the most part, steel and stainless steel are the most common materials for screw shafts. Depending on the purpose, a screw will be made of a material that is suitable for the application.
In addition to being used in fasteners, screw shafts are used in micrometers, drillers, conveyor belts, and helicopter blades. There are numerous applications of screw shafts, from weighing scales to measuring lengths. If you’re in the market for a screw, make sure to check out these applications. You’ll be happy you did! They can help you get the job done faster. So, don’t delay your next project.
If you’re interested in learning about screw sizing, then it’s important to know the axial and moment loads that your screws will experience. By following the laws of mechanics and knowing the load you can calculate the nominal life of your screw. You can also consider the effect of misalignment, uneven loading, and shocks on your screw. These will all affect the life of your screw. Then, you can select the right screw.


China supplier Transmission Motor Gearbox Unit Wp Nmrv Swl Screw Drive Lifts Stepper Cyclo Cycloidal Extruder Helical Planetary Bevel Worm Speed Variator Gear Reducer Gearbox near me manufacturer
Product Description
Transmission Motor Gearbox Unit Wp Nmrv Swl Screw Drive Lifts Stepper Cyclo Cycloidal Extruder Helical Planetary Bevel Worm Speed Variator Gear Reducer Gearbox
Features
1. Compact structure and simple assembly;
2. Wide speed ranges and high torque;
3. Low noise, good sealing performance, high efficiency;
4. Stable and safe, long lifetime, universal;
5. Multi-structure, various assembling methods
Product Photos
Product Description
| ANG Helical Gear Reducer | |
| Model | R17 ~ 187, F37-177, K37-187, S37-97, HB01-26 |
| Input power | 0.06kw ~ 5000kw |
| Input speed | 750rpm ~ 3000rpm |
| Reduction ratio | 1/1.3 ~ 1/27000 |
| Input motor | AC (1 phase or 3 phase) / DC / BLDC motor |
| Install type | Foot / Solid shaft / Hollow shaft / Output flange… |
| Efficiency | 94% ~ 98 % for R F K series |
| Material of housing | die-cast aluminum / Cast iron / Stainless steel |
| Precision of gear | Accurate grinding, class 6 |
| Heat treatment | Carburizing and quenching |
| Accessories | Brake / Flange / Motor adapter / Torque arm … |
Advantages
FAQ
Q: Can you make the gearbox with customization?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request, like power, voltage, speed, shaft size, flange, terminal box, IP grade, etc.
Q: Do you provide samples?
A: Yes. The sample is available for testing.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: It is 1pcs for the beginning of our business.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Standard product need 5-30days, a bit longer for customized products.
Q: Do you provide technical support?
A: Yes. Our company have design and development team, we can provide technical support if you
need.
Q: How to ship to us?
A: It is available by air, or by sea, or by train.
Q: How to pay the money?
A: T/T and L/C are preferred, with a different currency, including USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know the product is suitable for me?
A: >1ST confirm drawing and specification >2nd test sample >3rd start mass production.
Q: Can I come to your company to visit?
A: Yes, you are welcome to visit us at any time.
Q: How shall we contact you?
A: You can send inquiry directly, and we will respond within 24 hours.
Screw Shaft Features Explained
When choosing the screw shaft for your application, you should consider the features of the screws: threads, lead, pitch, helix angle, and more. You may be wondering what these features mean and how they affect the screw’s performance. This article explains the differences between these factors. The following are the features that affect the performance of screws and their properties. You can use these to make an informed decision and purchase the right screw. You can learn more about these features by reading the following articles.
Threads
The major diameter of a screw thread is the larger of the 2 extreme diameters. The major diameter of a screw is also known as the outside diameter. This dimension can’t be directly measured, but can be determined by measuring the distance between adjacent sides of the thread. In addition, the mean area of a screw thread is known as the pitch. The diameter of the thread and pitch line are directly proportional to the overall size of the screw.
The threads are classified by the diameter and pitch. The major diameter of a screw shaft has the largest number of threads; the smaller diameter is called the minor diameter. The thread angle, also known as the helix angle, is measured perpendicular to the axis of the screw. The major diameter is the largest part of the screw; the minor diameter is the lower end of the screw. The thread angle is the half distance between the major and minor diameters. The minor diameter is the outer surface of the screw, while the top surface corresponds to the major diameter.
The pitch is measured at the crest of a thread. In other words, a 16-pitch thread has a diameter of 1 sixteenth of the screw shaft’s diameter. The actual diameter is 0.03125 inches. Moreover, a large number of manufacturers use this measurement to determine the thread pitch. The pitch diameter is a critical factor in successful mating of male and female threads. So, when determining the pitch diameter, you need to check the thread pitch plate of a screw.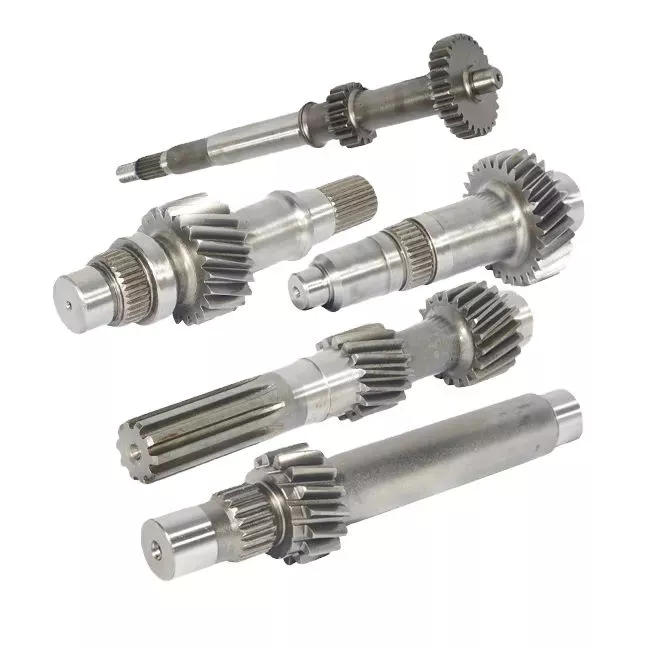
Lead
In screw shaft applications, a solid, corrosion-resistant material is an important requirement. Lead screws are a robust choice, which ensure shaft direction accuracy. This material is widely used in lathes and measuring instruments. They have black oxide coatings and are suited for environments where rusting is not acceptable. These screws are also relatively inexpensive. Here are some advantages of lead screws. They are highly durable, cost-effective, and offer high reliability.
A lead screw system may have multiple starts, or threads that run parallel to each other. The lead is the distance the nut travels along the shaft during a single revolution. The smaller the lead, the tighter the thread. The lead can also be expressed as the pitch, which is the distance between adjacent thread crests or troughs. A lead screw has a smaller pitch than a nut, and the smaller the lead, the greater its linear speed.
When choosing lead screws, the critical speed is the maximum number of revolutions per minute. This is determined by the minor diameter of the shaft and its length. The critical speed should never be exceeded or the lead will become distorted or cracked. The recommended operational speed is around 80 percent of the evaluated critical speed. Moreover, the lead screw must be properly aligned to avoid excessive vibrations. In addition, the screw pitch must be within the design tolerance of the shaft.
Pitch
The pitch of a screw shaft can be viewed as the distance between the crest of a thread and the surface where the threads meet. In mathematics, the pitch is equivalent to the length of 1 wavelength. The pitch of a screw shaft also relates to the diameter of the threads. In the following, the pitch of a screw is explained. It is important to note that the pitch of a screw is not a metric measurement. In the following, we will define the 2 terms and discuss how they relate to 1 another.
A screw’s pitch is not the same in all countries. The United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States have standardized screw threads according to the UN system. Therefore, there is a need to specify the pitch of a screw shaft when a screw is being manufactured. The standardization of pitch and diameter has also reduced the cost of screw manufacturing. Nevertheless, screw threads are still expensive. The United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States have introduced a system for the calculation of screw pitch.
The pitch of a lead screw is the same as that of a lead screw. The diameter is 0.25 inches and the circumference is 0.79 inches. When calculating the mechanical advantage of a screw, divide the diameter by its pitch. The larger the pitch, the more threads the screw has, increasing its critical speed and stiffness. The pitch of a screw shaft is also proportional to the number of starts in the shaft.
Helix angle
The helix angle of a screw shaft is the angle formed between the circumference of the cylinder and its helix. Both of these angles must be equal to 90 degrees. The larger the lead angle, the smaller the helix angle. Some reference materials refer to angle B as the helix angle. However, the actual angle is derived from calculating the screw geometry. Read on for more information. Listed below are some of the differences between helix angles and lead angles.
High helix screws have a long lead. This length reduces the number of effective turns of the screw. Because of this, fine pitch screws are usually used for small movements. A typical example is a 16-mm x 5-inch screw. Another example of a fine pitch screw is a 12x2mm screw. It is used for small moves. This type of screw has a lower lead angle than a high-helix screw.
A screw’s helix angle refers to the relative angle of the flight of the helix to the plane of the screw axis. While screw helix angles are not often altered from the standard square pitch, they can have an effect on processing. Changing the helix angle is more common in two-stage screws, special mixing screws, and metering screws. When a screw is designed for this function, it should be able to handle the materials it is made of.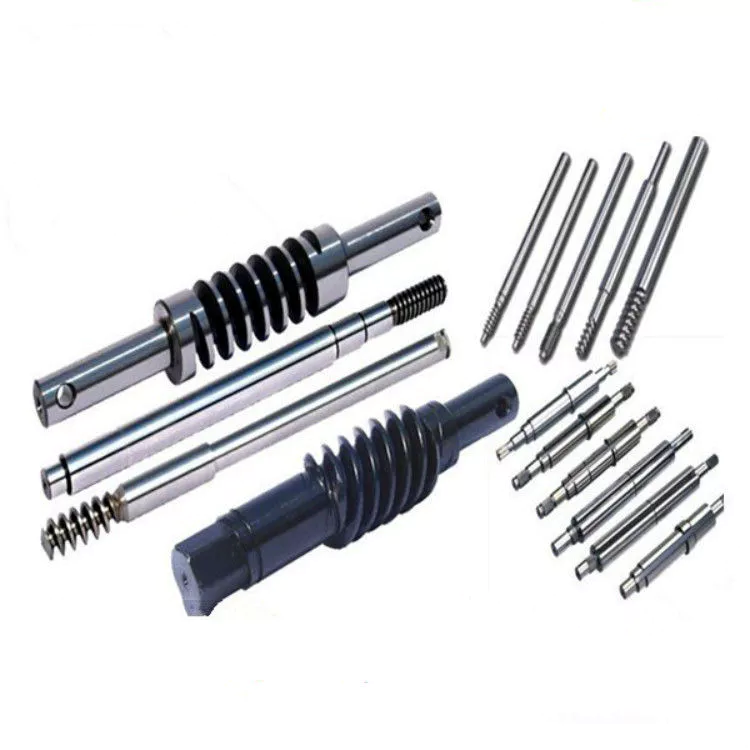
Size
The diameter of a screw is its diameter, measured from the head to the shaft. Screw diameters are standardized by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. The diameters of screws range from 3/50 inches to 16 inches, and more recently, fractions of an inch have been added. However, shaft diameters may vary depending on the job, so it is important to know the right size for the job. The size chart below shows the common sizes for screws.
Screws are generally referred to by their gauge, which is the major diameter. Screws with a major diameter less than a quarter of an inch are usually labeled as #0 to #14 and larger screws are labeled as sizes in fractions of an inch. There are also decimal equivalents of each screw size. These measurements will help you choose the correct size for your project. The screws with the smaller diameters were not tested.
In the previous section, we described the different shaft sizes and their specifications. These screw sizes are usually indicated by fractions of an inch, followed by a number of threads per inch. For example, a ten-inch screw has a shaft size of 2” with a thread pitch of 1/4″, and it has a diameter of 2 inches. This screw is welded to a two-inch Sch. 40 pipe. Alternatively, it can be welded to a 9-inch O.A.L. pipe.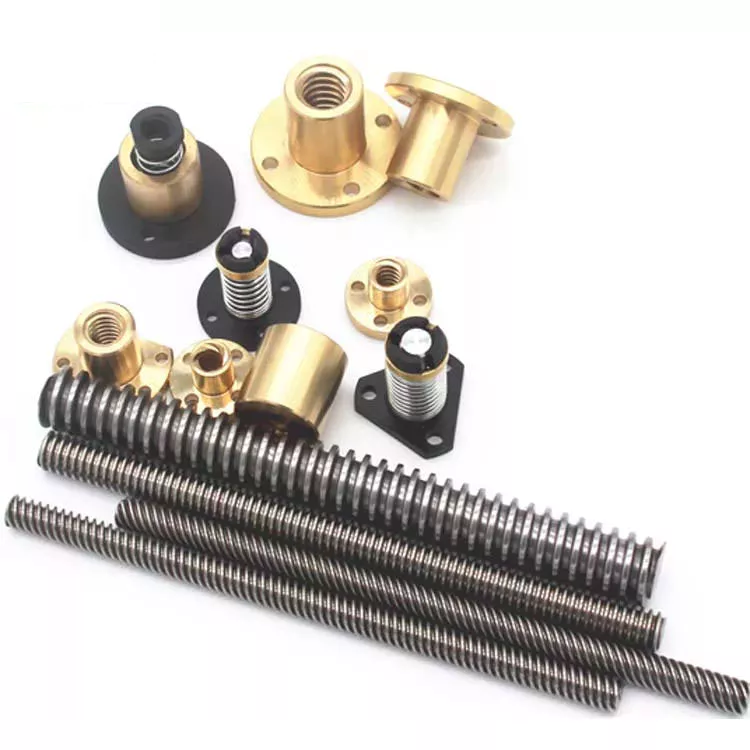
Shape
Screws come in a wide variety of sizes and shapes, from the size of a quarter to the diameter of a U.S. quarter. Screws’ main function is to hold objects together and to translate torque into linear force. The shape of a screw shaft, if it is round, is the primary characteristic used to define its use. The following chart shows how the screw shaft differs from a quarter:
The shape of a screw shaft is determined by 2 features: its major diameter, or distance from the outer edge of the thread on 1 side to the inner smooth surface of the shaft. These are generally 2 to 16 millimeters in diameter. Screw shafts can have either a fully threaded shank or a half-threaded shank, with the latter providing better stability. Regardless of whether the screw shaft is round or domed, it is important to understand the different characteristics of a screw before attempting to install it into a project.
The screw shaft’s diameter is also important to its application. The ball circle diameter refers to the distance between the center of 2 opposite balls in contact with the grooves. The root diameter, on the other hand, refers to the distance between the bottommost grooves of the screw shaft. These are the 2 main measurements that define the screw’s overall size. Pitch and nominal diameter are important measurements for a screw’s performance in a particular application.
Lubrication
In most cases, lubrication of a screw shaft is accomplished with grease. Grease is made up of mineral or synthetic oil, thickening agent, and additives. The thickening agent can be a variety of different substances, including lithium, bentonite, aluminum, and barium complexes. A common classification for lubricating grease is NLGI Grade. While this may not be necessary when specifying the type of grease to use for a particular application, it is a useful qualitative measure.
When selecting a lubricant for a screw shaft, the operating temperature and the speed of the shaft determine the type of oil to use. Too much oil can result in heat buildup, while too little can lead to excessive wear and friction. The proper lubrication of a screw shaft directly affects the temperature rise of a ball screw, and the life of the assembly. To ensure the proper lubrication, follow the guidelines below.
Ideally, a low lubrication level is appropriate for medium-sized feed stuff factories. High lubrication level is appropriate for larger feed stuff factories. However, in low-speed applications, the lubrication level should be sufficiently high to ensure that the screws run freely. This is the only way to reduce friction and ensure the longest life possible. Lubrication of screw shafts is an important consideration for any screw.


China supplier Best Gear Moter Jack Screw, Electric Screw Jack Can Also Be Called Motorized Screw Jack, It Includes a Worm Gear Screw Jack and an Electric Motor near me shop
Product Description
Best Gear Moter Jack Screw, Electric Screw Jack can also be called motorized screw jack, it includes a worm gear screw jack and an electric motor.
Motorized screw jack can also be called Electric screw jack, which includes a worm gear screw jack and an electric motor. The Motorized Jacks have higher efficiency than manual screw jack. There are 2 types worm gear screw jack for motorized screw jacks, they are self-locking machine screw jack or high precision ball screw jack. The motor can be a high-precision servomotor, stepping motor, geared motor, worm gear reducer, bevel helical gearmotor, worm helical gearmotor, three-phase motor, or single phase motor, and 12v, 24v, 48v Brush or Brushless DC motors and DC gear motors, etc. Note: If it is a electric ball screw jack, a brake motor or an external locking device is required to maintain the position. Electric screw jacks offer the most economic solutions for a wide range of industrial applications and the load capacity up to 16567X3, registered Capital 500000CNY) is a leading manufacturer and supplier of Screw Jacks (Mechanical Actuators), Bevel Gearboxes, Lifting Systems, Electric Linear Actuators, Gearmotors and Speed Reducers, Others Linear Motion and Power Transmission Products in China. We are located in Chang An, Xihu (West Lake) Dis. guan, Guang dong in China. We are an audited professional manufacturer and supplier by SGS (Serial NO.: QIP-ASI192186) and BV (Serial NO.: MIC-ASR257162) organizations. We have a strict quality system, with senior engineers, experienced skilled workers and practiced sales teams, and consistently provide the customers with the best engineered solution for precision linear actuation, power transmission and mechanical jacking systems. CZPT Industries guarantees quality, reliability, performance and value for today’s demanding industrial applications.
Company Advantages
* One of the biggest orders with 1750 units screw lift jacks.
* Standard products with 2D Drawings(DXF, DWG, PDF) and 3D CAD Model(STEP).
* 100% quality assured with double quality inspections. Original Inspection Reports, Operation Manual, and Book Catalogue are put into the packages.
* 100% safety transportation with strong standard export plywood cases materials (free fumigation).
* International standard materials for all standard products.
* Custom design available, OEM service available, Free engineering advice and Customer label available.
Products List
* Manual Screw Jacks
* Electric Screw Jacks
* Screw Jacks Series:
Cubic Screw Jack JTC Series, Machine Screw Jack JTW Series, Trapezoidal Screw Jack JT Series, Worm Screw Jack JTM Series, Stainless Steel Screw Jack JSS Series, Through Hole Screw Jack JTH Series, Ball Screw Jack JTB Series, Cubic Ball Screw Jack JTD Series, Bevel Gear Screw Jack JTS Series and JTG Series, and Electric Cylinder JTE Series.
* Bevel Gearboxes Series:
Cubic Bevel Gearbox JTP Series, Hollow Shaft Gearbox JTPH Series, Input Flange Gearbox JTPF Series, Input Flange and Hollow shaft Gearbox JTPG Series, Stainless Steel Gearbox JTP Series, Aluminum Gearbox JTA Series, and Bevel Gearboxes JT Series.
* Screw Jack Lifting Systems and Accessories:
2jacks lifting system, 3jacks lifting system, 4jacks lifting system, 6jacks lifting system, 8jacks lifting system……14jacks lifting system. Lifting systems accessories cover ac, dc motors, geared motors, servo motors, stepper motors, handwheels, couplings, universal joints, telescopic universal joints, connecting shafts, cardan shafts, limit switches, proximity switches, safety nut, travel nut, rod ends, stop nuts, pillow block bearings, flange blocks, motor flange nema or iec, encoder, potentiometer, frequency converter, position indicators, trunnion plate, and trunnion mounting brackets.
* Electric Linear Actuators Series:
Electro Mechanical Actuators LA Series, Electro Mechanical Actuators LAP Series.
* Gear Reducers Series:
Helical Gear Reducers R Series, Helical Bevel Gear Reducers K Series, Parallel Shaft Helical Gear Reducers F Series, Helical Worm Gear Reducers S Series, Helical Gear Motor GMH/GMV Series, and Worm Gear Reducers NMRV Series.
Customers Distribution Countries
* American Countries: United States, Mexico, Canada, Chile, Argentina, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.via, Brazil, Colombia, Guatemala, Honduras, Panama, Peru.
* European Countries: Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Poland, Romania, Netherlands, Belgium, Greece, Czech Republic, Portugal, Sweden, Hungary, Austria, Switzerland, Bulgaria, Denmark, Finland, Slovakia, Norway, Ireland, Georgia, Slovenia.
* Asian Countries: Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand, India, Israel, Cambodia, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Maldives, Pakistan, Iran, Turkey, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Georgia, Armenia.
* Oceanian Countries: Australia, New Zealand.
* African Countries: Egypt, Ethiopia, Nigeria, South Africa, Zambia, Mozambique.
The Four Basic Components of a Screw Shaft
There are 4 basic components of a screw shaft: the Head, the Thread angle, and the Threaded shank. These components determine the length, shape, and quality of a screw. Understanding how these components work together can make purchasing screws easier. This article will cover these important factors and more. Once you know these, you can select the right type of screw for your project. If you need help choosing the correct type of screw, contact a qualified screw dealer.
Thread angle
The angle of a thread on a screw shaft is the difference between the 2 sides of the thread. Threads that are unified have a 60 degree angle. Screws have 2 parts: a major diameter, also known as the screw’s outside diameter, and a minor diameter, or the screw’s root diameter. A screw or nut has a major diameter and a minor diameter. Each has its own angle, but they all have 1 thing in common – the angle of thread is measured perpendicularly to the screw’s axis.
The pitch of a screw depends on the helix angle of the thread. In a single-start screw, the lead is equal to the pitch, and the thread angle of a multiple-start screw is based on the number of starts. Alternatively, you can use a square-threaded screw. Its square thread minimizes the contact surface between the nut and the screw, which improves efficiency and performance. A square thread requires fewer motors to transfer the same load, making it a good choice for heavy-duty applications.
A screw thread has 4 components. First, there is the pitch. This is the distance between the top and bottom surface of a nut. This is the distance the thread travels in a full revolution of the screw. Next, there is the pitch surface, which is the imaginary cylinder formed by the average of the crest and root height of each tooth. Next, there is the pitch angle, which is the angle between the pitch surface and the gear axis.
Head
There are 3 types of head for screws: flat, round, and hexagonal. They are used in industrial applications and have a flat outer face and a conical interior. Some varieties have a tamper-resistant pin in the head. These are usually used in the fabrication of bicycle parts. Some are lightweight, and can be easily carried from 1 place to another. This article will explain what each type of head is used for, and how to choose the right 1 for your screw.
The major diameter is the largest diameter of the thread. This is the distance between the crest and the root of the thread. The minor diameter is the smaller diameter and is the distance between the major and minor diameters. The minor diameter is half the major diameter. The major diameter is the upper surface of the thread. The minor diameter corresponds to the lower extreme of the thread. The thread angle is proportional to the distance between the major and minor diameters.
Lead screws are a more affordable option. They are easier to manufacture and less expensive than ball screws. They are also more efficient in vertical applications and low-speed operations. Some types of lead screws are also self-locking, and have a high coefficient of friction. Lead screws also have fewer parts. These types of screw shafts are available in various sizes and shapes. If you’re wondering which type of head of screw shaft to buy, this article is for you.
Threaded shank
Wood screws are made up of 2 parts: the head and the shank. The shank is not threaded all the way up. It is only partially threaded and contains the drive. This makes them less likely to overheat. Heads on wood screws include Oval, Round, Hex, Modified Truss, and Flat. Some of these are considered the “top” of the screw.
Screws come in many sizes and thread pitches. An M8 screw has a 1.25-mm thread pitch. The pitch indicates the distance between 2 identical threads. A pitch of 1 is greater than the other. The other is smaller and coarse. In most cases, the pitch of a screw is indicated by the letter M followed by the diameter in millimetres. Unless otherwise stated, the pitch of a screw is greater than its diameter.
Generally, the shank diameter is smaller than the head diameter. A nut with a drilled shank is commonly used. Moreover, a cotter pin nut is similar to a castle nut. Internal threads are usually created using a special tap for very hard metals. This tap must be followed by a regular tap. Slotted machine screws are usually sold packaged with nuts. Lastly, studs are often used in automotive and machine applications.
In general, screws with a metric thread are more difficult to install and remove. Fortunately, there are many different types of screw threads, which make replacing screws a breeze. In addition to these different sizes, many of these screws have safety wire holes to keep them from falling. These are just some of the differences between threaded screw and non-threaded. There are many different types of screw threads, and choosing the right 1 will depend on your needs and your budget.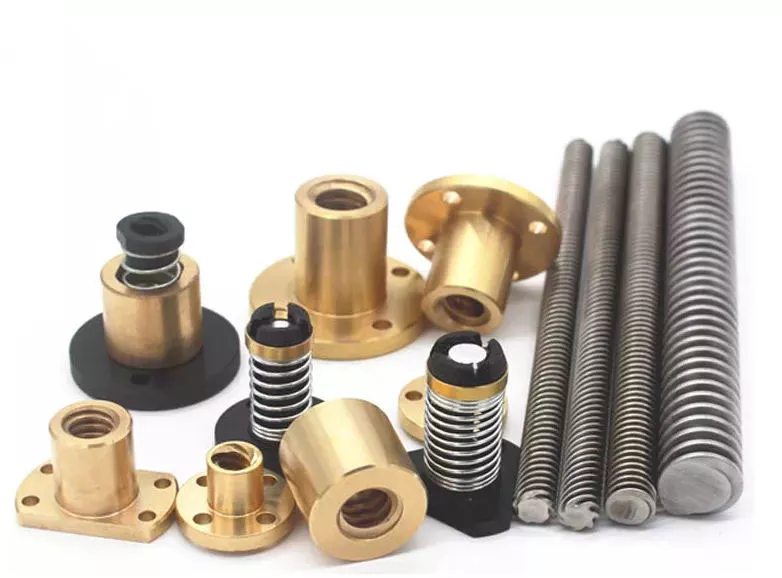
Point
There are 3 types of screw heads with points: cone, oval, and half-dog. Each point is designed for a particular application, which determines its shape and tip. For screw applications, cone, oval, and half-dog points are common. Full dog points are not common, and they are available in a limited number of sizes and lengths. According to ASTM standards, point penetration contributes as much as 15% of the total holding power of the screw, but a cone-shaped point may be more preferred in some circumstances.
There are several types of set screws, each with its own advantage. Flat-head screws reduce indentation and frequent adjustment. Dog-point screws help maintain a secure grip by securing the collar to the screw shaft. Cup-point set screws, on the other hand, provide a slip-resistant connection. The diameter of a cup-point screw is usually half of its shaft diameter. If the screw is too small, it may slack and cause the screw collar to slip.
The UNF series has a larger area for tensile stress than coarse threads and is less prone to stripping. It’s used for external threads, limited engagement, and thinner walls. When using a UNF, always use a standard tap before a specialized tap. For example, a screw with a UNF point is the same size as a type C screw but with a shorter length.
Spacer
A spacer is an insulating material that sits between 2 parts and centers the shaft of a screw or other fastener. Spacers come in different sizes and shapes. Some of them are made of Teflon, which is thin and has a low coefficient of friction. Other materials used for spacers include steel, which is durable and works well in many applications. Plastic spacers are available in various thicknesses, ranging from 4.6 to 8 mm. They’re suitable for mounting gears and other items that require less contact surface.
These devices are used for precision fastening applications and are essential fastener accessories. They create clearance gaps between the 2 joined surfaces or components and enable the screw or bolt to be torqued correctly. Here’s a quick guide to help you choose the right spacer for the job. There are many different spacers available, and you should never be without one. All you need is a little research and common sense. And once you’re satisfied with your purchase, you can make a more informed decision.
A spacer is a component that allows the components to be spaced appropriately along a screw shaft. This tool is used to keep space between 2 objects, such as the spinning wheel and an adjacent metal structure. It also helps ensure that a competition game piece doesn’t rub against an adjacent metal structure. In addition to its common use, spacers can be used in many different situations. The next time you need a spacer, remember to check that the hole in your screw is threaded.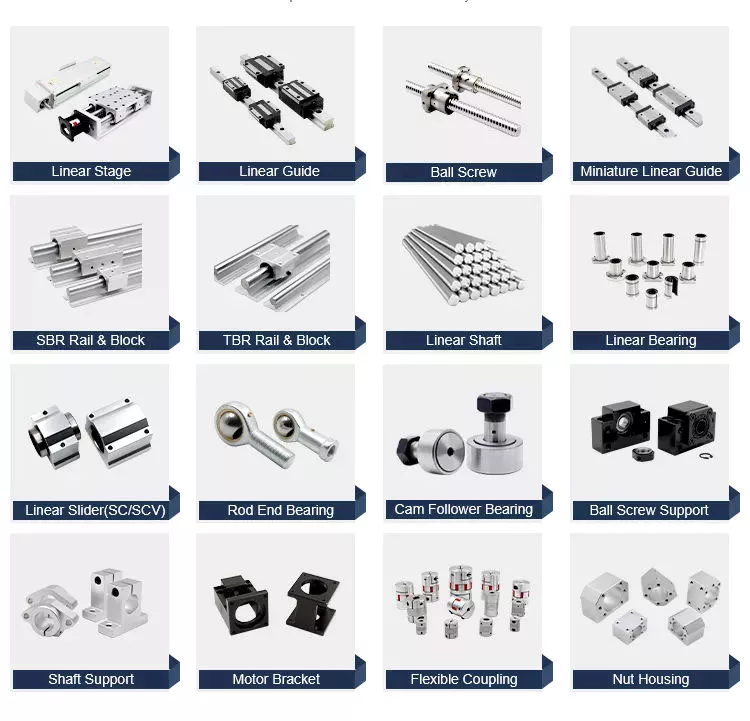
Nut
A nut is a simple device used to secure a screw shaft. The nut is fixed on each end of the screw shaft and rotates along its length. The nut is rotated by a motor, usually a stepper motor, which uses beam coupling to accommodate misalignments in the high-speed movement of the screw. Nuts are used to secure screw shafts to machined parts, and also to mount bearings on adapter sleeves and withdrawal sleeves.
There are several types of nut for screw shafts. Some have radial anti-backlash properties, which prevent unwanted radial clearances. In addition, they are designed to compensate for thread wear. Several nut styles are available, including anti-backlash radial nuts, which have a spring that pushes down on the nut’s flexible fingers. Axial anti-backlash nuts also provide thread-locking properties.
To install a ball nut, you must first align the tangs of the ball and nut. Then, you must place the adjusting nut on the shaft and tighten it against the spacer and spring washer. Then, you need to lubricate the threads, the ball grooves, and the spring washers. Once you’ve installed the nut, you can now install the ball screw assembly.
A nut for screw shaft can be made with either a ball or a socket. These types differ from hex nuts in that they don’t need end support bearings, and are rigidly mounted at the ends. These screws can also have internal cooling mechanisms to improve rigidity. In this way, they are easier to tension than rotating screws. You can also buy hollow stationary screws for rotator nut assemblies. This type is great for applications requiring high heat and wide temperature changes, but you should be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions.


China Custom BLDC DC Brushless Gear Motor with Gear Circular Shaft Ear Flat Hollow Screw Hole Through Hole Right Angle Hollow Solid Worm Gearbox with high quality
Product Description
| DC Blushless Gear Motor | ||||||
| G | 2 | BLD(P) | 40 | 220 | GN | 30S |
| Enterprise Code | Mounting Flange | Motor Type | Output Power | Voltage | Shape of Motor Shaft | Motor Speed |
| G – GPG | 2-60mm 3-70mm 4-80mm 5-90mm 6-100mm |
BLD – Brushless motor with square gearbox BLDP – Brushless motor |
10 – 10W 15 – 15W 25 – 25W 40 – 40W 60 – 60W 90 – 90W 200 – 200W 400 – 400W |
24 – DC24V 36 – DC36V 48 – DC48V 110 – DC110V 220 – DC220V |
GN – General Helival Gear GU – Reinforced Helival Gear A1 – Milling Keyway A – Flat type |
15S – 1500RPM 18S – 1800RPM 25S – 2500RPM 30S – 3000RPM |
| Gearbox | ||||||
| 2 | GN | 50 | RT | |||
| Model & Dimension | Gear Type | Reduction Ratio | Bearing Type | |||
| 2: 60mm 4: 80mm 5: 90mm 6: 104mm |
GN: General Helical Gear GU: Reinforced Helical Gear |
50: Reduction Ratio 1:50 10X Denotes The Mid-gearbox Ration 1:10 |
RT – Right Angle RC – Right-Angle Hollow |
|||
| 5 | GFS | 100 | K | 20 | ||
| Model & Dimension | Gear Type | Reduction Ratio | Bearing Type | Out-shaft Diameter | ||
| 2: 60mm 4: 80mm 5: 90mm 6: 100mm |
Flat Boxes Hollow Output |
100 The reduction ratio of reducer can be said speed ratio range, for example, 50-75, may also be a separate ratio, for example 100 |
K: standard rolling bearing H: sliding bearing L: axle type Z: hybrid bearings |
20: Φ20mm | ||
| Motor Performance Parameters | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Model | Voltage | No-load Current | No-load Speed | Rated Power | Rated Current | Rated Speed | Rated Torque | Grade Protection | |||||||||||||
| V | A | RPM | W | A | RPM | N.m | IP | ||||||||||||||
| G2BLD25-24GN-30S | 24 | MAX 0.4 | 3200 | 25 | 1.3 | 3000 | 0.08 | 44 | |||||||||||||
| G2BLD25-36GN-30S | 36 | MAX 0.3 | 0.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| G2BLD25-48GN-30S | 48 | MAX 0.2 | 0.7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Motor Model | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Pinion Shaft | Round Shaft | |||||||||||||||||||
| Lead Wire | G2BLD200-24GN-30S | G2BLD200-24A1-30S | |||||||||||||||||||
| G2BLD200-36GN-30S | G2BLD200-36A1-30S | ||||||||||||||||||||
| G2BLD200-48GN-30S | G2BLD200-48A1-30S | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Parallel Shaft Gearhead (Sold Separately) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gearhead Type | Gearhead Model | Gear Ratio | |||||||||||||||||||
| Long Life, Low Noise | 2GN/GU _ RC/RT | 3, 3.6, 5, 6, 7.5, 9, 12.5, 15, 18, 25, 30, 36, 50, 60, 75, 90, 100, 120, 150, 180, 200 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2GN10XK ( Decimal Gearhead ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance Torque Unit: Upside (N-m) / Belowside (kgf.cm) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gear Ratio | 3 | 3.6 | 5 | 6 | 7.5 | 9 | 12.5 | 15 | 18 | 25 | 30 | 36 | 50 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 100 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 200 |
| r/min Output Shaft Speed | 1000 | 830 | 600 | 500 | 400 | 330 | 240 | 200 | 166 | 120 | 100 | 83 | 60 | 50 | 40 | 33 | 30 | 25 | 20 | 16 | 15 |
| GU Allowance Torque N·m | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 1.16 | 1.44 | 1.73 | 2.07 | 2.52 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
FAQ
Q: How about your company?
A: We are a gear motor factory established in 1995 and located in HangZhou city of china.
We have more than 1200 workers. Our main product is AC micro gear motor 6W to 250W,
AC small gear motor 100W to 3700W, brush DC motor 10W to 400W, brushless motor10W to 750W,
drum motor 60W to 3700W, planetary gearbox,and worm gearbox,etc.
Q: How about your quality control?
A: From raw material to finished products, we have strict and complete IPQC.
And the advanced test-ing machine can assure of qualified products delivered.
Q: How to choose a suitable motor?
A: If you have gear motor pictures or drawings to show us,
or you tell us detailed specs like volt-age, speed, torque, motor size, the working model of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level, etc.
please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can suggest a suitable motor per your request.
Q: Can you make the gear motor with customizing specifications?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque, and shaft size and shape.
if you need additional wires or cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors, or EMC we can make it too.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Usually our regular standard product will need 10-15days, a bit longer for customized products.
But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: If delivered by sea, the minimum order is 100 pieces, if deliver by express, there is no limit.
Q: Do you have the item in stock?
A: l am sorry we do not have the item in stock, All products are made with orders.
Q: How to contact us?
A: You can send us an inquiry.
Lead Screws and Clamp Style Collars
If you have a lead screw, you’re probably interested in learning about the Acme thread on this type of shaft. You might also be interested in finding out about the Clamp style collars and Ball screw nut. But before you buy a new screw, make sure you understand what the terminology means. Here are some examples of screw shafts:
Acme thread
The standard ACME thread on a screw shaft is made of a metal that is resistant to corrosion and wear. It is used in a variety of applications. An Acme thread is available in a variety of sizes and styles. General purpose Acme threads are not designed to handle external radial loads and are supported by a shaft bearing and linear guide. Their design is intended to minimize the risk of flank wedging, which can cause friction forces and wear. The Centralizing Acme thread standard caters to applications without radial support and allows the thread to come into contact before its flanks are exposed to radial loads.
The ACME thread was first developed in 1894 for machine tools. While the acme lead screw is still the most popular screw in the US, European machines use the Trapezoidal Thread (Metric Acme). The acme thread is a stronger and more resilient alternative to square threads. It is also easier to cut than square threads and can be cut by using a single-point threading die.
Similarly to the internal threads, the metric versions of Acme are similar to their American counterparts. The only difference is that the metric threads are generally wider and are used more frequently in industrial settings. However, the metric-based screw threads are more common than their American counterparts worldwide. In addition, the Acme thread on screw shafts is used most often on external gears. But there is still a small minority of screw shafts that are made with a metric thread.
ACME screws provide a variety of advantages to users, including self-lubrication and reduced wear and tear. They are also ideal for vertical applications, where a reduced frictional force is required. In addition, ACME screws are highly resistant to back-drive and minimize the risk of backlash. Furthermore, they can be easily checked with readily available thread gauges. So, if you’re looking for a quality ACME screw for your next industrial project, look no further than ACME.
Lead screw coatings
The properties of lead screw materials affect their efficiency. These materials have high anti-corrosion, thermal resistance, and self-lubrication properties, which eliminates the need for lubrication. These coating materials include polytetrafluoroethylene (PFE), polyether ether ketone (PEK), and Vespel. Other desirable properties include high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and rigidity.
The most common materials for lead screws are carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Lead screw coatings can be PTFE-based to withstand harsh environments and remove oil and grease. In addition to preventing corrosion, lead screw coatings improve the life of polymer parts. Lead screw assembly manufacturers offer a variety of customization options for their lead screw, including custom-molded nuts, thread forms, and nut bodies.
Lead screws are typically measured in rpm, or revolutions per minute. The PV curve represents the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. This value is affected by the material used in the construction of the screw, lubrication conditions, and end fixity. The critical speed of lead screws is determined by their length and minor diameter. End fixity refers to the support for the screw and affects its rigidity and critical speed.
The primary purpose of lead screws is to enable smooth movement. To achieve this, lead screws are usually preloaded with axial load, enabling consistent contact between a screw’s filets and nuts. Lead screws are often used in linear motion control systems and feature a large area of sliding contact between male and female threads. Lead screws can be manually operated or mortised and are available in a variety of sizes and materials. The materials used for lead screws include stainless steel and bronze, which are often protected by a PTFE type coating.
These screws are made of various materials, including stainless steel, bronze, and various plastics. They are also made to meet specific requirements for environmental conditions. In addition to lead screws, they can be made of stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Surface coatings can improve the screw’s corrosion resistance, while making it more wear resistant in tough environments. A screw that is coated with PTFE will maintain its anti-corrosion properties even in tough environments.
Clamp style collars
The screw shaft clamp style collar is a basic machine component, which is attached to the shaft via multiple screws. These collars act as mechanical stops, load bearing faces, or load transfer points. Their simple design makes them easy to install. This article will discuss the pros and cons of this style of collar. Let’s look at what you need to know before choosing a screw shaft clamp style collar. Here are some things to keep in mind.
Clamp-style shaft collars are a versatile mounting option for shafts. They have a recessed screw that fully engages the thread for secure locking. Screw shaft clamp collars come in different styles and can be used in both drive and power transmission applications. Listed below are the main differences between these 2 styles of collars. They are compatible with all types of shafts and are able to handle axial loads of up to 5500 pounds.
Clamp-style shaft collars are designed to prevent the screw from accidentally damaging the shaft when tightened. They can be tightened with a set screw to counteract the initial clamping force and prevent the shaft from coming loose. However, when tightening the screw, you should use a torque wrench. Using a set screw to tighten a screw shaft collar can cause it to warp and reduce the surface area that contacts the shaft.
Another key advantage to Clamp-style shaft collars is that they are easy to install. Clamp-style collars are available in one-piece and two-piece designs. These collars lock around the shaft and are easy to remove and install. They are ideal for virtually any shaft and can be installed without removing any components. This type of collar is also recommended for those who work on machines with sensitive components. However, be aware that the higher the OD, the more difficult it is to install and remove the collar.
Screw shaft clamp style collars are usually one-piece. A two-piece collar is easier to install than a one-piece one. The two-piece collars provide a more effective clamping force, as they use the full seating torque. Two-piece collars have the added benefit of being easy to install because they require no tools to install. You can disassemble one-piece collars before installing a two-piece collar.
Ball screw nut
The proper installation of a ball screw nut requires that the nut be installed on the center of the screw shaft. The return tubes of the ball nut must be oriented upward so that the ball nut will not overtravel. The adjusting nut must be tightened against a spacer or spring washer, then the nut is placed on the screw shaft. The nut should be rotated several times in both directions to ensure that it is centered.
Ball screw nuts are typically manufactured with a wide range of preloads. Large preloads are used to increase the rigidity of a ball screw assembly and prevent backlash, the lost motion caused by a clearance between the ball and nut. Using a large amount of preload can lead to excessive heat generation. The most common preload for ball screw nuts is 1 to 3%. This is usually more than enough to prevent backlash, but a higher preload will increase torque requirements.
The diameter of a ball screw is measured from its center, called the ball circle diameter. This diameter represents the distance a ball will travel during 1 rotation of the screw shaft. A smaller diameter means that there are fewer balls to carry the load. Larger leads mean longer travels per revolution and higher speeds. However, this type of screw cannot carry a greater load capacity. Increasing the length of the ball nut is not practical, due to manufacturing constraints.
The most important component of a ball screw is a ball bearing. This prevents excessive friction between the ball and the nut, which is common in lead-screw and nut combinations. Some ball screws feature preloaded balls, which avoid “wiggle” between the nut and the ball. This is particularly desirable in applications with rapidly changing loads. When this is not possible, the ball screw will experience significant backlash.
A ball screw nut can be either single or multiple circuits. Single or multiple-circuit ball nuts can be configured with 1 or 2 independent closed paths. Multi-circuit ball nuts have 2 or more circuits, making them more suitable for heavier loads. Depending on the application, a ball screw nut can be used for small clearance assemblies and compact sizes. In some cases, end caps and deflectors may be used to feed the balls back to their original position.


China high quality Transmission Geared Motor Unit Wp Nmrv Swl Screw Drive Lifts Stepper Cyclo Cycloidal Extruder Helical Plenetary Bevel Worm Speed Variator Gear Reducer Gearbox with Hot selling
Product Description
Transmission Geared Motor Unit Wp NMRV Swl Screw Drive Lifts Stepper Cyclo Cycloidal Extruder Helical Plenetary Bevel Worm Speed Variator Gear Reducer Gearbox
Types of Screw Shafts
Screw shafts come in various types and sizes. These types include fully threaded, Lead, and Acme screws. Let’s explore these types in more detail. What type of screw shaft do you need? Which 1 is the best choice for your project? Here are some tips to choose the right screw:
Machined screw shaft
The screw shaft is a basic piece of machinery, but it can be further customized depending on the needs of the customer. Its features include high-precision threads and ridges. Machined screw shafts are generally manufactured using high-precision CNC machines or lathes. The types of screw shafts available vary in shape, size, and material. Different materials are suitable for different applications. This article will provide you with some examples of different types of screw shafts.
Ball screws are used for a variety of applications, including mounting machines, liquid crystal devices, measuring devices, and food and medical equipment. Various shapes are available, including miniature ball screws and nut brackets. They are also available without keyway. These components form a high-accuracy feed mechanism. Machined screw shafts are also available with various types of threaded ends for ease of assembly. The screw shaft is an integral part of linear motion systems.
When you need a machined screw shaft, you need to know the size of the threads. For smaller machine screws, you will need a mating part. For smaller screw sizes, the numbers will be denominated as industry Numeric Sizes. These denominations are not metric, but rather in mm, and they may not have a threads-per-inch designation. Similarly, larger machine screws will usually have threads that have a higher pitch than those with a lower pitch.
Another important feature of machine screws is that they have a thread on the entire shaft, unlike their normal counterparts. These machine screws have finer threads and are intended to be screwed into existing tapped holes using a nut. This means that these screws are generally stronger than other fasteners. They are usually used to hold together electronic components, industrial equipment, and engines. In addition to this, machine screws are usually made of a variety of materials.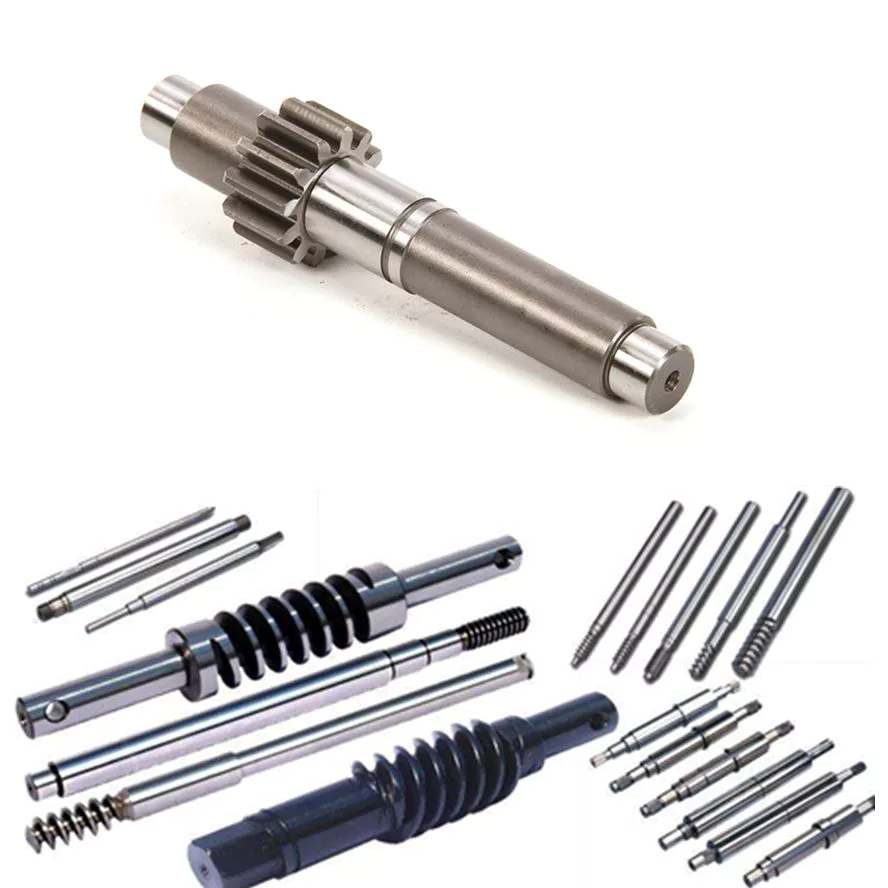
Acme screw
An Acme screw is the most common type of threaded shaft available. It is available in a variety of materials including stainless steel and carbon steel. In many applications, it is used for large plates in crushing processes. ACME screws are self-locking and are ideal for applications requiring high clamping force and low friction. They also feature a variety of standard thread forms, including knurling and rolled worms.
Acme screws are available in a wide range of sizes, from 1/8″ to 6″. The diameter is measured from the outside of the screw to the bottom of the thread. The pitch is equal to the lead in a single start screw. The lead is equal to the pitch plus the number of starts. A screw of either type has a standard pitch and a lead. Acme screws are manufactured to be accurate and durable. They are also widely available in a wide range of materials and can be customized to fit your needs.
Another type of Acme screw is the ball screw. These have no back drive and are widely used in many applications. Aside from being lightweight, they are also able to move at faster speeds. A ball screw is similar to an Acme screw, but has a different shape. A ball screw is usually longer than an Acme screw. The ball screw is used for applications that require high linear speeds. An Acme screw is a common choice for many industries.
There are many factors that affect the speed and resolution of linear motion systems. For example, the nut position and the distance the screw travels can all affect the resolution. The total length of travel, the speed, and the duty cycle are all important. The lead size will affect the maximum linear speed and force output. If the screw is long, the greater the lead size, the higher the resolution. If the lead length is short, this may not be the most efficient option.
Lead screw
A lead screw is a threaded mechanical device. A lead screw consists of a cylindrical shaft, which includes a shallow thread portion and a tightly wound spring wire. This spring wire forms smooth, hard-spaced thread convolutions and provides wear-resistant engagement with the nut member. The wire’s leading and trailing ends are anchored to the shaft by means appropriate to the shaft’s composition. The screw is preferably made of stainless steel.
When selecting a lead screw, 1 should first determine its critical speed. The critical speed is the maximum rotations per minute based on the natural frequency of the screw. Excessive backlash will damage the lead screw. The maximum number of revolutions per minute depends on the screw’s minor diameter, length, assembly alignment, and end fixity. Ideally, the critical speed is 80% of its evaluated critical speed. A critical speed is not exceeded because excessive backlash would damage the lead screw and may be detrimental to the screw’s performance.
The PV curve defines the safe operating limits of a lead screw. This relationship describes the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. As the PV value increases, a lower rotation speed is required for heavier axial loads. Moreover, PV is affected by material and lubrication conditions. Besides, end fixity, which refers to the way the lead screw is supported, also affects its critical speed. Fixed-fixed and free end fixity are both possible.
Lead screws are widely used in industries and everyday appliances. In fact, they are used in robotics, lifting equipment, and industrial machinery. High-precision lead screws are widely used in the fields of engraving, fluid handling, data storage, and rapid prototyping. Moreover, they are also used in 3D printing and rapid prototyping. Lastly, lead screws are used in a wide range of applications, from measuring to assembly.
Fully threaded screw
A fully threaded screw shaft can be found in many applications. Threading is an important feature of screw systems and components. Screws with threaded shafts are often used to fix pieces of machinery together. Having fully threaded screw shafts ensures that screws can be installed without removing the nut or shaft. There are 2 major types of screw threads: coarse and fine. When it comes to coarse threads, UTS is the most common type, followed by BSP.
In the 1840s, a British engineer named Joseph Whitworth created a design that was widely used for screw threads. This design later became the British Standard Whitworth. This standard was used for screw threads in the United States during the 1840s and 1860s. But as screw threads evolved and international standards were established, this system remained largely unaltered. A new design proposed in 1864 by William Sellers improved upon Whitworth’s screw threads and simplified the pitch and surface finish.
Another reason for using fully threaded screws is their ability to reduce heat. When screw shafts are partially threaded, the bone grows up to the screw shaft and causes the cavity to be too narrow to remove it. Consequently, the screw is not capable of backing out. Therefore, fully threaded screws are the preferred choice for inter-fragmentary compression in children’s fractures. However, surgeons should know the potential complication when removing metalwork.
The full thread depth of a fully threaded screw is the distance at which a male thread can freely thread into the shaft. This dimension is typically 1 millimeter shy of the total depth of the drilled hole. This provides space for tap lead and chips. The full-thread depth also makes fully threaded screws ideal for axially-loaded connections. It is also suitable for retrofitting applications. For example, fully threaded screws are commonly used to connect 2 elements.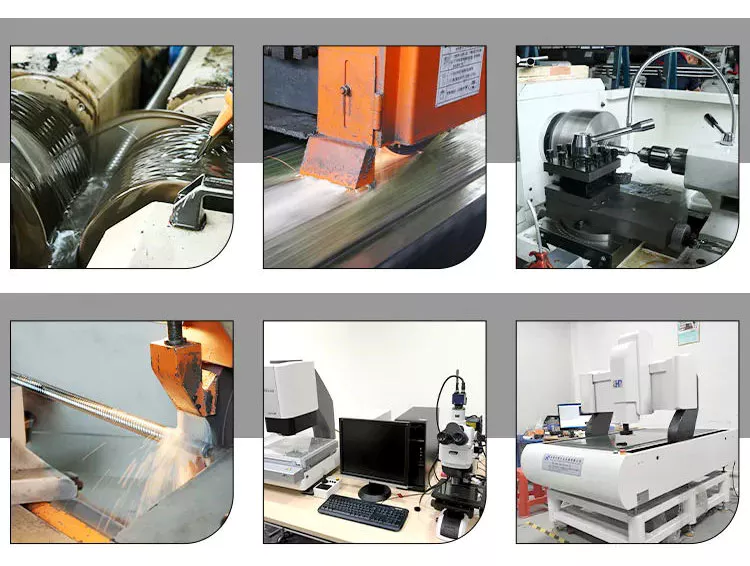
Ball screw
The basic static load rating of a ball screw is determined by the product of the maximum axial static load and the safety factor “s0”. This factor is determined by past experience in similar applications and should be selected according to the design requirements of the application. The basic static load rating is a good guideline for selecting a ball screw. There are several advantages to using a ball screw for a particular application. The following are some of the most common factors to consider when selecting a ball screw.
The critical speed limit of a ball screw is dependent on several factors. First of all, the critical speed depends on the mass, length and diameter of the shaft. Second, the deflection of the shaft and the type of end bearings determine the critical speed. Finally, the unsupported length is determined by the distance between the ball nut and end screw, which is also the distance between bearings. Generally, a ball screw with a diameter greater than 1.2 mm has a critical speed limit of 200 rpm.
The first step in manufacturing a high-quality ball screw is the choice of the right steel. While the steel used for manufacturing a ball screw has many advantages, its inherent quality is often compromised by microscopic inclusions. These microscopic inclusions may eventually lead to crack propagation, surface fatigue, and other problems. Fortunately, the technology used in steel production has advanced, making it possible to reduce the inclusion size to a minimum. However, higher-quality steels can be expensive. The best material for a ball screw is vacuum-degassed pure alloy steel.
The lead of a ball screw shaft is also an important factor to consider. The lead is the linear distance between the ball and the screw shaft. The lead can increase the amount of space between the balls and the screws. In turn, the lead increases the speed of a screw. If the lead of a ball screw is increased, it may increase its accuracy. If not, the lead of a ball screw can be improved through preloading, lubrication, and better mounting accuracy.

