Product Description
You can kindly find the specification details below:
HangZhou Mastery Machinery Technology Co., LTD helps manufacturers and brands fulfill their machinery parts by precision manufacturing. High precision machinery products like the shaft, worm screw, bushing, couplings, joints……Our products are used widely in electronic motors, the main shaft of the engine, the transmission shaft in the gearbox, couplers, printers, pumps, drones, and so on. They cater to different industries, including automotive, industrial, power tools, garden tools, healthcare, smart home, etc.
Mastery caters to the industrial industry by offering high-level Cardan shafts, pump shafts, and a bushing that come in different sizes ranging from diameter 3mm-50mm. Our products are specifically formulated for transmissions, robots, gearboxes, industrial fans, and drones, etc.
Mastery factory currently has more than 100 main production equipment such as CNC lathe, CNC machining center, CAM Automatic Lathe, grinding machine, hobbing machine, etc. The production capacity can be up to 5-micron mechanical tolerance accuracy, automatic wiring machine processing range covering 3mm-50mm diameter bar.
Key Specifications:
| Name | Shaft/Motor Shaft/Drive Shaft/Gear Shaft/Pump Shaft/Worm Screw/Worm Gear/Bushing/Ring/Joint/Pin |
| Material | 40Cr/35C/GB45/70Cr/40CrMo |
| Process | Machining/Lathing/Milling/Drilling/Grinding/Polishing |
| Size | 2-400mm(Customized) |
| Diameter | φ12(Customized) |
| Diameter Tolerance | 0.015mm |
| Roundness | 0.01mm |
| Roughness | Ra0.2-0.6 |
| Straightness | 0.01mm |
| Hardness | Customized |
| Length | 153mm(Customized) |
| Heat Treatment | Customized |
| Surface treatment | Coating/Ni plating/Zn plating/QPQ/Carbonization/Quenching/Black Treatment/Steaming Treatment/Nitrocarburizing/Carbonitriding |
Quality Management:
- Raw Material Quality Control: Chemical Composition Analysis, Mechanical Performance Test, ROHS, and Mechanical Dimension Check
- Production Process Quality Control: Full-size inspection for the 1st part, Critical size process inspection, SPC process monitoring
- Lab ability: CMM, OGP, XRF, Roughness meter, Profiler, Automatic optical inspector
- Quality system: ISO9001, IATF 16949, ISO14001
- Eco-Friendly: ROHS, Reach.
Packaging and Shipping:
Throughout the entire process of our supply chain management, consistent on-time delivery is vital and very important for the success of our business.
Mastery utilizes several different shipping methods that are detailed below:
For Samples/Small Q’ty: By Express Services or Air Fright.
For Formal Order: By Sea or by air according to your requirement.
Mastery Services:
- One-Stop solution from idea to product/ODM&OEM acceptable
- Individual research and sourcing/purchasing tasks
- Individual supplier management/development, on-site quality check projects
- Muti-varieties/small batch/customization/trial orders are acceptable
- Flexibility on quantity/Quick samples
- Forecast and raw material preparation in advance are negotiable
- Quick quotes and quick responses
General Parameters:
If you are looking for a reliable machinery product partner, you can rely on Mastery. Work with us and let us help you grow your business using our customizable and affordable products. /* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
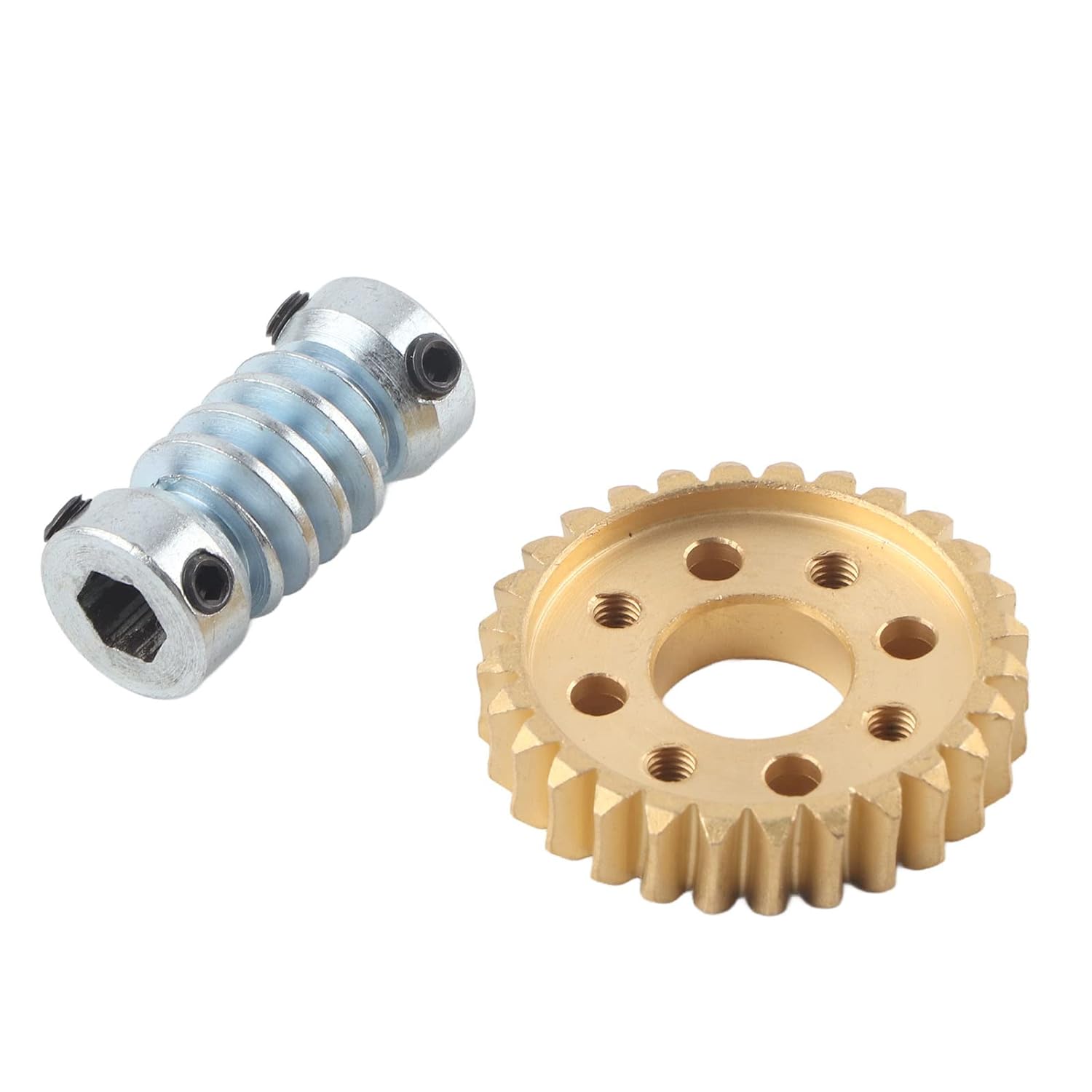

How do you properly lubricate a worm screw and gear assembly?
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of a worm screw and gear assembly. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, thereby extending the lifespan of the components. Here are the steps to properly lubricate a worm screw and gear assembly:
- Clean the Assembly: Before applying lubrication, ensure that the worm screw and gear assembly is free from dirt, debris, and old lubricant residues. Clean the surfaces using an appropriate cleaning agent or solvent, followed by a thorough drying process.
- Select the Right Lubricant: Choose a lubricant specifically designed for gear systems or worm screw applications. Consider factors such as viscosity, temperature range, load capacity, and compatibility with the materials used in the assembly. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or lubrication guidelines for the specific assembly to determine the suitable lubricant type and grade.
- Apply the Lubricant: Apply the lubricant to the contacting surfaces of the worm screw and gear assembly. Use an appropriate applicator, such as a brush, oil can, or grease gun, depending on the lubricant form (oil or grease) and the accessibility of the components. Ensure complete coverage of the gear teeth, worm screw threads, and other relevant surfaces. Pay attention to areas where the most significant friction and wear occur.
- Monitor the Lubricant Level: Check the lubricant level regularly to ensure an adequate supply. Depending on the application and operating conditions, lubricant consumption or degradation may occur over time. It is important to maintain the lubricant level within the recommended range to ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear or overheating.
- Periodic Lubrication Maintenance: Establish a lubrication maintenance schedule based on the operating conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect the assembly for signs of lubricant degradation, contamination, or insufficient lubrication. Replace the lubricant as needed and follow the recommended intervals for lubricant replenishment or reapplication.
- Consideration for Grease Lubrication: If using grease as the lubricant, it is important to choose a high-quality grease suitable for worm screw applications. Grease provides better adhesion to surfaces and tends to stay in place, offering longer-lasting lubrication compared to oil. However, excessive grease accumulation or over-greasing should be avoided, as it can lead to increased friction and inefficiency.
It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for lubrication specific to the worm screw and gear assembly. Different assemblies may have unique lubrication requirements based on their design, load capacity, operating conditions, and materials used. By properly lubricating the worm screw and gear assembly, you can ensure optimal performance, reduce wear, and extend the operational life of the components.

What are the latest innovations in worm screw design and materials?
In recent years, there have been several notable innovations in worm screw design and materials that aim to improve performance, efficiency, durability, and overall functionality. Here are some of the latest advancements in this field:
- Advanced Materials: One of the significant trends in worm screw design is the use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring materials with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and fatigue properties. For example, advanced alloys and composite materials are being employed to improve load capacity, reduce weight, and increase the longevity of worm screws. Additionally, advancements in material science and engineering are leading to the development of self-lubricating materials, which can minimize friction and improve efficiency by reducing the need for external lubrication.
- Improved Thread Geometries: Innovations in thread geometries have focused on optimizing load distribution, reducing friction, and improving efficiency. Researchers and engineers are developing novel thread profiles and forms that enhance contact between the worm screw and the worm wheel. These designs help minimize backlash, increase load-carrying capacity, and improve overall system performance. Additionally, advancements in computer simulations and modeling techniques enable more accurate analysis and optimization of thread geometries for specific applications.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Surface treatments and coatings are being applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. For instance, advanced coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings or specialized lubricious coatings help reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and minimize the need for external lubrication. Surface treatments like nitriding or carburizing can improve hardness and provide resistance against abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of worm screws.
- Precision Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing processes and technologies have enabled the production of worm screws with higher precision and tighter tolerances. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC grinding and high-precision gear hobbing, allow for the creation of worm screws with superior dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and better tooth profile control. These manufacturing advancements contribute to enhanced performance, reduced backlash, and increased overall system efficiency.
- Computer-Aided Design and Simulation: The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools has revolutionized worm screw design and optimization. Engineers can now create virtual models, simulate the behavior of worm gear systems, and analyze various design parameters to optimize performance before physical prototypes are manufactured. This iterative design process helps reduce development time, minimize costs, and improve the final design and performance of worm screws.
- Integration with Digitalization and Automation: The integration of worm gear systems with digitalization and automation technologies is another area of innovation. Worm screws are being designed to work seamlessly with sensor technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load. This data can be utilized for predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and optimization of the overall system performance.
It’s important to note that the field of worm screw design and materials is continuously evolving, and new innovations are being introduced regularly. Keeping up with the latest research, advancements, and industry developments is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in worm gear system applications.
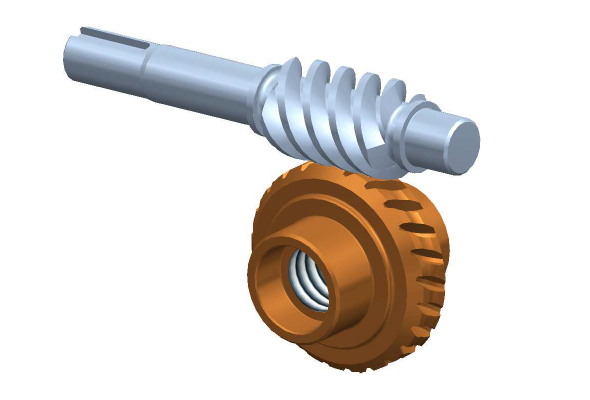
How do you calculate the gear ratio for a worm screw and gear setup?
In a worm screw and gear setup, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the worm wheel (gear) and the number of threads on the worm screw. The gear ratio represents the relationship between the rotational speed of the worm screw and the resulting rotational speed of the worm wheel. The formula to calculate the gear ratio is as follows:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Worm Wheel / Number of Threads on Worm Screw
Here’s a step-by-step process to calculate the gear ratio:
- Count the number of teeth on the worm wheel. This can be done by visually inspecting the gear or referring to its specifications.
- Count the number of threads on the worm screw. The threads refer to the number of complete turns or helical grooves wrapped around the cylindrical body of the worm screw.
- Divide the number of teeth on the worm wheel by the number of threads on the worm screw.
- The result of the division is the gear ratio. It represents the number of revolutions of the worm screw required to complete one revolution of the worm wheel.
For example, let’s say the worm wheel has 40 teeth, and the worm screw has 2 threads. Using the formula, we can calculate the gear ratio as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 teeth / 2 threads = 20
In this case, for every full revolution of the worm screw, the worm wheel will rotate 1/20th of a revolution. This indicates a significant speed reduction, resulting in high torque output at the worm wheel.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio calculated using this formula assumes an ideal scenario without considering factors like friction, efficiency losses, or the pitch diameter of the gears. In practical applications, these factors may affect the actual gear ratio and performance of the worm screw and gear setup.


editor by CX 2024-01-11
China Good quality CHINAMFG 6mm Shaft Stepped Type Ball Screw with Nut for CNC Machinery (BSD Series, Lead: 2mm, Shaft: 6mm)
Product Description
BSD Series Stepped Cold Rolled Ball Screw (C5/Ct7)
| Table of Shaft dia. and Lead combination for Rolled Ball Screw | ||||||||||||||||
| Lead (mm) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 30 | ||
| Shaft dia (mm) | 4 | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 5 | / | |||||||||||||||
| 6 | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 8 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||
| 10 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||
| 12 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 14 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||
Accuracy Class & Axial Clearance
Accuracy grade of BSD series(standard stepped cold rolled ball screw) are based on C5 and Ct7(JIS B 1192-3). According to accuracy grade, Axial play 0.005(Preload :C5) and 0.02mm or less(Ct7).
Material & Surface Hardness
BSD series (Standard Stepped cold rolled ball screw) of screw shaft screw material S55C (induction hardening), nut material SCM415H (carburizing and hardening), the surface hardness of the ball screw part is HRC58 or higher.
Shaft End Shape
The shape of the shaft end of the BSD series (stepped cold rolled ball screw) has been standardized.
Application:
1. Medical industry
2.Lithium battery industry
3.Solar photovoltaic industry
4. Semi conductor Industry
5. General industry machinery
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment
9. 3C industry etc
Technical Drawing
Specification List
FACTORY DETAILED PROCESSING PHOTOS
HIGH QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
FAQ
1. Why choose CHINAMFG China?
Over the past 14 years, CHINAMFG has always insisted that “products and services” start from Japanese industry standards,taking ZheJiang standards as the bottom line, actively invest in the development of new transmission components and self-experiment and test. With the service tenet of “exceeding customer expectations”, establish a “trusted” partnership.
2. What is your main products ?
We are a leading manufacturer and distributor of linear motion components in China. Especially miniature size of Ball Screws and Linear Actuators and linear motion guideways. Our brand “KGG” stands for ” Know-how,” ” Great Quality,” and ” Good value” and our factory is located in the most advanced city in China: ZheJiang with the best equipment and sophisticated technology, completely strict quality control system. Our aim is to supply world leader class linear motion components but with most reasonable price in the world.
3. How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
4. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
5. How can I get a sample to check the quality?
After confirmation of our quoted price, you can place the sample order. The sample will be started after you CHINAMFG back our detailed technical file.
6. What’s your payment terms?
Our payment terms is 30% deposit,balance 70% before shipment. /* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C5/C7 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 6mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 3-Row |
| Nut Type: | Stepped Type |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What maintenance is required for worm screw gear systems?
Maintaining worm screw gear systems is essential to ensure their smooth operation, longevity, and optimal performance. Here are the key maintenance tasks typically required for worm screw gear systems:
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in worm screw gear systems. Regularly monitor lubricant levels and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types of lubricants to use. Inspect lubricant quality and cleanliness, and replenish or replace the lubricant as needed. Pay attention to proper lubrication in both the worm screw and the worm wheel to ensure efficient torque transmission and minimize wear.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the worm screw gear system to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can accumulate on the threads, teeth, and other contacting surfaces. Use appropriate cleaning methods and solvents recommended by the manufacturer. Ensure that the cleaning process does not damage the components or compromise the lubrication system.
- Inspection: Conduct routine inspections to identify any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment in the worm screw gear system. Check for excessive backlash, abnormal noise, vibration, or irregularities in operation. Inspect the teeth, threads, and other critical areas for signs of wear, pitting, or scoring. If any issues are detected, take appropriate measures to address them promptly, such as adjusting the backlash or replacing worn components.
- Alignment: Proper alignment is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of worm screw gear systems. Periodically check and adjust the alignment of the worm screw and the worm wheel to ensure smooth and efficient meshing. Misalignment can result in increased friction, wear, and reduced performance. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for alignment procedures and use precision measurement tools as necessary.
- Load Distribution: Monitor the load distribution across the teeth of the worm wheel. Uneven load distribution can lead to premature wear and failure of the system. If necessary, adjust loads, redistribute the load by using multiple worm screws, or consider using additional supporting mechanisms to ensure uniform load distribution.
- Temperature Monitoring: Keep an eye on the operating temperature of the worm screw gear system. Excessive heat can indicate problems such as inadequate lubrication, overloading, or inefficiencies. Monitor temperature using appropriate sensors or thermal imaging techniques and take corrective actions if the temperature exceeds recommended limits.
- Periodic Overhaul: Depending on the application and usage conditions, consider scheduling periodic overhauls or maintenance intervals for the worm screw gear system. During these overhauls, disassemble the system, inspect components thoroughly, replace worn or damaged parts, reassemble with proper lubrication, and perform necessary adjustments. The frequency of overhauls will depend on factors such as operating conditions, loads, and manufacturer recommendations.
- Documentation: Maintain proper documentation of maintenance activities, including lubrication schedules, inspection records, repair or replacement history, and any troubleshooting performed. This documentation provides a valuable reference for future maintenance, helps identify recurring issues, and enables better tracking of the system’s performance over time.
It’s important to note that specific maintenance requirements may vary depending on the design, materials, operating conditions, and manufacturer recommendations for the worm screw gear system. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation and guidelines for the particular system being used, and consult with experts or maintenance professionals if needed.

What are the latest innovations in worm screw design and materials?
In recent years, there have been several notable innovations in worm screw design and materials that aim to improve performance, efficiency, durability, and overall functionality. Here are some of the latest advancements in this field:
- Advanced Materials: One of the significant trends in worm screw design is the use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring materials with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and fatigue properties. For example, advanced alloys and composite materials are being employed to improve load capacity, reduce weight, and increase the longevity of worm screws. Additionally, advancements in material science and engineering are leading to the development of self-lubricating materials, which can minimize friction and improve efficiency by reducing the need for external lubrication.
- Improved Thread Geometries: Innovations in thread geometries have focused on optimizing load distribution, reducing friction, and improving efficiency. Researchers and engineers are developing novel thread profiles and forms that enhance contact between the worm screw and the worm wheel. These designs help minimize backlash, increase load-carrying capacity, and improve overall system performance. Additionally, advancements in computer simulations and modeling techniques enable more accurate analysis and optimization of thread geometries for specific applications.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Surface treatments and coatings are being applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. For instance, advanced coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings or specialized lubricious coatings help reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and minimize the need for external lubrication. Surface treatments like nitriding or carburizing can improve hardness and provide resistance against abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of worm screws.
- Precision Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing processes and technologies have enabled the production of worm screws with higher precision and tighter tolerances. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC grinding and high-precision gear hobbing, allow for the creation of worm screws with superior dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and better tooth profile control. These manufacturing advancements contribute to enhanced performance, reduced backlash, and increased overall system efficiency.
- Computer-Aided Design and Simulation: The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools has revolutionized worm screw design and optimization. Engineers can now create virtual models, simulate the behavior of worm gear systems, and analyze various design parameters to optimize performance before physical prototypes are manufactured. This iterative design process helps reduce development time, minimize costs, and improve the final design and performance of worm screws.
- Integration with Digitalization and Automation: The integration of worm gear systems with digitalization and automation technologies is another area of innovation. Worm screws are being designed to work seamlessly with sensor technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load. This data can be utilized for predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and optimization of the overall system performance.
It’s important to note that the field of worm screw design and materials is continuously evolving, and new innovations are being introduced regularly. Keeping up with the latest research, advancements, and industry developments is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in worm gear system applications.

What are the advantages of using a worm screw in gear systems?
Using a worm screw in gear systems offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in certain applications. Here are some of the advantages of using a worm screw:
- High Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw is its ability to provide a high gear reduction ratio in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a significant reduction in rotational speed. This allows for efficient torque multiplication, enabling the transmission of high torque output from the worm screw to the worm wheel. The high gear reduction is beneficial in applications that require slow and powerful movements, such as lifting heavy loads or controlling conveyor systems.
- Compact Design: Worm screw mechanisms are known for their compact design. Compared to other gear systems, such as spur gears or helical gears, a worm screw setup can achieve a similar gear reduction with fewer components. This makes it a space-saving solution, especially in applications where limited space is available or where a compact design is desired.
- Self-Locking: The self-locking property of a worm screw is a significant advantage in many applications. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a natural tendency to hold its position and prevent backward rotation of the worm wheel. This self-locking feature eliminates the need for additional braking mechanisms or external locking devices, simplifying the overall system design and improving safety and stability in applications that require load holding or position locking.
- Right-Angle Transmission: Worm screw mechanisms provide motion transmission at a right angle, allowing for the transfer of motion between non-parallel shafts. This makes them suitable for applications where the input and output shafts are oriented perpendicular to each other. Examples include automotive steering systems, where the rotational motion from the steering wheel needs to be converted into lateral motion for steering the vehicle.
- Quiet Operation: Worm screw gear systems tend to operate quietly compared to other gear configurations. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation. This can be advantageous in applications where noise reduction is desirable, such as in office equipment, appliances, or environments where low noise levels are required.
It’s important to note that while worm screw mechanisms offer these advantages, there are also some considerations to keep in mind. For instance, worm screws can have lower mechanical efficiency compared to other gear systems due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth, leading to energy losses. Additionally, they may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which can affect precision and introduce a small amount of lost motion in the system. Nevertheless, the unique characteristics of worm screws make them a valuable choice in various applications where high gear reduction, self-locking, compactness, and right-angle transmission are essential.


editor by CX 2023-12-25
China OEM High Torque Power Transmission Part Speed Reducer Planetary Gear Boxes for Textile Machinery supplier
Product Description
Power Transmission Part Speed Reducer Planetary Gear Boxes For Textile Machinery
Planetary gearbox is a kind of reducer with wide versatility. The inner gear adopts low carbon alloy steel carburizing quenching and grinding or nitriding process. Planetary gearbox has the characteristics of small structure size, large output torque, high speed ratio, high efficiency, safe and reliable performance, etc. The inner gear of the planetary gearbox can be divided into spur gear and helical gear. Customers can choose the right precision reducer according to the needs of the application.
Product Description
Characteristics:
1. Split design, more output options
2. The input and output dimensions can be seamlessly switched with the straight tooth series
3. The double support cage planet carrier has high reliability and is suitable for high-speed and frequent CZPT and reverse rotation
4. The design of double-stage single support support has high cost performance
5. Keyway can be opened for the force shaft
6. Helical gear transmission is more stable and has large bearing capacity
7. Accurate positioning of low return clearance
8. Specification range: 60-120mm
9. Speed ratio range: 3-100
10. Accuracy range: 1-3 arcmin (P1); 3-5 arcmin (P2)
| Specifications | PW60 | PW90 | PW120 | |||
| Technal Parameters | ||||||
| Max. Torque | Nm | 1.5times rated torque | ||||
| Emergency Stop Torque | Nm | 2.5times rated torque | ||||
| Max. Radial Load | N | 1350 | 3100 | 6100 | ||
| Max. Axial Load | N | 630 | 1300 | 2800 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity | Nm/arcmin | 5 | 10 | 20 | ||
| Max.Input Speed | rpm | 6000 | 6000 | 6000 | ||
| Rated Input Speed | rpm | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | ||
| Noise | dB | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤65 | ||
| Average Life Time | h | 20000 | ||||
| Efficiency Of Full Load | % | L1≥95% L2≥90% | ||||
| Return Backlash | P1 | L1 | arcmin | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 |
| L2 | arcmin | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| P2 | L1 | arcmin | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| L2 | arcmin | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Moment Of Inertia Table | L1 | 3 | Kg*cm2 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 |
| 4 | Kg*cm2 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | ||
| 5 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | ||
| 7 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | ||
| 8 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | ||
| 10 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 2.57 | ||
| L2 | 12 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.61 | 0.45 | |
| 15 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.61 | 0.45 | ||
| 20 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.45 | ||
| 25 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.40 | ||
| 28 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.45 | ||
| 30 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.67 | 0.45 | ||
| 35 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.45 | ||
| 40 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.45 | ||
| 50 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.40 | ||
| 70 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.40 | ||
| 100 | Kg*cm2 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.40 | ||
| Technical Parameter | Level | Ratio | PW60 | PW90 | PW120 | |
| Rated Torque | L1 | 3 | Nm | 35 | 100 | 165 |
| 4 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 220 | ||
| 5 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 220 | ||
| 7 | Nm | 40 | 98 | 200 | ||
| 8 | Nm | 40 | 90 | 200 | ||
| 10 | Nm | 25 | 70 | 150 | ||
| L2 | 12 | Nm | 35 | / | 165 | |
| 15 | Nm | 35 | 100 | 165 | ||
| 20 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 220 | ||
| 25 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 220 | ||
| 28 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 220 | ||
| 30 | Nm | 35 | 100 | 165 | ||
| 35 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 210 | ||
| 40 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 210 | ||
| 50 | Nm | 43 | 125 | 210 | ||
| 70 | Nm | 40 | 98 | 200 | ||
| 100 | Nm | 25 | 70 | 150 | ||
| Degree Of Protection | IP65 | |||||
| Operation Temprature | ºC | – 10ºC to -90ºC | ||||
| Weight | L1 | kg | 1.2 | 2.8 | 7.6 | |
| L2 | kg | 1.55 | 3.95 | 10.5 | ||
Company Profile
Packaging & Shipping
1. Lead time: 7-10 working days as usual, 20 working days in busy season, it will be based on the detailed order quantity;
2. Delivery: DHL/ UPS/ FEDEX/ EMS/ TNT
| Application: | Machine Tool |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Starting Mode: | Direct on-line Starting |
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
| Samples: |
US$ 185/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What is a worm gear reducer gearbox?
The worm gear reducer gearbox is used to change the output speed of the mechanical device. It consists of worm and helical gears mounted on the input side of the equipment. In some cases, this gear reduction system can be multi-stage, enabling extremely low output speeds. It has the advantages of low energy consumption and low vibration.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearbox
Worm gear reducer gearbox is an effective device to reduce the speed of mechanical equipment. The use of hard steel or non-ferrous metals for the worm increases its efficiency. Worms made of hard steel generate more heat than worms made of mild steel. Different thermal expansion results in gaps between mating surfaces. Despite its many benefits, worm gear reducer gearboxes are prone to oil leakage, which can be a problem for a number of reasons.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes are available in different gear ratios and are compatible with many motor types. Some are available in dual-axis and single-axis configurations and can be mounted horizontally or vertically. They are also available in intermediate ratios, as well as four- and five-speed transmission types. They can also be connected with additional output shafts.
Another type of worm gear reducer gearbox is the multi-stage variety. This gear reducer gearbox has multiple stages, enabling it to reduce speed with extremely low output speeds. In addition to the large transmission ratio, the multi-stage gear reducer gearbox has low noise, low vibration and low energy consumption.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes offer space-saving solutions as well as increased torque. Agknx Gearbox offers worm gear reducer gearboxes that solve common deceleration problems. The company has also expanded its product range into the bathroom market. Compared with the standard gearbox, the worm gear reducer gearbox has the characteristics of lower price and better torque output.
Agknx worm gear
The Agknx type worm gear reducer gearbox has multi-tooth line contact and is widely used in heavy machinery. These gears are characterized by a high load-carrying capacity, but they are highly sensitive to misalignment and manufacturing errors. However, by employing point contact, these gears can be made more reliable and can withstand higher loads.
Another major advantage of the Agknx worm gear is its high load capacity. The tooth profile design of the gears has a high relative slip ratio, which improves efficiency and load capacity. In addition, the large angle between the sliding direction and the contact line provides a low coefficient of friction. The Agknx worm gear also features premium carburized steel and phosphor bronze castings for exceptional durability. In addition, the tooth profile is very precise, the operation is quiet, and the speed fluctuation is small.
Agknx worm gear reducer gearboxes are designed to operate for up to ten hours per day with an even load. The design of this worm gear reducer gearbox stems from Sumitomo Heavy Industries’ extensive experience in gear reducer gearboxes. The smooth surface texture and precise tooth profile of the gears ensure that the gears can withstand high loads without damaging the lubricant film. In addition, Agknx worm shafts are specially designed to have the right stiffness.
Agknx worm gear reducer gearboxes are designed to maximize load capacity while minimizing energy consumption. Its fully meshed teeth reduce surface pressure on the worm gear teeth and increase load capacity. Double throat worm gear
Double throat worm gear
There are a few things to consider when choosing a dual-throat worm gear. First, the diameter of the root circle must match the circle pitch of the larger gear. This measurement is usually done by measuring the distance between adjacent teeth. Alternatively, the worm’s normal module can be used. It is the value entered in the worm module dialog. In addition, the axial pitch of the worm should be equal to the pitch diameter of the circular pitch.
Double-throat worm gears are an excellent choice for heavy and heavy-duty applications. The design of this worm gear is ideal for heavy-duty applications as it provides a tighter connection between the worm and the gear. It is also more compact than other types of gear and is comparable to a fine-pitch lead screw.
The efficiency of a double-throat worm gear depends on the material of the gear and worm. Typically, gears are made of case-hardened steel, while worm gears are made of bronze or cast iron. In some cases, a combination of cast iron and bronze can be used.
The deflection of the worm shaft is also affected by the tooth parameters. Tooth height, pressure angle, and size factors all affect the deflection of the worm shaft. In addition, the number of worm threads is another important parameter that affects the deflection of the worm shaft.
Double-throat worm gears are commonly used in industrial applications where high drive reduction is required. The worm has a concave and internal tooth structure that can be adjusted to achieve various ratios. Worm gears and worm gear assemblies must be properly mounted on their shafts to prevent back drive.
Brass worm gear
The basic working principle of the brass worm gear reducer gearbox is the same as that of the traditional worm gear reducer gearbox. Its axial pitch must be equal to the circumferential pitch of the larger gear. The single-thread design advances one tooth per revolution, while the double-thread design advances two teeth. The threads on the worm are either left-handed or right-handed. The lead of a worm is the distance a point on the thread of the worm moves in one revolution. The lead angle is the angle tangent to the pitch of the cylinder and the axis of the worm.
Double-thread worm gear reducer gearboxes are best for heavy loads. It provides the tightest connection between the worm and the gear. Assembly of the worm gear requires precise mounting. The keyway installation method involves drilling a square cut in the gear hole. This prevents the worm from rotating on the shaft and helps transmit torque. Then use the set screw to secure the gear to the hub.
The large fuel tank helps keep the worm gear clean and reduces heat. It also provides lubrication for extended life. Worm gear reducer gearboxes with oil reservoirs provide a lubricated environment and low-friction surfaces. Additionally, it offers multi-position installation flexibility. Additionally, its housing is cross-milled for precise alignment. It also features internal baffles for leak-free ventilation.
I260 series worm gear reducer gearboxes are one-piece iron casings with solid or hollow output shafts and tapered roller bearings. This gear reducer gearbox is designed for low to medium-horsepower applications. This gear reducer gearbox is a cost-effective option with low initial cost, the high gear ratio, and high torque in a compact package. Also, it is more shock resistant than other gear reducer gearboxes. Brass worm gear
Brass worm gear
Brass worm gear reducer gearbox is a reduction gear. This type of gear can provide a lot of reduction in a small package. This type of gear reducer gearbox also has the ability to generate high torque. However, it is important to understand that this gear reducer gearbox has thermal limitations, which reduce its efficiency. The choice of lubricant for this gear reducer gearbox is very flexible. However, being a yellow metal, it is important to remember that the lubricant must be non-reactive.
Worm gears are used in many consumer and industrial applications and have high reduction ratios. These gears are produced in various configurations and sizes. Worm gears are similar to spur gears but have non-parallel shafts. Worm gears are also suitable for applications requiring low output speed but high torque.
Worm gears have some distinct advantages over other gears. First, unlike standard gears, the worm rotates in a worm-like motion. This mechanism prevents reverse movement. This is because the lead angle of the worm gear is small. Additionally, the worms self-lock, helping to prevent reversal. However, this mechanism is not entirely reliable. Worm gears can be found in elevators, fishing reels, sprockets, and automotive power steering.
Another advantage of worm gears is that they are easy to manufacture. The rationale behind this design is to have two mutually perpendicular axes. Then, two or more threads are added to the worm gear. The common tangent between these two shafts intersects the pitch line of the worm gear shaft. This is the basis of transfer speed.


editor by CX 2023-06-13
China Tractor Pto Gearbox Gear Box for Machinery Application Durable Speed Increaser Manufacturers Suppliers Power Take Offs 540 or 1000 Rpm Tractor Pto Gearbox worm gearbox efficiency
Item Description
Tractor Pto Gearbox Equipment Box for Equipment Application Tough Velocity Increaser Companies Suppliers Electricity Take Offs 540 or 1000 rpm Tractor Pto Gearbox
|
/ Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Three-Ring |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Torque Arm Type |
| Step: | Stepless |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
|
/ Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction, Speed Increase |
| Layout: | Three-Ring |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Torque Arm Type |
| Step: | Stepless |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
Worm gear reducer gearbox
A worm gear reducer gearbox is a gear reducer gearbox that uses a worm gear train to reduce the required force. Unlike traditional gear reducer gearboxes, these units are small and require low horsepower ratings. This reduces their efficiency, but their low cost and compact design help make up for this shortcoming. However, these gear reducer gearboxes have some drawbacks, including their tendency to lock up when reversing.
high efficiency
High-efficiency worm reducer gearboxes are ideal for applications where high performance, repeatability, and accuracy are critical. It consists of an input hypoid gear and an output hypoid bevel gear. The input worm rotates perpendicular to the output worm, so for every revolution of the input worm, the output gear makes one revolution. This arrangement reduces friction (another source of energy loss) in a high-efficiency worm gear to at least two arc minutes.
Compared with worm gear reducer gearboxes, hypoid gearmotors offer several advantages, including lower operating costs and higher efficiency. For example, hypoid gear motors can transmit more torque even at high reduction ratios. Also, they are more efficient than worm gear reducer gearboxes, which means they can produce the same output with a smaller motor.
In recent years, the efficiency of worm gear reducer gearboxes has been dramatically improved. Manufacturers have made great strides in materials, design, and manufacturing. New designs, including dual-enveloping worm gear reducer gearboxes, increase efficiency by 3 to 8 percent. These improvements were made possible through countless hours of testing and development. Worm gear reducer gearboxes also offer lower initial costs and higher overload capability than competing systems.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes are popular because they provide maximum reduction in a small package. Their compact size makes them ideal for low to medium-horsepower applications and they are reticent. They also offer higher torque output and better shock load tolerance. Finally, they are an economical option to reduce the device’s power requirements.
low noise
Low-noise worm gear reducer gearboxes are designed to reduce noise in industrial applications. This type of reducer gearbox uses fewer bearings and can work in various mounting positions. Typically, a worm reducer gearbox is a single-stage unit with only one shaft and one gear. Since there is only one gear, the noise level of the worm gear reducer gearbox will be lower than other types.
A worm gear reducer gearbox can be integrated into the electric power steering system to reduce noise. Worm reducer gearboxes can be made and from many different materials. The following three-stage process will explain the components of a low-noise worm reducer gearbox.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes can be mounted at a 90-degree angle to the input worm shaft and are available with various types of hollow or solid output shafts. These reducer gearboxes are especially beneficial for applications where noise reduction is essential. They also have fewer parts and are smaller than other types of reducer gearboxes, making them easier to install.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes are available from various manufacturers. Due to their widespread availability, gear manufacturers maintain extensive inventories of these reducer gearboxes. The worm gear ratio is standard, and the size of the worm gear reducer gearbox is universal. Also, worm gear reducer gearboxes do not need to be sized for a specific purpose, unlike other load interruptions.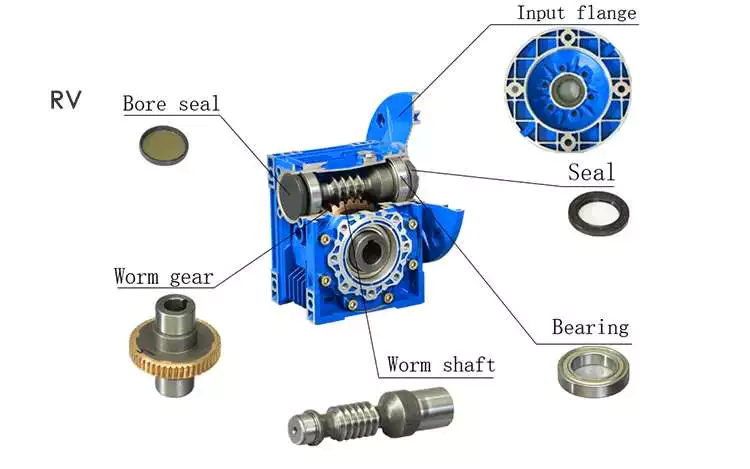
A worm gear reducer gearbox is a transmission mechanism with a compact structure, large transmission ratio, and self-locking function under certain conditions. The worm gear reducer gearbox series products are designed with American technology and have the characteristics of stable transmission, strong bearing capacity, low noise, and compact structure. In addition, these products can provide a wide range of power supplies. However, these worm reducer gearboxes are prone to leaks, usually caused by design flaws.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes are available in single-stage and double-stage. The first type consists of an oil tank that houses the worm gear and bearings. The second type uses a worm gear with a sleeve for the first worm gear.
When choosing a gear reducer gearbox, it is essential to choose a high-quality unit. Improper gear selection can cause rapid wear of the worm gear. While worm gear reducer gearboxes are generally durable, their degree of wear depends on the selection and operating conditions. For example, overuse, improper assembly, or working in extreme conditions can lead to rapid wear.
Worm reducer gearboxes reduce speed and torque. Worm gears can be used to reduce the speed of rotating machines or inertial systems. Worm gears are a type of bevel gear, and their meshing surfaces have great sliding force. Because of this, worm gears can carry more weight than spur gears. They are also harder to manufacture. However, the high-quality design of the worm gear makes it an excellent choice for applications requiring high torque and high-speed rotation.
Worm gears can be manufactured using three types of gears. For large reduction ratios, the input and output gears are irreversible. However, the worm reducer gearbox can be constructed with multiple helices. The multi-start worm drive also minimizes braking effects.
Self-locking function
The worm reducer gearbox is self-locking to prevent the load from being driven back to the ground. The self-locking function is achieved by a worm that meshes with the rack and pinion. When the load reaches the highest position, the reverse signal is disabled. The non-locking subsystem back-drives the load to its original position, while the self-locking subsystem remains in its uppermost position.
The self-locking function of the worm reducer gearbox is a valuable mechanical feature. It helps prevent backing and saves the cost of the braking system. Additionally, self-locking worm gears can be used to lift and hold loads.
The self-locking worm gear reducer gearbox prevents the drive shaft from driving backward. It works with the axial force of the worm gear. A worm reducer gearbox with a self-locking function is a very efficient machine tool.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes can be made with two or four teeth. Single-ended worms have a single-tooth design, while double-ended worms have two threads on the cylindrical gear. A multi-boot worm can have up to four boots. Worm reducer gearboxes can use a variety of gear ratios, but the main advantage is their compact design. It has a larger load capacity than a cross-shaft helical gear mechanism.
The self-locking function of the worm reducer gearbox can also be used for gear sets that are not necessarily parallel to the shaft. It also prevents backward travel and allows forward travel. The self-locking function is achieved by a ratchet cam arranged around the gear member. It also enables selective coupling and decoupling between gear members.
high gear ratio
Worm reducer gearboxes are an easy and inexpensive way to increase gear ratios. These units consist of two worm gears – an input worm gear and an output worm gear. The input worm rotates perpendicular to the output worm gear, which also rotates perpendicular to itself. For example, a 5:1 worm gearbox requires 5 revolutions per worm gear, while a 60:1 worm gearbox requires 60 revolutions. However, this arrangement is prone to inefficiency since the worm gear experiences only sliding friction, not rolling friction.
High-reduction applications require many input revolutions to rotate the output gear. Conversely, low input speed applications suffer from the same friction issues, albeit with a different amount of friction. Worms that spin at low speeds require more energy to maintain their movement. Worm reducer gearboxes can be used in many types of systems, but only some are suitable for high-speed applications.
Worm gears are challenging to produce, but the envelope design is the best choice for applications requiring high precision, high efficiency, and minimal backlash. Envelope design involves modifying gear teeth and worm threads to improve surface contact. However, this type of worm gear is more expensive to manufacture.
Worm gear motors have lower initial meshing ratios than hypoid gear motors, which allows the use of smaller motors. So a 1 hp worm motor can achieve the same output as a 1/2 hp motor. A study by Agknx compared two different types of geared motors, comparing their power, torque, and gear ratio. The results show that the 1/2 HP hypoid gear motor is more efficient than the worm gear motor despite the same output.
Another advantage of the worm gear reducer gearbox is the low initial cost and high efficiency. It offers high ratios and high torque in a small package, making it ideal for low to medium-horsepower applications. Worm gear reducer gearboxes are also more shock-resistant.

editor by CX 2023-04-18
China Premium Quality Wp Series Speed Reducer Worm Gearbox for Agricultural Machinery worm gearbox exploded view
Solution Description
Solution Description
Product Parameters
Packaging & Shipping
Business Profile
|
US $100-500 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Gear Shape: | Conical – Cylindrical Gear |
| Step: | Single-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 60/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
|
US $100-500 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Gear Shape: | Conical – Cylindrical Gear |
| Step: | Single-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 60/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
Advantages and disadvantages of worm gear reducer gearbox
If you are looking for a worm gear reducer gearbox, you have come to the right place. This article will cover the pros and cons of worm gear reducer gearboxes and discuss the different types available. You will learn about multi-head worm gear reducer gearboxes, hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes as well as hypoid gear sets and motors.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearbox
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes are used to connect two or more rotating parts. They are available in single-axis and dual-axis versions and can be connected to various motor types. They can also have different ratios. The ratios of these gear reducer gearboxes depend on the quality of the bearings and assembly process.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes are made of bronze worm gears and cast iron hubs. The gears are lubricated with synthetic oil. They are lightweight and durable. They can be installed in various engine housings. Additionally, these gear reducer gearboxes are available in a variety of sizes. The range includes 31.5, 40, 50, 63, and 75mm models. Other sizes are available upon request.
In addition to worm gear reducer gearboxes, there are also helical gear reducer gearboxes. These reducer gearboxes can achieve very low output speeds. They are also suitable for all-around installations. In addition, the advantage of a multi-stage reducer gearbox is that it is more efficient than a single-stage gear reducer gearbox. They also feature low noise, low vibration, and low energy consumption.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes are generally less expensive and last longer. They are also a suitable replacement for solid shaft gearboxes for machines that require high torque without compromising strength. Typical gear arrangements include worm, spur, helical and bevel gears. Gear ratio is the ratio of input torque to output torque.
Multi-head worm gear reducer gearbox
The multi-head worm gear reducer gearbox is used to reduce the speed of the machine. It uses friction to hold the worm in place while transmitting power. These gears can also be called ground worms and hardened worm gears. They are useful in conveying systems and most engineering applications.
Multiple worm reducer gearboxes have a large number of gear ratios. These gear designs have a central cross-section that forms the front and rear boundaries of the worm gear. This design is a better choice than other worm gears because it is less prone to wear and can be used with a variety of motors and other electronics.
Adjustable multi-head worm gear reducer gearbox to reduce axial play. Usually, the backlash on the left and right sides of the worm is the same. However, if you need less backlash, you can buy a double lead worm gear. This design is ideal for precision applications requiring small clearances. The lead of the opposing teeth of the double worm gear is different from the right side, so the backlash can be adjusted without adjusting the center distance between the worm gears.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes are available from a variety of manufacturers. Many gear manufacturers stock these gears. Since the gear ratios are standardized, there is no need to adjust the height, diameter, or length of the shaft. Worm gears have fewer moving parts, which means they require less maintenance.
Hypoid Gear Set
Worm gears are the most common type of gear. While these gears are great for high-to-low ratios, hypoid gear sets are much more efficient in all ratios. This difference is due to higher torque density, better geometry and materials, and the way hypoid gears transmit force differently than worm gears.
Hypoid gear sets have curved helical teeth. This results in smooth gear meshing and little noise. This is because the hypoid gears start to slowly contact each other, but the contact progresses smoothly from tooth to tooth. This reduces friction and wears, thereby increasing the efficiency of the machine.
The main advantages of hypoid gears over worm gears are higher torque capacity and lower noise levels. Although their upfront cost may be higher, hypoid gears are more efficient than worm gears. They are able to handle higher initial inertia loads and can deliver more torque with a smaller motor. This saves money in the long run.
Another advantage of hypoid gears is the lower operating temperature. They also do not require oil lubrication or ventilation holes, reducing maintenance requirements. The hypoid gear set is maintenance-free, and the grease on the hypoid gear set lasts for decades.
Hypoid gear motor
A hypoid gear motor is a good choice for a worm gear reducer gearbox as it allows for a smaller motor and more efficient energy transfer. In fact, a 1 hp motor driving a hypoid reducer gearbox can provide the same output as a 1/2 hp motor driving a worm reducer gearbox. A study by Agknx compared two gear reduction methods and determined that a hypoid gear motor produces more torque and power than a worm reducer gearbox when using a fixed reduction ratio of 60:1. The study also showed that the 1/2 HP hypoid gear motor is more energy efficient and reduces electricity bills.
Worm reducer gearboxes run hotter than hypoid gears, and the added heat can shorten their lifespan. This can cause components to wear out faster, and the motor may require more frequent oil changes. In addition, hypoid gear motors are more expensive to manufacture.
Compared to worm gears, hypoid gears offer higher efficiency and lower operating noise. However, they require additional processing techniques. They are made of bronze, a softer metal capable of absorbing heavy shock loads. Worm drives require work hardening and are less durable. Operating noise is reduced by up to 30%, and hypoid gears are less prone to breakage than bevel gears.
Hypoid gear motors are prized for their efficiency and are used in applications requiring lower torque. A unique hypoid tooth profile reduces friction. In addition, hypoid gear motors are ideal for applications where space is limited. These geared motors are often used with pulleys and levers.
R series worm gear reducer gearbox
R series worm gear reducer gearboxes have a variety of characteristics that make them ideal for different applications. Its high rigidity cast iron housing and rigid side gears are designed for smooth drive and low noise. It also features high load capacity and long service life. Additionally, it can be assembled into many different configurations as required.
High efficiency, large output torque and good use efficiency. It comes in four basic models ranging from 0.12KW to 200KW. It can be matched with right angle bevel gearbox to provide large speed ratio and high torque. This combination is also suitable for low output and high torque.
AGKNX Electric Worm Gear reducer gearbox
AGKNX Electric worm gear reducer gearboxes are available with NEMA C-face mounting flanges for a variety of motors. These reducer gearboxes feature double lip oil seals, an aluminum alloy housing, and two bearings on the input and output shafts. These reducer gearboxes are rust-proof and have epoxy paint on the inside. They are available in a variety of ratios, from 7.5:1 to 100:1.
Worm reducer gearboxes are one of the most cost-effective and compact gears. These reducer gearboxes increase output torque while reducing input speed. AGKNX Electric’s worm gear reducer gearboxes are pre-installed with Mobil SHC634 Synthetic Gear Oil. These reducer gearboxes have an internal oil gallery guide to protect the shaft. They also have a one-piece cast iron housing.
AGKNX Electric Corporation is the leading independent distributor of electric motors in the United States. They have eight strategically located warehouses, enabling them to ship most orders on the same day. They offer motors of various sizes up to 20,000 hp. They also offer a variety of motor controls and variable speed drives.

editor by czh 2023-02-04
China best Wp Series Worm Reducer for Packaging Machinery and Cable Equipment with Best Sales
Product Description
Wpa Wps Low Speed Worm Gear Speed Reducer
Structure Feature
1. Widely used in light industry, good resistance to wearing, with high precision in dimensions, lower noise, advanced centric running castings
2. The housing is of strong hardness, compact structure
3. Stable transmission, low vibration, large ratio, canbe matched with various machines
Product Structural Drawing
Model Description
Total 60 families and more than 20,000types with different models, ratios, connections and installations can be selected to meet requirements of customers.
View Of Item
WPA worm gearbox
WPS worm gearbox
Notice of installation
1. The base-plate must be plane and stoutness, and the base-plate must be screwed down and shockproof
2. The connecting shaft of prime mover, gearbox and operation device must be coaxial installatios
3. The diameter tolerance zone of input and output shaft is H6, the holes of fittings(such as couplings, belt-pulley, sprocket wheel and so on) must properly mate the shaft, which prevents bearing from breakage because of over-loose mate
4. Drivers such as sprocket wheel and gear must be fitted close to bearings in order to reduce bending stress of hanging shaft
5. White assembling motor of WPD reducer, it is necessary that proper amount of butter applies to the worm shaft input hole and keyway, avoiding assembling too tightly and rusting after using for a long time
6. When ordering or using all kinds of WPD type, if the motor weight is bigger than the common, supporting set is required
Notice of usage
1. Before using, please check carefully whether the gearbox model, distance, ratio, input connecting method, output shaft structure, input and output shaft direction and revolving direction accord with requirement
2. According to the requirement of selecting lubricant oil in the product manual, please fill proper category and brand lubricant. And then screw on the vent-plug; Unlock the small cone-plug of vent-plug. Only after doing these, reducer is already for starting up running. The proper brand and adequate lubricant oil is required, replacing oil in time conforming to the request of product manual is also necessary, especially after using first 100 hours, it is required refilling new oil
3. When abnormal circumstances occur, please stop and check reducer per solutions and reasons for faults of reducer (allowable highest oil temperature is 95, under this temperature limit, if oil temperature no more goes up, please let reducer continue running)
COMPANY OVERVIEW
About Greensky Power
- History: Greensky Power Co.,ltd was founded in Los Angeles in 2008 and has focused on manufacturing and supplying motor and gearbox for 8 years since 2008.
- Market: Greensky Power has customers in 30 different countries. Germany, Austria, Japan, USA and Middle-East are our main market.
- Honors:Greensky Power is member of a council in ZHangZhoug Solar Association which is the biggest renewable energy association in Southeast of China.
Greensky’s Advantage
|
Price |
Competitive & Reasonable. Our mission is to “Greening the World”. Distributing massively in a cheap price is our strategy. We want more and more people are using high effeciency motor and gearbox. |
|
Quality |
Quality control is done by 4 processes: Manufacturer Control + Material Control + Production Control + Finished Goods Control. |
|
Delivery |
100% on-time delivery Guaranteed |
|
Evaluation |
100% Customer Satisfaction Guaranteed |
|
Services |
English, German, Japanese and Chinese sales representatives are available for One-stop full services. |
|
Business type |
Manufacture & Trading & EPC. Greensky Power has subsidiary company producing solar panels which makes our price very competitive. At same time, Greensky Power has a subsidiary EPC company which can give professional technical support for complicated technical questions. |
|
Experience |
Our products have been sold to strict clients in Germany and Japan. They are all satisfied with our products. Delivering quality products and convenient communication service are our goal. |
On the site you can find a range of products including worm gearbox, DC gear motor,AC gear motor, and their relevant components.
FAQ
1 Q:What infomation should I tell you to confirm the worm gearbox?
A: Model/Size B:Ratio and output torque C:Power and flange type D:Order quantity.
2 Q: What if I don’t know which worm gearbox need?
A:Don’t worry, Send as much information as you can, our team will help you find the right 1 you are looking for.
3 Q:How long should I wait for the feedback after I send the enquiry?
A: Within 12 hours.
4 Q:What is your warrenty period for worm gearbox?
A:We offer 1 year warrenty since the vessel departure date left China.
5 Q:What industries are your worm gearbox being used?
A:Our worm gearbox are widely used in the areas of household appliances and light industry,etc.
6. Q:How to delivery:
A: By sea – Buyer appoint forwarder, or our sales team find suitable forwarder for buyers.
By air – Buyer offer collect express account, or our sales team find suitable express for buyers. (Mostly for sample)
Others – We arrange to delivery goods to some place in China appointed by buyers.
7. When you place an order, our team will confirm with you about color, package,method of payment and delivery, then a sales contract will be sent to you to confirm.
If you have any other questions, please feel free to contact us.
Screw Shaft Types
A screw shaft is a cylindrical part that turns. Depending on its size, it is able to drive many different types of devices. The following information outlines the different types of screws, including their sizes, material, function, and applications. To help you select the right screw shaft, consider the following factors:
Size
A screw can come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from a quarter to a quarter-inch in diameter. A screw is a cylindrical shaft with an inclined plane wrapped around it, and its main function is to fasten objects together by translating torque into a linear force. This article will discuss the dimensions of screws and how to determine the size of a screw. It is important to note that screw sizes can be large and small depending on the purpose.
The diameter of a screw is the diameter of its shaft, and it must match the inner diameter of its nuts and washers. Screws of a certain diameter are also called machine screws, and they can be larger or smaller. Screw diameters are measured on the shaft underneath the screw head. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standardized screw diameters in 3/50-inch to 16 (3/8-inch) inches, and more recently, sizes were added in U.S. fractions of an inch. While shaft and head diameters are standardized, screw length may vary from job to job.
In the case of the 2.3-mm screw group, the construct strength was not improved by the 1.2-mm group. The smaller screw size did not increase the strength of the construct. Further, ABS material did not improve the construct strength. Thus, the size of screw shaft is an important consideration in model design. And remember that the more complex your model is, the larger it will be. A screw of a given size will have a similar failure rate as a screw of a different diameter.
Although different screw sizes are widely used, the differences in screw size were not statistically significant. Although there are some limitations, screws of different sizes are generally sufficient for fixation of a metacarpal shaft fracture. However, further clinical studies are needed to compare screw sizes for fracture union rates. So, if you are unsure of what size of screw shaft you need for your case, make sure to check the metric chart and ensure you use the right one.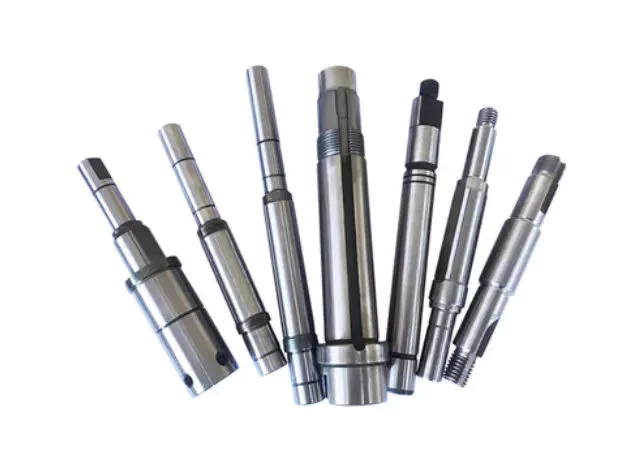
Material
The material of a screw shaft plays an important role in the overall performance of a screw. Axial and central forces act to apply torque to the screw, while external forces, such as friction, exert a bending moment. The torsional moments are reflected in the torque, and this causes the screw to rotate at a higher rate than necessary. To ensure the longevity of the screw, the material of the screw shaft should be able to handle the bending moment, while the diameter of the shaft should be small enough to avoid causing damage.
Screws are made from different metals, such as steel, brass, titanium, and bronze. Manufacturers often apply a top coating of chromium, brass, or zinc to improve corrosion resistance. Screws made of aluminum are not durable and are prone to rusting due to exposure to weather conditions. The majority of screw shafts are self-locking. They are suited for many applications, including threaded fasteners, C-clamps, and vises.
Screws that are fabricated with conical sections typically feature reduced open cross-sectional areas at the discharge point. This is a key design parameter of conical screw shafts. In fact, reductions of up to 72% are common across a variety of applications. If the screw is designed to have a hard-iron hanger bearing, it must be hardened. If the screw shaft is not hardened, it will require an additional lubricant.
Another consideration is the threads. Screw shafts are typically made of high-precision threads and ridges. These are manufactured on lathes and CNC machines. Different shapes require different materials. Materials for the screw shaft vary. There are many different sizes and shapes available, and each 1 has its own application. In addition to helical and conical screw shafts, different materials are also available. When choosing material, the best 1 depends on the application.
The life of the screw depends on its size, load, and design. In general, the material of the screw shaft, nut body, and balls and rollers determine its fatigue life. This affects the overall life of the screw. To determine whether a specific screw has a longer or shorter life, the manufacturer must consider these factors, as well as the application requirements. The material should be clean and free of imperfections. It should be smooth and free of cracks or flaking, which may result in premature failure.
Function
The function of a screw shaft is to facilitate the rotation of a screw. Screws have several thread forms, including single-start, double-start and multi-start. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article we’ll explore each of them in detail. The function of a screw shaft can vary based on its design, but the following are common types. Here are some examples of screw shaft types and their purposes.
The screw’s torque enables it to lift objects. It can be used in conjunction with a bolt and nut to lift a load. Screws are also used to secure objects together. You can use them in screw presses, vises, and screw jacks. But their primary function is to hold objects together. Listed below are some of their main functions. When used to lift heavy loads, they can provide the required force to secure an object.
Screws can be classified into 2 types: square and round. Square threads are more efficient than round ones because they apply 0deg of angle to the nut. Square threads are also stronger than round threads and are often used in high-load applications. They’re generally cheaper to manufacture and are more difficult to break. And unlike square threads, which have a 0deg thread angle, these threads can’t be broken easily with a screwdriver.
A screw’s head is made of a series of spiral-like structures that extend from a cylindrical part to a tip. This portion of the screw is called the shank and is made of the smallest area. The shank is the portion that applies more force to the object. As the shaft extends from the head, it becomes thinner and narrow, forming a pointed tip. The head is the most important part of the screw, so it needs to be strong to perform its function.
The diameter of the screw shaft is measured in millimeters. The M8 screw has a thread pitch of 1.25 mm. Generally, the size of the screw shaft is indicated by the major and minor diameter. These dimensions are appended with a multiplication sign (M8x1).
Applications
The design of screws, including their size and shape, determines their critical rotating speeds. These speeds depend on the threaded part of the screw, the helix angle, and the geometry of the contact surfaces. When applied to a screw, these limits are referred to as “permissible speed limits.” These maximum speeds are meant for short periods of time and optimized running conditions. Continuous operation at these speeds can reduce the calculated life of a nut mechanism.
The main materials used to manufacture screws and screw shafts include steel, stainless steel, titanium, bronze, and brass. Screws may be coated for corrosion resistance, or they may be made of aluminium. Some materials can be threaded, including Teflon and nylon. Screw threads can even be molded into glass or porcelain. For the most part, steel and stainless steel are the most common materials for screw shafts. Depending on the purpose, a screw will be made of a material that is suitable for the application.
In addition to being used in fasteners, screw shafts are used in micrometers, drillers, conveyor belts, and helicopter blades. There are numerous applications of screw shafts, from weighing scales to measuring lengths. If you’re in the market for a screw, make sure to check out these applications. You’ll be happy you did! They can help you get the job done faster. So, don’t delay your next project.
If you’re interested in learning about screw sizing, then it’s important to know the axial and moment loads that your screws will experience. By following the laws of mechanics and knowing the load you can calculate the nominal life of your screw. You can also consider the effect of misalignment, uneven loading, and shocks on your screw. These will all affect the life of your screw. Then, you can select the right screw.


China manufacturer OEM Foundry Customized Steel Worm Shaft/Screw for Machinery near me factory
Product Description
China Supplier Forging And Machining Wheel Spline Hub For Machinery
Brass and special material Machined Parts main usage range is:
1) Medical equipment parts
2) Electric/electronic equipment parts
3) Other machined parts
Our Capacity is:
1) Material: Steel, copper, brass, aluminum, staineless steel, Very special Material
2) Equipment: CNC lathe, CNC milling machine, CNC high-speed engraving machine
3) Precision machining capability:
A) Machine’s rotating speed: 5, 000rpm – 30, 000rpm
B) Machining precision tolerance: 0.005 – 0.01mm
C) Roughness value: < Ra 0.2
D) Minimum cutting tool: 0.1mm
4) Strick inspection instrument and ISO9001 control
Our advantages:
1. We have been engaged in machinery components industry for 30 years supplying casting parts, forging parts, stamping parts, machining parts and plastic injection parts with good quality and competitive price. We have the advanced equipments for foundry, 66 sets of metal cutting machineries, 35 sets CNC, and 2 sets of machining centers.
2. We have lots of experience in export, All of our products are exported to Europe, America, Japan and Middle-east. The sale is enlarging smoothly, and the funds are withdrawed rapidly.
3. We can supply all kinds of die casting.
4. OEM /Design/Buyer label survice offered
5. We gained quality certificate ISO9001 in 1995, and have full sets of inspection instruments.
6. High quality, Low price
7. Continuous innovation of products assured by our strong R&D team.
|
Product Name |
Customized Stainless Steel/Brass/Aluminum CNC Machining Parts/Hardware |
|
Material |
Stainless steel ASTM 316L |
|
Equipment |
CNC Lathe,Turn-milling CZPT machine,Drilling machine,CMM,stamping |
|
Processing |
Turning, Milling,welding,chrome plated |
|
Tolerance |
+/-0.003mm |
|
Surface Finish |
Polishing, anodize,zinc plating, nickel plating, chrome plating, powder coating, e-coating, electro-polishing, laser marking.etc. |
|
Certificate |
ISO9001-2008 |
|
Design |
As per customer’s drawing or design for customers |
Screw Sizes and Their Uses
Screws have different sizes and features. This article will discuss screw sizes and their uses. There are 2 main types: right-handed and left-handed screw shafts. Each screw features a point that drills into the object. Flat tipped screws, on the other hand, need a pre-drilled hole. These screw sizes are determined by the major and minor diameters. To determine which size of screw you need, measure the diameter of the hole and the screw bolt’s thread depth.
The major diameter of a screw shaft
The major diameter of a screw shaft is the distance from the outer edge of the thread on 1 side to the tip of the other. The minor diameter is the inner smooth part of the screw shaft. The major diameter of a screw is typically between 2 and 16 inches. A screw with a pointy tip has a smaller major diameter than 1 without. In addition, a screw with a larger major diameter will have a wider head and drive.
The thread of a screw is usually characterized by its pitch and angle of engagement. The pitch is the angle formed by the helix of a thread, while the crest forms the surface of the thread corresponding to the major diameter of the screw. The pitch angle is the angle between the gear axis and the pitch surface. Screws without self-locking threads have multiple starts, or helical threads.
The pitch is a crucial component of a screw’s threading system. Pitch is the distance from a given thread point to the corresponding point of the next thread on the same shaft. The pitch line is 1 element of pitch diameter. The pitch line, or lead, is a crucial dimension for the thread of a screw, as it controls the amount of thread that will advance during a single turn.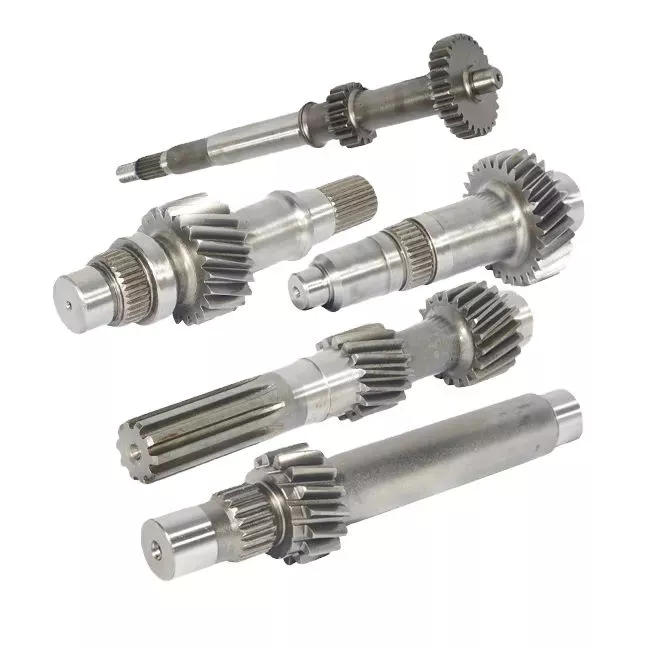
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft
When choosing the appropriate screw, it is important to know its pitch diameter and pitch line. The pitch line designates the distance between adjacent thread sides. The pitch diameter is also known as the mean area of the screw shaft. Both of these dimensions are important when choosing the correct screw. A screw with a pitch of 1/8 will have a mechanical advantage of 6.3. For more information, consult an application engineer at Roton.
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft is measured as the distance between the crest and the root of the thread. Threads that are too long or too short will not fit together in an assembly. To measure pitch, use a measuring tool with a metric scale. If the pitch is too small, it will cause the screw to loosen or get stuck. Increasing the pitch will prevent this problem. As a result, screw diameter is critical.
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft is measured from the crest of 1 thread to the corresponding point on the next thread. Measurement is made from 1 thread to another, which is then measured using the pitch. Alternatively, the pitch diameter can be approximated by averaging the major and minor diameters. In most cases, the pitch diameter of a screw shaft is equal to the difference between the two.
The thread depth of a screw shaft
Often referred to as the major diameter, the thread depth is the outermost diameter of the screw. To measure the thread depth of a screw, use a steel rule, micrometer, or caliper. In general, the first number in the thread designation indicates the major diameter of the thread. If a section of the screw is worn, the thread depth will be smaller, and vice versa. Therefore, it is good practice to measure the section of the screw that receives the least amount of use.
In screw manufacturing, the thread depth is measured from the crest of the screw to the root. The pitch diameter is halfway between the major and minor diameters. The lead diameter represents the amount of linear distance traveled in 1 revolution. As the lead increases, the load capacity decreases. This measurement is primarily used in the construction of screws. However, it should not be used for precision machines. The thread depth of a screw shaft is essential for achieving accurate screw installation.
To measure the thread depth of a screw shaft, the manufacturer must first determine how much material the thread is exposed to. If the thread is exposed to side loads, it can cause the nut to wedge. Because the nut will be side loaded, its thread flanks will contact the nut. The less clearance between the nut and the screw, the lower the clearance between the nut and the screw. However, if the thread is centralized, there is no risk of the nut wedgeing.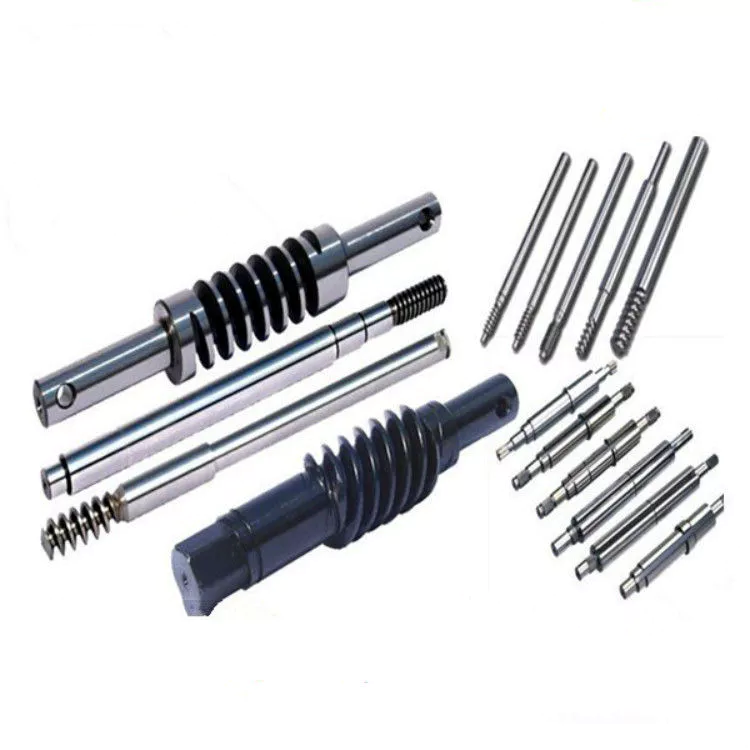
The lead of a screw shaft
Pitch and lead are 2 measurements of a screw’s linear distance per turn. They’re often used interchangeably, but their definitions are not the same. The difference between them lies in the axial distance between adjacent threads. For single-start screws, the pitch is equal to the lead, while the lead of a multi-start screw is greater than the pitch. This difference is often referred to as backlash.
There are 2 ways to calculate the pitch and lead of a screw. For single-start screws, the lead and pitch are equal. Multiple-start screws, on the other hand, have multiple starts. The pitch of a multiple-start screw is the same as its lead, but with 2 or more threads running the length of the screw shaft. A square-thread screw is a better choice in applications requiring high load-bearing capacity and minimal friction losses.
The PV curve defines the safe operating limits of lead screw assemblies. It describes the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. As the load increases, the lead screw assembly must slow down in order to prevent irreversible damage from frictional heat. Furthermore, a lead screw assembly with a polymer nut must reduce rpm as the load increases. The more speed, the lower the load capacity. But, the PV factor must be below the maximum allowed value of the material used to make the screw shaft.
The thread angle of a screw shaft
The angle between the axes of a thread and the helix of a thread is called the thread angle. A unified thread has a 60-degree angle in all directions. Screws can have either a tapped hole or a captive screw. The screw pitch is measured in millimeters (mm) and is usually equal to the screw major diameter. In most cases, the thread angle will be equal to 60-degrees.
Screws with different angles have various degrees of thread. Originally, this was a problem because of the inconsistency in the threading. However, Sellers’s thread was easier to manufacture and was soon adopted as a standard throughout the United States. The United States government began to adopt this thread standard in the mid-1800s, and several influential corporations in the railroad industry endorsed it. The resulting standard is called the United States Standard thread, and it became part of the ASA’s Vol. 1 publication.
There are 2 types of screw threads: coarse and fine. The latter is easier to tighten and achieves tension at lower torques. On the other hand, the coarse thread is deeper than the fine one, making it easier to apply torque to the screw. The thread angle of a screw shaft will vary from bolt to bolt, but they will both fit in the same screw. This makes it easier to select the correct screw.
The tapped hole (or nut) into which the screw fits
A screw can be re-threaded without having to replace it altogether. The process is different than that of a standard bolt, because it requires threading and tapping. The size of a screw is typically specified by its major and minor diameters, which is the inside distance between threads. The thread pitch, which is the distance between each thread, is also specified. Thread pitch is often expressed in threads per inch.
Screws and bolts have different thread pitches. A coarse thread has fewer threads per inch and a longer distance between threads. It is therefore larger in diameter and longer than the material it is screwed into. A coarse thread is often designated with an “A” or “B” letter. The latter is generally used in smaller-scale metalworking applications. The class of threading is called a “threaded hole” and is designated by a letter.
A tapped hole is often a complication. There is a wide range of variations between the sizes of threaded holes and nut threads, so the tapped hole is a critical dimension in many applications. However, even if you choose a threaded screw that meets the requisite tolerance, there may be a mismatch in the thread pitch. This can prevent the screw from freely rotating.


