Product Description
TXR Series Sleeve Type Single Nut Ball Screw (C5/Ct7/Ct10)
| Table of Shaft dia. and Lead combination for Rolled Ball Screw | ||||||||||||||||
| Lead (mm) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 30 | ||
| Shaft dia (mm) | 4 | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 5 | / | |||||||||||||||
| 6 | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 8 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||
| 10 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||
| 12 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 14 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||
Accuracy Class & Axial Clearance
Accuracy grade of TXR series(sleeve type single nut ball screw)are based on C5,Ct7 and Ct10(JIS B 1192-3). According to accuracy grade, Axial play 0.005(Preload :C5),0.02(Ct7) and 0.05mm or less(Ct10).
Material & Surface Hardness
TXR series (sleeve type single nut ball screw) of screw shaft screw material S55C (induction hardening), nut material SCM415H (carburizing and hardening), the surface hardness of the ball screw part is HRC58 or higher.
Shaft End Shape
The shape of the shaft end of the TXR series (sleeve type single nut ball screws) has been standardized.
Application:
1. Medical industry
2.Lithium battery industry
3.Solar photovoltaic industry
4. Semi conductor Industry
5. General industry machinery
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment
9. 3C industry etc
Technical Drawing
Specification List
FACTORY DETAILED PROCESSING PHOTOS
HIGH QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
FAQ
1. Why choose CHINAMFG China?
Over the past 14 years, CHINAMFG has always insisted that “products and services” start from Japanese industry standards,taking ZheJiang standards as the bottom line, actively invest in the development of new transmission components and self-experiment and test. With the service tenet of “exceeding customer expectations”, establish a “trusted” partnership.
2. What is your main products ?
We are a leading manufacturer and distributor of linear motion components in China. Especially miniature size of Ball Screws and Linear Actuators and linear motion guideways. Our brand “KGG” stands for ” Know-how,” ” Great Quality,” and ” Good value” and our factory is located in the most advanced city in China: ZheJiang with the best equipment and sophisticated technology, completely strict quality control system. Our aim is to supply world leader class linear motion components but with most reasonable price in the world.
3. How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
4. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
5. How can I get a sample to check the quality?
After confirmation of our quoted price, you can place the sample order. The sample will be started after you CHINAMFG back our detailed technical file.
6. What’s your payment terms?
Our payment terms is 30% deposit,balance 70% before shipment. /* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C7 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 4mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 3-Row |
| Nut Type: | Sleeve Type Single Nut |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
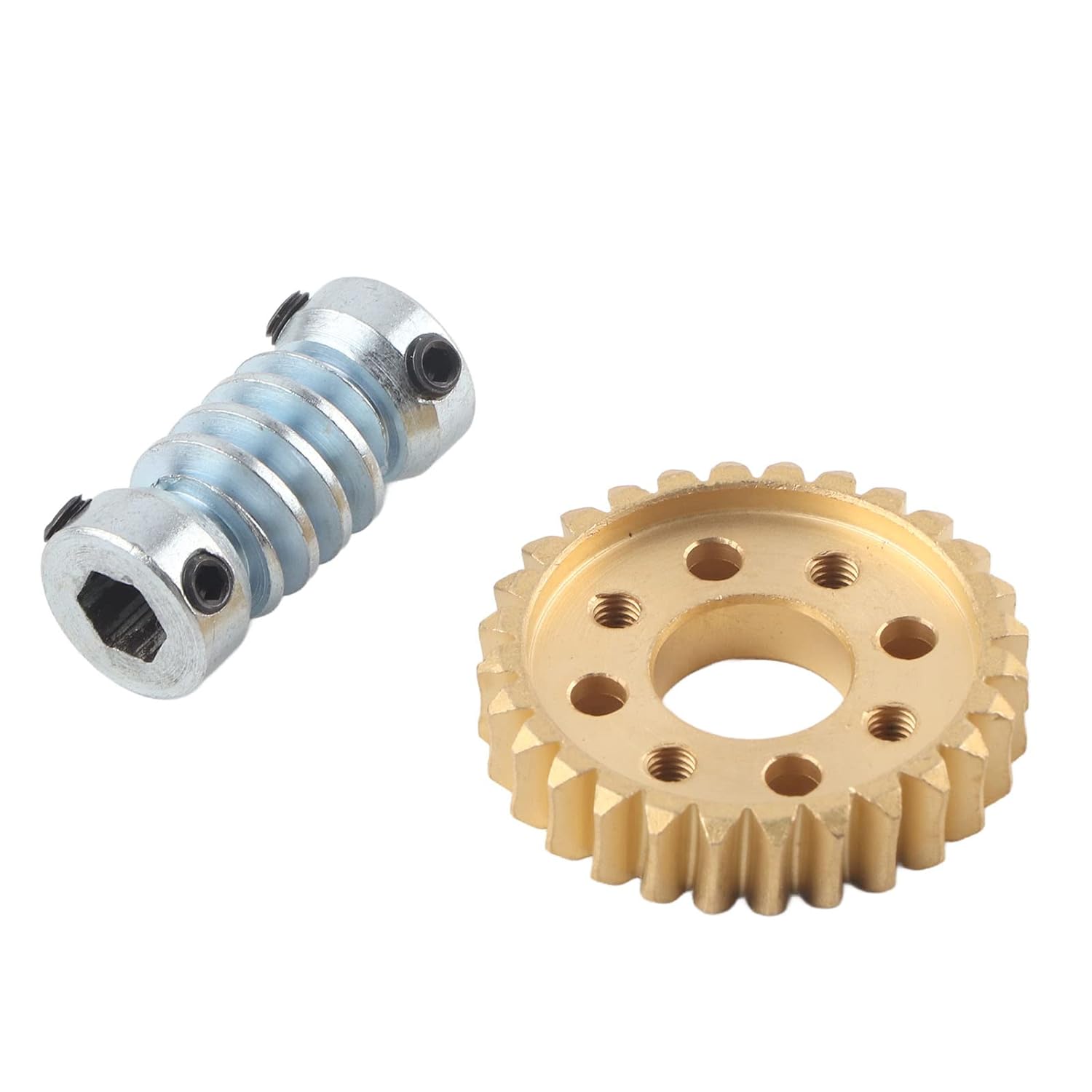

How do you properly lubricate a worm screw and gear assembly?
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of a worm screw and gear assembly. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, thereby extending the lifespan of the components. Here are the steps to properly lubricate a worm screw and gear assembly:
- Clean the Assembly: Before applying lubrication, ensure that the worm screw and gear assembly is free from dirt, debris, and old lubricant residues. Clean the surfaces using an appropriate cleaning agent or solvent, followed by a thorough drying process.
- Select the Right Lubricant: Choose a lubricant specifically designed for gear systems or worm screw applications. Consider factors such as viscosity, temperature range, load capacity, and compatibility with the materials used in the assembly. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or lubrication guidelines for the specific assembly to determine the suitable lubricant type and grade.
- Apply the Lubricant: Apply the lubricant to the contacting surfaces of the worm screw and gear assembly. Use an appropriate applicator, such as a brush, oil can, or grease gun, depending on the lubricant form (oil or grease) and the accessibility of the components. Ensure complete coverage of the gear teeth, worm screw threads, and other relevant surfaces. Pay attention to areas where the most significant friction and wear occur.
- Monitor the Lubricant Level: Check the lubricant level regularly to ensure an adequate supply. Depending on the application and operating conditions, lubricant consumption or degradation may occur over time. It is important to maintain the lubricant level within the recommended range to ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive wear or overheating.
- Periodic Lubrication Maintenance: Establish a lubrication maintenance schedule based on the operating conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect the assembly for signs of lubricant degradation, contamination, or insufficient lubrication. Replace the lubricant as needed and follow the recommended intervals for lubricant replenishment or reapplication.
- Consideration for Grease Lubrication: If using grease as the lubricant, it is important to choose a high-quality grease suitable for worm screw applications. Grease provides better adhesion to surfaces and tends to stay in place, offering longer-lasting lubrication compared to oil. However, excessive grease accumulation or over-greasing should be avoided, as it can lead to increased friction and inefficiency.
It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for lubrication specific to the worm screw and gear assembly. Different assemblies may have unique lubrication requirements based on their design, load capacity, operating conditions, and materials used. By properly lubricating the worm screw and gear assembly, you can ensure optimal performance, reduce wear, and extend the operational life of the components.
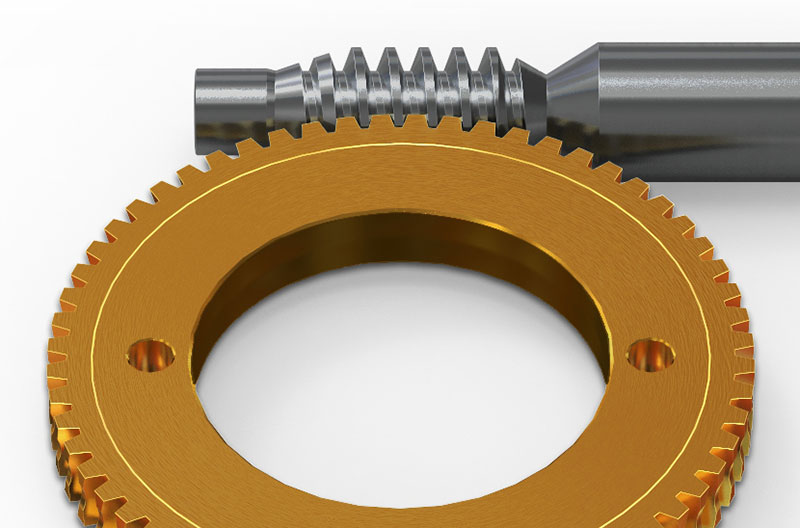
Are there different types of worm screws available?
Yes, there are different types of worm screws available to suit various applications and requirements. The design and characteristics of a worm screw can vary based on factors such as the material used, the thread geometry, the type of worm wheel, and the intended application. Here are some common types of worm screws:
- Standard Worm Screws: Standard worm screws are the most commonly used type and are available in a wide range of sizes and materials. They typically have a single-start thread and are made from materials such as steel, stainless steel, or bronze. Standard worm screws are suitable for general-purpose applications where moderate precision and load capacity are required.
- Double-Enveloping Worm Screws: Double-enveloping worm screws, also known as hourglass worm screws, have a unique thread profile that improves contact and load distribution between the worm screw and the worm wheel. This design offers enhanced torque transmission, higher efficiency, and increased load-carrying capacity compared to standard worm screws. Double-enveloping worm screws are often used in heavy-duty applications, such as gearboxes and high-load power transmission systems.
- Low-Lead Worm Screws: Low-lead worm screws have a smaller thread lead angle compared to standard worm screws. This design reduces the amount of sliding contact between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel, resulting in lower friction and improved efficiency. Low-lead worm screws are commonly used in applications where high efficiency and reduced heat generation are critical, such as in precision machinery and high-speed gear systems.
- Self-Locking Worm Screws: Self-locking worm screws are designed to have a high friction angle between the threads, making them capable of preventing reverse motion or backdriving. This self-locking feature eliminates the need for additional braking mechanisms or external locking devices in certain applications. Self-locking worm screws are commonly used in vertical lift systems, hoists, and other applications where holding the load position is essential.
- High-Precision Worm Screws: High-precision worm screws are manufactured to tighter tolerances and have improved accuracy compared to standard worm screws. They are designed to provide precise positioning and motion control in applications where high accuracy and repeatability are required. High-precision worm screws are often used in CNC machines, robotics, and other precision equipment.
- Customized Worm Screws: In addition to the standard types mentioned above, worm screws can also be customized to meet specific application requirements. Customized worm screws may involve variations in thread geometry, pitch, diameter, materials, or other parameters to suit unique applications or performance specifications.
The selection of the appropriate type of worm screw depends on factors such as the desired load capacity, efficiency requirements, backlash tolerance, positional accuracy, and environmental conditions. It is important to consult with manufacturers, engineers, or experts familiar with worm screw applications to determine the most suitable type for a specific application.
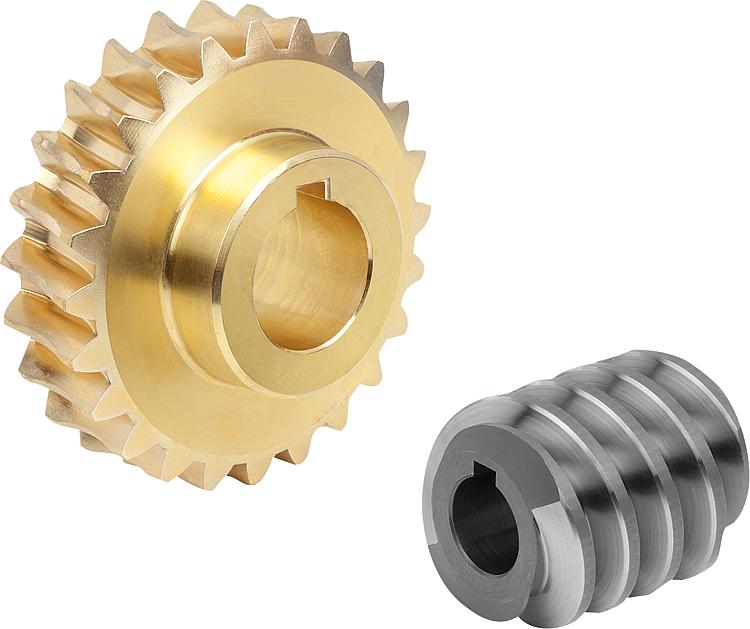

What are the advantages of using a worm screw in gear systems?
Using a worm screw in gear systems offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in certain applications. Here are some of the advantages of using a worm screw:
- High Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw is its ability to provide a high gear reduction ratio in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a significant reduction in rotational speed. This allows for efficient torque multiplication, enabling the transmission of high torque output from the worm screw to the worm wheel. The high gear reduction is beneficial in applications that require slow and powerful movements, such as lifting heavy loads or controlling conveyor systems.
- Compact Design: Worm screw mechanisms are known for their compact design. Compared to other gear systems, such as spur gears or helical gears, a worm screw setup can achieve a similar gear reduction with fewer components. This makes it a space-saving solution, especially in applications where limited space is available or where a compact design is desired.
- Self-Locking: The self-locking property of a worm screw is a significant advantage in many applications. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a natural tendency to hold its position and prevent backward rotation of the worm wheel. This self-locking feature eliminates the need for additional braking mechanisms or external locking devices, simplifying the overall system design and improving safety and stability in applications that require load holding or position locking.
- Right-Angle Transmission: Worm screw mechanisms provide motion transmission at a right angle, allowing for the transfer of motion between non-parallel shafts. This makes them suitable for applications where the input and output shafts are oriented perpendicular to each other. Examples include automotive steering systems, where the rotational motion from the steering wheel needs to be converted into lateral motion for steering the vehicle.
- Quiet Operation: Worm screw gear systems tend to operate quietly compared to other gear configurations. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation. This can be advantageous in applications where noise reduction is desirable, such as in office equipment, appliances, or environments where low noise levels are required.
It’s important to note that while worm screw mechanisms offer these advantages, there are also some considerations to keep in mind. For instance, worm screws can have lower mechanical efficiency compared to other gear systems due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth, leading to energy losses. Additionally, they may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which can affect precision and introduce a small amount of lost motion in the system. Nevertheless, the unique characteristics of worm screws make them a valuable choice in various applications where high gear reduction, self-locking, compactness, and right-angle transmission are essential.


editor by CX 2024-02-23
China supplier High Power Low Backlash CZPT Electric AC Geared Reducer Precision Planetary Gearhead Gearbox for Servo Motors helical worm gearbox
Product Description
TaiBang Motor Industry Group Co., Ltd.
The main products is induction motor, reversible motor, DC brush gear motor, DC brushless gear motor, CH/CV big gear motors, Planetary gear motor ,Worm gear motor etc, which used widely in various fields of manufacturing pipelining, transportation, food, medicine, printing, fabric, packing, office, apparatus, entertainment etc, and is the preferred and matched product for automatic machine.
Model Instruction
GB090-10-P2
| GB | 090 | 571 | P2 |
| Reducer Series Code | External Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:High Precision Square Flange Output
GBR:High Precision Right Angle Square Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:High Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm 120:ø120mm 155:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm 180:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
571 means 1:10 | P0:High Precision Backlash
P1:Precison Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
Main Technical Performance
| Item | Number of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 | 9.21 | 28.98 | 69.61 | ||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.67 | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | 53.27 | ||||
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.65 | 7.25 | 22.75 | 51.72 | ||||
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.48 | 50.97 | ||||
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | 50.84 | ||||
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.04 | 22.53 | 50.63 | ||||
| 10 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | 50.56 | ||||
| 2 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | |
| 20 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 25 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 45 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 70 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 80 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 |
| Item | Number of stage | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | 1 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| 2 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | 1,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
Noise test standard:Distance 1m,no load.Measured with an input speed 3000rpm
| Application: | Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
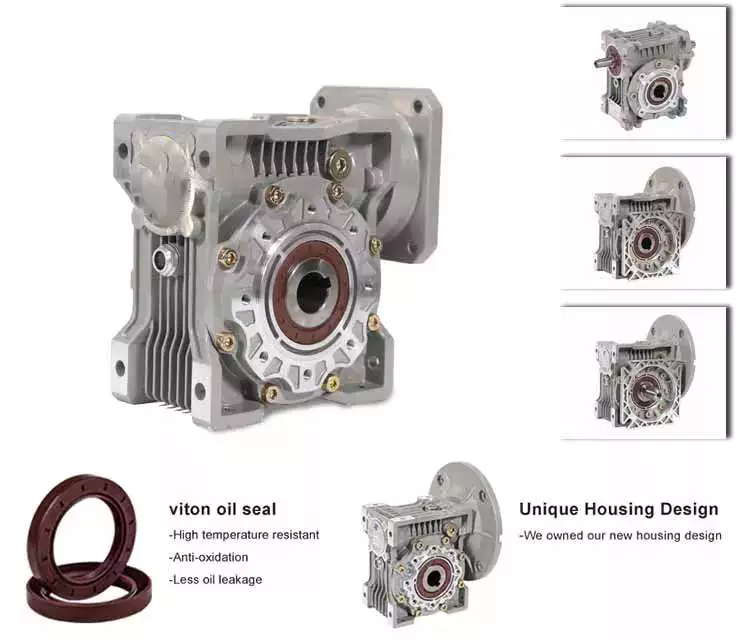

A-Drive PWC single worm reducer gearbox
A worm gear is a gear used to reduce the speed of a mechanical device. Often used in the automotive and shipbuilding industries, these gears have a lifespan comparable to many other types of reducer gearboxes. As a result, worm gears continue to be popular with engineers.
Agknx driver
Conical drive worm reducer gearboxes are an excellent choice for a variety of applications. The double-enveloping worm gear geometry of the Agknx Drive reducer gearbox provides a larger contact area and higher torque carrying capacity. This specialized gear system is also ideal for applications requiring higher precision.
Agknx Drive’s products are ideal for the solar, packaging, steel, food and pulp and paper industries. Additionally, Agknx Drive’s products are ideal for motion control and medium to heavy duty applications. The company’s dedicated sales and service teams are available to assist with your specific needs.
Agknx drive worm gear reducer gearboxes are available in single, double and triple reductions. Depending on the application, a single stage unit can transport up to 7,500 lbs. of torque. Its low-cost, compact design makes it a convenient option. Conical drive gearboxes are versatile and durable.
X & H
X & H worm gear units feature worm gear sets and are available in two different series. The X-Series includes XA versions with shaft and XF to XC versions with motor mounts. Compared to the XC compact series, the XF series offers outstanding versatility and higher efficiency. The H series combines the features of the X series with a spur gear pre-stage on the input. The H series has a die cast aluminum housing and cast iron shaft.
The X & H Worm reducer gearbox Series “H” helical gears are compatible with NMRV and C side input 56F wired motors. These gear reducer gearboxes are low cost and easy to install. They feature a cast iron housing and four threaded mounting holes.
RV seriese aluminum right angle
RV seriese aluminum right angle worm reduces versatility and durability. They are available in a variety of sizes including 25, 30, 40, 50, 63, 75, 110, 130, 150. Featuring standard NEMA motor input flanges and torque arm or foot mounting options, these reducer gearboxes are ideal for a variety of applications.
RV series worm gear reducer gearbox is made of high-quality aluminum alloy with compact structure. It also features light weight, corrosion resistance and low noise. Its housing is made of die-cast aluminum alloy, while the worm gear is made of 20CrM. The worm gear is heat treated by carbon quenching to increase its hardness. The thickness of the carbide layer is between 0.3-0.5mm.
These worm gear reducer gearboxes have multiple functions to maximize efficiency. In addition to being corrosion resistant, they are available in a variety of sizes to suit any application. Other features include a corrosion-resistant cast iron housing, enclosed breather, double-lip seal and magnetic drain plug. These worm gear reducer gearboxes are available with single or dual input shafts and are interchangeable with NMRVs.
Aluminum alloy right angle worm reducer gearbox is a light, durable and efficient gear reduction device. Its compact design makes it lighter than other gearheads, while its rust-resistant surface and long life make it an excellent choice for industrial and automotive applications. It is available in a variety of sizes, including inches. AGknx Single
AGknx Single
Worm reducer gearboxes can be classified as sacrificial gears. It is used to reduce the torque of the machine. It has two parts: a worm and wheels. The worm can be made of brass or steel. Brass worm gears corrode easily. Phosphorus EP gear fluid can run on brass worm gears. It creates a thin oxide layer on the gear teeth, protecting them from impact forces and extreme mechanical conditions. Unfortunately, it can also cause serious damage to the brass wheels.
Worm reducer gearboxes work by transferring energy only when the worm is sliding. This process wears away the lubricating layer and metal of the wheel. Eventually, the worm surface reaches the top of the wheel and absorbs more lubricant. This process will repeat itself in the next revolution.
Worm reducer gearboxes have two benefits: they are compact and take up little space. They can slow down high-output motors while maintaining their torque. Another important feature of the worm gear reducer gearbox is its high transmission ratio capability. It can be installed in both vertical and horizontal positions, and a bidirectional version is also available.
Worm gears have some complications compared to standard gear sets, but overall they are reliable and durable. Proper installation and lubrication can make them sturdy, efficient devices.
A-Drive AGknx Single
If you’re considering purchasing a new worm gear reducer gearbox for your A-Drive AGknx single, you need to understand your goals. While single-stage worm reducer gearboxes can be used, their reduction ratios are often limited. In most cases, they can only achieve a reduction ratio of 10:1. However, there are other types of gears that provide additional speed reduction capabilities.
The worm reducer gearbox consists of two parts: the input worm and the output worm. Each component has its own rotational speed, the input worm rotates in a single direction and the output worm wheel rotates vertically. In a five-to-one ratio, the input worm rotates five times for each output worm. Likewise, a 60-to-1 ratio requires 60 revolutions of each worm. Due to this arrangement, the worm reducer gearbox is inefficient. Gear reduction is inefficient due to sliding friction rather than rolling friction.
Worm reducer gearboxes are also susceptible to thermal stress. They run hotter than hypoid reducer gearboxes, which reduces their useful life. In addition to higher heat, worm reducer gearboxes can experience component failure over time. In addition, an oil change is imminent due to the deterioration of lubrication.
The worm gear reducer gearbox of the A-Drive PPC single is a direct drive gearbox for personal watercraft. It has bronze bushings, aluminum gears, and a spool box. The spool box has a quarter-inch plated spool to wrap 1/4-inch 7 x 19 aircraft cable. Its design also makes it a more efficient alternative to belt-driven AGknx cranes. AGknx X & H
AGknx X & H
The AGknx X & H worm gear reducer gearbox series is a high-performance universal mount worm gear reducer gearbox. It features a spur gear primary on the input for higher performance and a wider range of gear ratios. Its design also allows it to be used with a variety of input shaft types, including shaft and closed-coupled applications.
It is available in a variety of sizes, including popular frame sizes 90 and 110. The worm shaft is made of case-hardened alloy steel with a cast iron hub and bronze ring gear. The standard output shaft is hollow. There are also models with dual single-shaft outputs.


editor by CX 2023-06-06
China Best Price Drive Shaft Support Newtech Alfa Spring For Pneumatic Shaft Shaft Drive Motors worm gearbox components
Problem: New
Guarantee: 3 months
Applicable Industries: Lodges, Garment Outlets, Constructing Materials Retailers, Producing Plant, Equipment Repair Outlets, Foodstuff & Beverage Manufacturing unit, Farms, Restaurant, Property Use, Retail, Food Store, Printing Outlets, Building works , Power & Mining, Meals & Beverage Stores, Marketing Business
Weight (KG): thirty
Showroom Area: None
Movie outgoing-inspection: Not Accessible
Machinery Test Report: Not Obtainable
Marketing and advertising Kind: New Solution 2571
Guarantee of main parts: 1 Year
Core Factors: PLC, Engine, Bearing, Gearbox, Motor, Pressure vessel, 30mm 35mm 40mm 45mm 50mm 55mm 60mm 65mm 70mm thirteen CJ5E6C525AE 5234910 CJ5E6C525AD 518571 LR033733 s reques

Worm gear reducer gearbox
A worm gear reducer gearbox is a mechanical device used to reduce the viscosity of fluids. It can be used in a variety of applications and is available in a variety of sizes. Read on to learn more about these devices. They come in different shapes, sizes and prices. Also, these products are very reliable.
Viscosity
A new study shows that polymers derived from worms reduce the viscosity of aqueous solutions. The researchers mixed the worms with water and then applied shearing force to the mixture. Polymer-filled solutions are more resistant to shear forces than simple liquids. This is because when the solution is sheared, the filaments become entangled with each other. When the solution is sheared, the filaments line up, reducing the viscosity of the solution.
The researchers then used live insects to study the polymer’s shear thinning properties. By measuring “worm activity”, the researchers could calculate the viscosity of the mixture. The researchers then altered the worms’ activity and measured changes in the viscosity of the mixture.
The PSMA13 precursor was synthesized from BzMA at 90 °C. The resulting PSMA13-PBzMA65 worms were studied using SAXS, 1H NMR and TEM. They were found to be highly anisotropic over a wide temperature range.
The efficiency of a worm gear reducer gearbox increases with the number of revolutions of the input shaft. Braking torque also increases with the viscosity of the oil. These three factors are used to determine the efficiency of a worm gear reducer gearbox. A worm gear reducer gearbox with a helical pinion on the motor shaft will achieve a 40:1 gear ratio. The combination of a 4 liter ratio helical primary gear with a 10:l worm secondary gear will achieve high efficiency and overload capability.
The PSMA13-PBzMA65 dispersion has the same effective viscosity at 20 degrees Celsius and variable temperature. The transition time is 0.01 Pa s, indicating good thermal reversibility.
Self-locking function
Worm reducer gearboxes have many advantages. This gear has a high capacity and can transmit a lot of power. It’s also very quiet. Its advantages also include a space-saving design. Another benefit of worm reducer gearboxes is their ease of lubrication and cooling. It is also an excellent choice for transmitting high power with high gear ratios.
The self-locking function of the worm gear unit ensures that torque is only transmitted in one direction. When the load peaks, the torque signal is disabled. Unlike conventional gear reducer gearboxes, self-locking worm gears are not interchangeable.
Self-locking worm gears are not suitable for high mass applications because the weight of the driven mass can overwhelm the gear. The large mass can cause a huge side load on the worm, which can cause the worm to break. To solve this problem, a self-locking worm gear train with special provisions can be designed to reduce the heat generated.
The self-locking properties of worm reducer gearboxes are helpful in many industrial applications. It prevents reversing, which saves money on the braking system. It can also be used to lift and hold loads. The self-locking function is very useful in preventing backing.
The self-locking function depends on the pitch diameter and lead angle. A larger pitch diameter will make the self-locking function easier. However, the lead angle decreases as the pitch diameter increases. The higher pitch diameter will also make the worm reducer gearbox more resistant to backlash.
Self-locking worm gears are also useful in lifting and hoisting applications. If the worm gear is self-locking, it cannot reverse its direction without positive torque.s This makes the worm gear ideal for applications where the worm must be lowered.
application
The worm gear reducer gearbox market is a global industry consisting of several sub-sectors. This report analyzes past and current market trends and discusses key challenges and opportunities in this market. It also highlights leading marketing players and their marketing strategies. Furthermore, the report covers important segments and provides information on emerging segments.
Worm reducer gearboxes can be used in a variety of applications, such as reducing the speed and torque of rotating parts. These gears are usually available as gear sets and seat units and are available in multi-speed designs. Some manufacturers also offer precision worms and zero-backlash worms for high precision reduction.
Typically, worm gears are used on vertical axes that do not intersect. Compared to other gear drives, they are inefficient but produce a lot of reduction. There are two basic types of worm gears: double envelope and single envelope. The difference is in how they work. When the two axes do not intersect, a double-enveloping worm gear is used.
In the industrial world, worm gear reducer gearboxes are the most popular type of reducer gearbox. They are known for their high torque output multipliers and high reduction ratios. They are used in many power transmission applications including elevators, safety gates, and conveyor belts. They are especially suitable for low to medium-horsepower applications.
Worm gears can also be used for noise control. Its unique shape and size make it suitable for tight spaces. They are also suitable for conveying heavy materials and the packaging industry. In addition, they have high gear ratios, which make them suitable for small and compact machinery.
cost
The cost of a worm gear reducer gearbox depends on several factors, including the type of worm used, the materials used to manufacture the equipment, and the number of users. The worm gear reducer gearbox market is divided into two types: vertical and horizontal. Furthermore, the market is segmented by application, including the automotive industry, shipping industry, and machinery and equipment.
Worm gear reducer gearbox is a popular type of reducer gearbox. They are available in standard and flush-type packaging. They feature C-side inputs for standard NEMA motors and multiple mounting positions to suit the application. For example, a soup factory can use the same hollow reducer gearbox in multiple installation locations.
Another application for worm gear reducer gearboxes is in conveyors. They provide torque and speed reduction to move products efficiently. They are also widely used in security doors that automatically lock when they are closed. Typically, these doors use two separate worm drives. In this way, they cannot be reversed.
The cost of a worm gear reducer gearbox is determined by several factors. Size and material are important. Worm gear reducer gearboxes can be made of aluminum, cast iron, or stainless steel. Its efficiency depends on its size and proportions. It is usually used as a retarder in low-speed machinery, but can also be used as a secondary braking device.
There are two types of worms: standard worm and double worm gear. Standard worms have one or two threads, and double worm gears have one left-hand and right-hand thread. A single-threaded combination will give you a 50 reduction ratio, while a dual-threaded combination will only give you a 25% reduction.
manufacturing
Agknx Transmission Ltd. manufactures premium worm gear reducer gearboxes with robust construction and premium case-hardened steel worms. They use phosphor bronze centrifugally cast rims and attach them to the output shaft in the center. They also feature dual-purpose bearings and a large overhang load margin on the output shaft. The high-quality reducer gearbox also has a full range of positive lubrication functions. This means that they do not need special attention when using low-speed shaft extensions.

editor by Cx 2023-05-04
China Bldc Motor Geared Escooter 24V DC Nema17 Worm Geared Electric Motors 18W 3.2RPM CE ROHS Approved with high quality
Error:获取返回内容失败,
Your session has expired. Please reauthenticate.
Advantages and disadvantages of worm gear reducer gearbox
If you are looking for a worm gear reducer gearbox, you have come to the right place. This article will cover the pros and cons of worm gear reducer gearboxes and discuss the different types available. You will learn about multi-head worm gear reducer gearboxes, hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes as well as hypoid gear sets and motors.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearbox
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes are used to connect two or more rotating parts. They are available in single-axis and dual-axis versions and can be connected to various motor types. They can also have different ratios. The ratios of these gear reducer gearboxes depend on the quality of the bearings and assembly process.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes are made of bronze worm gears and cast iron hubs. The gears are lubricated with synthetic oil. They are lightweight and durable. They can be installed in various engine housings. Additionally, these gear reducer gearboxes are available in a variety of sizes. The range includes 31.5, 40, 50, 63, and 75mm models. Other sizes are available upon request.
In addition to worm gear reducer gearboxes, there are also helical gear reducer gearboxes. These reducer gearboxes can achieve very low output speeds. They are also suitable for all-around installations. In addition, the advantage of a multi-stage reducer gearbox is that it is more efficient than a single-stage gear reducer gearbox. They also feature low noise, low vibration, and low energy consumption.
Hollow shaft worm gear reducer gearboxes are generally less expensive and last longer. They are also a suitable replacement for solid shaft gearboxes for machines that require high torque without compromising strength. Typical gear arrangements include worm, spur, helical and bevel gears. Gear ratio is the ratio of input torque to output torque.
Multi-head worm gear reducer gearbox
The multi-head worm gear reducer gearbox is used to reduce the speed of the machine. It uses friction to hold the worm in place while transmitting power. These gears can also be called ground worms and hardened worm gears. They are useful in conveying systems and most engineering applications.
Multiple worm reducer gearboxes have a large number of gear ratios. These gear designs have a central cross-section that forms the front and rear boundaries of the worm gear. This design is a better choice than other worm gears because it is less prone to wear and can be used with a variety of motors and other electronics.
Adjustable multi-head worm gear reducer gearbox to reduce axial play. Usually, the backlash on the left and right sides of the worm is the same. However, if you need less backlash, you can buy a double lead worm gear. This design is ideal for precision applications requiring small clearances. The lead of the opposing teeth of the double worm gear is different from the right side, so the backlash can be adjusted without adjusting the center distance between the worm gears.
Worm gear reducer gearboxes are available from a variety of manufacturers. Many gear manufacturers stock these gears. Since the gear ratios are standardized, there is no need to adjust the height, diameter, or length of the shaft. Worm gears have fewer moving parts, which means they require less maintenance.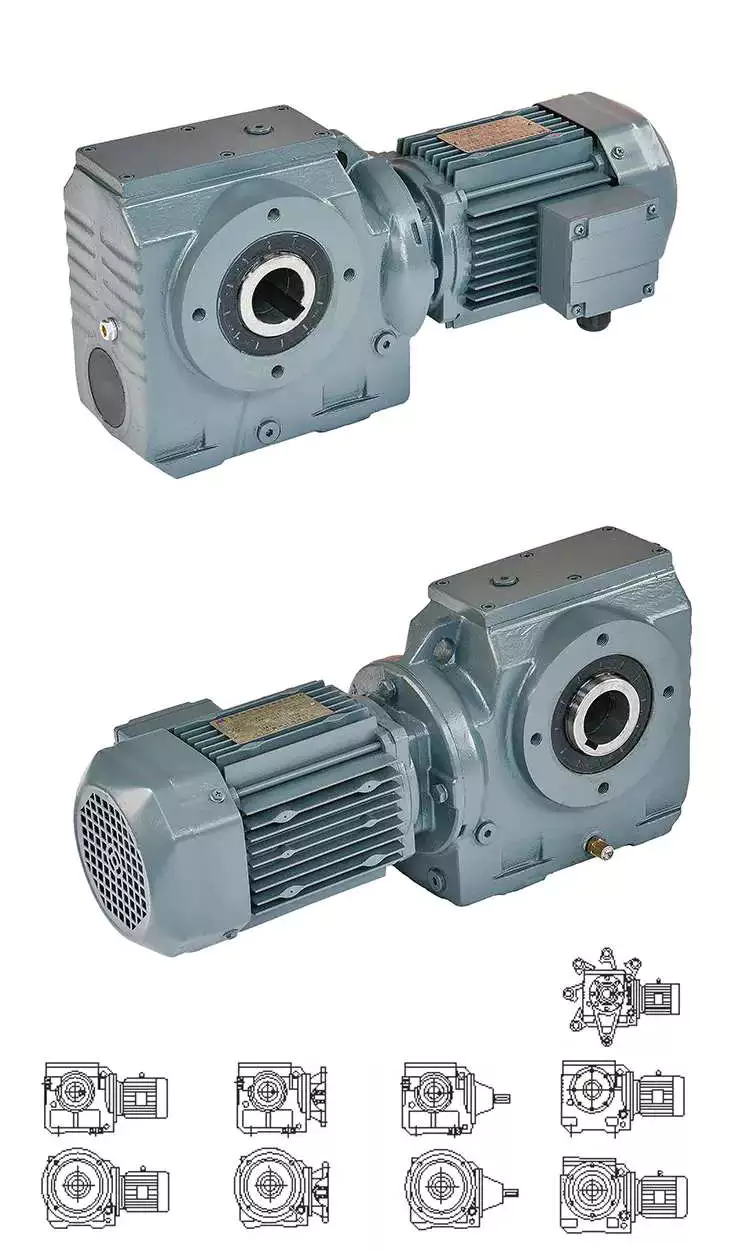
Hypoid Gear Set
Worm gears are the most common type of gear. While these gears are great for high-to-low ratios, hypoid gear sets are much more efficient in all ratios. This difference is due to higher torque density, better geometry and materials, and the way hypoid gears transmit force differently than worm gears.
Hypoid gear sets have curved helical teeth. This results in smooth gear meshing and little noise. This is because the hypoid gears start to slowly contact each other, but the contact progresses smoothly from tooth to tooth. This reduces friction and wears, thereby increasing the efficiency of the machine.
The main advantages of hypoid gears over worm gears are higher torque capacity and lower noise levels. Although their upfront cost may be higher, hypoid gears are more efficient than worm gears. They are able to handle higher initial inertia loads and can deliver more torque with a smaller motor. This saves money in the long run.
Another advantage of hypoid gears is the lower operating temperature. They also do not require oil lubrication or ventilation holes, reducing maintenance requirements. The hypoid gear set is maintenance-free, and the grease on the hypoid gear set lasts for decades.
Hypoid gear motor
A hypoid gear motor is a good choice for a worm gear reducer gearbox as it allows for a smaller motor and more efficient energy transfer. In fact, a 1 hp motor driving a hypoid reducer gearbox can provide the same output as a 1/2 hp motor driving a worm reducer gearbox. A study by Agknx compared two gear reduction methods and determined that a hypoid gear motor produces more torque and power than a worm reducer gearbox when using a fixed reduction ratio of 60:1. The study also showed that the 1/2 HP hypoid gear motor is more energy efficient and reduces electricity bills.
Worm reducer gearboxes run hotter than hypoid gears, and the added heat can shorten their lifespan. This can cause components to wear out faster, and the motor may require more frequent oil changes. In addition, hypoid gear motors are more expensive to manufacture.
Compared to worm gears, hypoid gears offer higher efficiency and lower operating noise. However, they require additional processing techniques. They are made of bronze, a softer metal capable of absorbing heavy shock loads. Worm drives require work hardening and are less durable. Operating noise is reduced by up to 30%, and hypoid gears are less prone to breakage than bevel gears.
Hypoid gear motors are prized for their efficiency and are used in applications requiring lower torque. A unique hypoid tooth profile reduces friction. In addition, hypoid gear motors are ideal for applications where space is limited. These geared motors are often used with pulleys and levers.
R series worm gear reducer gearbox
R series worm gear reducer gearboxes have a variety of characteristics that make them ideal for different applications. Its high rigidity cast iron housing and rigid side gears are designed for smooth drive and low noise. It also features high load capacity and long service life. Additionally, it can be assembled into many different configurations as required.
High efficiency, large output torque and good use efficiency. It comes in four basic models ranging from 0.12KW to 200KW. It can be matched with right angle bevel gearbox to provide large speed ratio and high torque. This combination is also suitable for low output and high torque.
AGKNX Electric Worm Gear reducer gearbox
AGKNX Electric worm gear reducer gearboxes are available with NEMA C-face mounting flanges for a variety of motors. These reducer gearboxes feature double lip oil seals, an aluminum alloy housing, and two bearings on the input and output shafts. These reducer gearboxes are rust-proof and have epoxy paint on the inside. They are available in a variety of ratios, from 7.5:1 to 100:1.
Worm reducer gearboxes are one of the most cost-effective and compact gears. These reducer gearboxes increase output torque while reducing input speed. AGKNX Electric’s worm gear reducer gearboxes are pre-installed with Mobil SHC634 Synthetic Gear Oil. These reducer gearboxes have an internal oil gallery guide to protect the shaft. They also have a one-piece cast iron housing.
AGKNX Electric Corporation is the leading independent distributor of electric motors in the United States. They have eight strategically located warehouses, enabling them to ship most orders on the same day. They offer motors of various sizes up to 20,000 hp. They also offer a variety of motor controls and variable speed drives.

editor by czh 2023-02-10
China Best Sales Brush 12V Gear High Torque Low Rpm Price Worm DC Screw Motors with Best Sales
Product Description
Brush 12v Gear High Torque Low Rpm Price Worm Dc Screw Motors
1.Features
1) Step Angle Accuracy: ±5%
2) Resistance Accuracy: ±10%
3) Inductance Accuracy: ±20%
4) Temperature Rise: 80°C Max
5) Ambient Temperature: -20°C~+50°C
6) Insulation Resistance: 100MΩ Min., 500VDC
7) Dielectric Strength: 500VAC for 1 minute
8) Shaft Radial Play: 0.02Max (450g-load)
9) Shaft Axial Play: 0.08Max (450g-load)
2.Related Specifications
1) 42mm series
| Model | DMW421 | DMW422 | DMW423 | |
| Voltage | V | 24 | ||
| No load speed | rpm | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 |
| Rated torque | Nm | 0.063 | 0.094 | 0.125 |
| Rated Speed | rpm | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 |
| Rated Current | A | 1.7 | 2.5 | 3.5 |
| Torque(max) | Nm | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.38 |
| Back-EMF constant | V/Krpm | 3.13 | 3.13 | 3.15 |
| Torque Constant | Nm/A | 0.039 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Resistance | ohm | 1.5 | 0.53 | 0.74 |
| Weight | Kg | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Length | mm | 41 | 51 | 6 |
2) 70mmSeries
| Model | Rated Voltage | No load speed |
Rated torque | Rated Speed | Rated Current |
Rated power |
L |
| VDC | RPM | Nm | rpm | A | W | mm | |
| DMW701 | 48 | 3500 | 0.5 | 3000 | 4.3 | 157 | 86 |
| DMW702 | 48 | 3500 | 1 | 3000 | 8.7 | 314 | 116 |
| DMW703 | 48 | 3500 | 1.5 | 3000 | 12.9 | 471 | 136 |
3) 80mmSeries
| Model | DMW801 | DMW802 | DMW803 | |
| Voltage | V | 24 | ||
| No load speed | rpm | 4200 | 4200 | 4200 |
| Rated torque | Nm | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| Rated Speed | rpm | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
| Rated Current | A | 5.2 | 10.5 | 15 |
| Rated power | W | 79 | 157 | 236 |
| Back-EMF constant | V/Krpm | 9 | 9.2 | 9.5 |
| Torque Constant | Nm/A | 0.06 | 0.052 | 0.05 |
| Resistance | ohm | 0.5 | 0.43 | 0.35 |
| Weight | Kg | 1.6 | 2.2 | 3 |
| Length | mm | 75 | 95 | 115 |
4) 86mmSeries
| Model | DMW861 | DMW862 | DMW863 | |
| Voltage | V | 48 | ||
| No load speed | rpm | 3500 | 3500 | 3400 |
| Rated torque | Nm | 1.0 | 1.8 | 2.5 |
| Rated Speed | rpm | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
| Rated Current | A | 8.6 | 14.8 | 20 |
| Torque(max) | Nm | 3.0 | 5.4 | 7.5 |
| Back-EMF constant | V/Krpm | 9.8 | 9.8 | 10 |
| Torque Constant | Nm/A | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
| Resistance | ohm | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
| Weight | Kg | 2.2 | 3.2 | 4.2 |
| Length | mm | 80 | 105 | 130 |
5) 60mmSeries
| Model | DMW601 | DMW602 | DMW603 | |
| Voltage | V | 36 | ||
| No load speed | rpm | 4100 | 4100 | 4100 |
| Rated torque | Nm | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| Rated Speed | rpm | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
| Rated Current | A | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| Torque(max) | Nm | 0.75 | 1.5 | 2 |
| Back-EMF constant | V/Krpm | 6.2 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| Torque Constant | Nm/A | 0.043 | 0.045 | 0.041 |
| Resistance | ohm | 0.59 | 0.26 | 0.2 |
| Weight | Kg | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| Length | mm | 78 | 99 | 120 |
6) 57mm Series
| Model | DMW571 | DMW572 | DMW573 | DMW574 | ||
| Voltage | V | 36 | ||||
| No load speed | rpm | 5200 | 5200 | 5300 | 5400 | |
| Rated torque | Nm | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.42 | |
| Rated Speed | rpm | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | |
| Rated Current | A | 1.8 | 3.2 | 4.7 | 6.5 | |
| Torque(max) | Nm | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.2 | |
| Back-EMF constant | V/Krpm | 4.5 | 4.8 | 4.83 | 4.9 | |
| Torque Constant | Nm/A | 0.072 | 0.078 | 0.08 | 0.09 | |
| Resistance | ohm | 1.7 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.39 | |
| Weight | Kg | 0.45 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.4 | |
| Length | mm | 55 | 75 | 95 | 115 | |
7) 57 High Torque
| Model | DMW571 | DMW572 | DMW573 | DMW574 | |
| Voltage | V | 36 | |||
| No load speed | rpm | 5200 | 5200 | 5200 | 5200 |
| Rated torque | Nm | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.43 | 0.49 |
| Rated Speed | rpm | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 |
| Rated Current | A | 2.2 | 4.5 | 6.8 | 7.9 |
| Torque(max) | Nm | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.5 |
| Back-EMF constant | V/Krpm | 4.5 | 4.8 | 4.83 | 4.9 |
| Torque Constant | Nm/A | 0.072 | 0.078 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| Resistance | ohm | 2 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| Weight | Kg | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.8 |
| Length | mm | 55 | 75 | 95 | 115 |
3.Outlines/Drawings
4.About US
5.Main Products
HangZhou Shnmotor is a developing manufacturing and trading company which aims at the electrical products of refrigeration market.
We have a highly qualified team, which has over 8 years experience on Machinery designing, manufacturing, managing and customer service concept heart & soul.
ISO 9000 standard and 6S management guarantee the most effective quality control on every part and every process of the products.
Our Main Products as below:
1)Brushless DC Motor
2)Setpping Motor
3)AC Motor
4)Motor Group
(Motor+Reducer+Driver+Brake)
6.Application
Package and Shipping
1.FedEX / DHL / UPS / TNT for samples,Door to door service;
2.By sea for batch goods;
3.Customs specifying freight forwarders or negotiable shipping methods;
4.Delivery Time:20-25 Days for samples;30-35 Days for batch goods;
5.Payment Terms:T/T,L/C at sight,D/P etc.
FAQ
Q1. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are urgent to get the price, please send the message on and or call us directly.
Q2. How can I get a sample to check your quality?
After price confirmed, you can requiry for samples to check quality.
If you need the samples, we will charge for the sample cost. But the sample cost can be refundable when your quantity of first order is above the MOQ
Q3. Can you do OEM for us?
Yes, the product packing can be designed as you want.
Q4. How about MOQ?
1 pcs for carton box.
Q5. What is your main market?
Eastern Europe, Southeast Asia, South America.
Please feel free to contact us if you have any question.
Screw Shaft Features Explained
When choosing the screw shaft for your application, you should consider the features of the screws: threads, lead, pitch, helix angle, and more. You may be wondering what these features mean and how they affect the screw’s performance. This article explains the differences between these factors. The following are the features that affect the performance of screws and their properties. You can use these to make an informed decision and purchase the right screw. You can learn more about these features by reading the following articles.
Threads
The major diameter of a screw thread is the larger of the 2 extreme diameters. The major diameter of a screw is also known as the outside diameter. This dimension can’t be directly measured, but can be determined by measuring the distance between adjacent sides of the thread. In addition, the mean area of a screw thread is known as the pitch. The diameter of the thread and pitch line are directly proportional to the overall size of the screw.
The threads are classified by the diameter and pitch. The major diameter of a screw shaft has the largest number of threads; the smaller diameter is called the minor diameter. The thread angle, also known as the helix angle, is measured perpendicular to the axis of the screw. The major diameter is the largest part of the screw; the minor diameter is the lower end of the screw. The thread angle is the half distance between the major and minor diameters. The minor diameter is the outer surface of the screw, while the top surface corresponds to the major diameter.
The pitch is measured at the crest of a thread. In other words, a 16-pitch thread has a diameter of 1 sixteenth of the screw shaft’s diameter. The actual diameter is 0.03125 inches. Moreover, a large number of manufacturers use this measurement to determine the thread pitch. The pitch diameter is a critical factor in successful mating of male and female threads. So, when determining the pitch diameter, you need to check the thread pitch plate of a screw.
Lead
In screw shaft applications, a solid, corrosion-resistant material is an important requirement. Lead screws are a robust choice, which ensure shaft direction accuracy. This material is widely used in lathes and measuring instruments. They have black oxide coatings and are suited for environments where rusting is not acceptable. These screws are also relatively inexpensive. Here are some advantages of lead screws. They are highly durable, cost-effective, and offer high reliability.
A lead screw system may have multiple starts, or threads that run parallel to each other. The lead is the distance the nut travels along the shaft during a single revolution. The smaller the lead, the tighter the thread. The lead can also be expressed as the pitch, which is the distance between adjacent thread crests or troughs. A lead screw has a smaller pitch than a nut, and the smaller the lead, the greater its linear speed.
When choosing lead screws, the critical speed is the maximum number of revolutions per minute. This is determined by the minor diameter of the shaft and its length. The critical speed should never be exceeded or the lead will become distorted or cracked. The recommended operational speed is around 80 percent of the evaluated critical speed. Moreover, the lead screw must be properly aligned to avoid excessive vibrations. In addition, the screw pitch must be within the design tolerance of the shaft.
Pitch
The pitch of a screw shaft can be viewed as the distance between the crest of a thread and the surface where the threads meet. In mathematics, the pitch is equivalent to the length of 1 wavelength. The pitch of a screw shaft also relates to the diameter of the threads. In the following, the pitch of a screw is explained. It is important to note that the pitch of a screw is not a metric measurement. In the following, we will define the 2 terms and discuss how they relate to 1 another.
A screw’s pitch is not the same in all countries. The United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States have standardized screw threads according to the UN system. Therefore, there is a need to specify the pitch of a screw shaft when a screw is being manufactured. The standardization of pitch and diameter has also reduced the cost of screw manufacturing. Nevertheless, screw threads are still expensive. The United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States have introduced a system for the calculation of screw pitch.
The pitch of a lead screw is the same as that of a lead screw. The diameter is 0.25 inches and the circumference is 0.79 inches. When calculating the mechanical advantage of a screw, divide the diameter by its pitch. The larger the pitch, the more threads the screw has, increasing its critical speed and stiffness. The pitch of a screw shaft is also proportional to the number of starts in the shaft.
Helix angle
The helix angle of a screw shaft is the angle formed between the circumference of the cylinder and its helix. Both of these angles must be equal to 90 degrees. The larger the lead angle, the smaller the helix angle. Some reference materials refer to angle B as the helix angle. However, the actual angle is derived from calculating the screw geometry. Read on for more information. Listed below are some of the differences between helix angles and lead angles.
High helix screws have a long lead. This length reduces the number of effective turns of the screw. Because of this, fine pitch screws are usually used for small movements. A typical example is a 16-mm x 5-inch screw. Another example of a fine pitch screw is a 12x2mm screw. It is used for small moves. This type of screw has a lower lead angle than a high-helix screw.
A screw’s helix angle refers to the relative angle of the flight of the helix to the plane of the screw axis. While screw helix angles are not often altered from the standard square pitch, they can have an effect on processing. Changing the helix angle is more common in two-stage screws, special mixing screws, and metering screws. When a screw is designed for this function, it should be able to handle the materials it is made of.
Size
The diameter of a screw is its diameter, measured from the head to the shaft. Screw diameters are standardized by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. The diameters of screws range from 3/50 inches to 16 inches, and more recently, fractions of an inch have been added. However, shaft diameters may vary depending on the job, so it is important to know the right size for the job. The size chart below shows the common sizes for screws.
Screws are generally referred to by their gauge, which is the major diameter. Screws with a major diameter less than a quarter of an inch are usually labeled as #0 to #14 and larger screws are labeled as sizes in fractions of an inch. There are also decimal equivalents of each screw size. These measurements will help you choose the correct size for your project. The screws with the smaller diameters were not tested.
In the previous section, we described the different shaft sizes and their specifications. These screw sizes are usually indicated by fractions of an inch, followed by a number of threads per inch. For example, a ten-inch screw has a shaft size of 2” with a thread pitch of 1/4″, and it has a diameter of 2 inches. This screw is welded to a two-inch Sch. 40 pipe. Alternatively, it can be welded to a 9-inch O.A.L. pipe.
Shape
Screws come in a wide variety of sizes and shapes, from the size of a quarter to the diameter of a U.S. quarter. Screws’ main function is to hold objects together and to translate torque into linear force. The shape of a screw shaft, if it is round, is the primary characteristic used to define its use. The following chart shows how the screw shaft differs from a quarter:
The shape of a screw shaft is determined by 2 features: its major diameter, or distance from the outer edge of the thread on 1 side to the inner smooth surface of the shaft. These are generally 2 to 16 millimeters in diameter. Screw shafts can have either a fully threaded shank or a half-threaded shank, with the latter providing better stability. Regardless of whether the screw shaft is round or domed, it is important to understand the different characteristics of a screw before attempting to install it into a project.
The screw shaft’s diameter is also important to its application. The ball circle diameter refers to the distance between the center of 2 opposite balls in contact with the grooves. The root diameter, on the other hand, refers to the distance between the bottommost grooves of the screw shaft. These are the 2 main measurements that define the screw’s overall size. Pitch and nominal diameter are important measurements for a screw’s performance in a particular application.
Lubrication
In most cases, lubrication of a screw shaft is accomplished with grease. Grease is made up of mineral or synthetic oil, thickening agent, and additives. The thickening agent can be a variety of different substances, including lithium, bentonite, aluminum, and barium complexes. A common classification for lubricating grease is NLGI Grade. While this may not be necessary when specifying the type of grease to use for a particular application, it is a useful qualitative measure.
When selecting a lubricant for a screw shaft, the operating temperature and the speed of the shaft determine the type of oil to use. Too much oil can result in heat buildup, while too little can lead to excessive wear and friction. The proper lubrication of a screw shaft directly affects the temperature rise of a ball screw, and the life of the assembly. To ensure the proper lubrication, follow the guidelines below.
Ideally, a low lubrication level is appropriate for medium-sized feed stuff factories. High lubrication level is appropriate for larger feed stuff factories. However, in low-speed applications, the lubrication level should be sufficiently high to ensure that the screws run freely. This is the only way to reduce friction and ensure the longest life possible. Lubrication of screw shafts is an important consideration for any screw.

