Product Description
FXR Series Square Nut Cold Rolled Ball Screw (C5/Ct7/Ct10)
| Table of Shaft dia. and Lead combination for Rolled Ball Screw | ||||||||||||||||
| Lead (mm) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 30 | ||
| Shaft dia (mm) | 4 | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 5 | / | |||||||||||||||
| 6 | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 8 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||
| 10 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||
| 12 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 14 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||
Accuracy Class & Axial Clearance
Accuracy grade of FXR series square nut cold rolled ball screw are based on C5,Ct7 and Ct10(JIS B 1192-3). According to accuracy grade, Axial play 0.005(Preload :C5), 0.02(Ct7) and 0.05mm or less(Ct10).
Material & Surface Hardness
FXR series square nut cold rolled ball screw of screw shaft screw material S55C (induction hardening), nut material SCM415H (carburizing and hardening), the surface hardness of the ball screw part is HRC58 or higher.
Shaft End Shape
The shape of the shaft end of the FXR series (square nut cold rolled ball screw) has been standardized.
Application:
1. Medical industry
2.Lithium battery industry
3.Solar photovoltaic industry
4. Semi conductor Industry
5. General industry machinery
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment
9. 3C industry etc
Technical Drawing
Specification List
FACTORY DETAILED PROCESSING PHOTOS
HIGH QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
FAQ
1. Why choose CHINAMFG China?
Over the past 14 years, CHINAMFG has always insisted that “products and services” start from Japanese industry standards,taking ZheJiang standards as the bottom line, actively invest in the development of new transmission components and self-experiment and test. With the service tenet of “exceeding customer expectations”, establish a “trusted” partnership.
2. What is your main products ?
We are a leading manufacturer and distributor of linear motion components in China. Especially miniature size of Ball Screws and Linear Actuators and linear motion guideways. Our brand “KGG” stands for ” Know-how,” ” Great Quality,” and ” Good value” and our factory is located in the most advanced city in China: ZheJiang with the best equipment and sophisticated technology, completely strict quality control system. Our aim is to supply world leader class linear motion components but with most reasonable price in the world.
3. How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
4. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
5. How can I get a sample to check the quality?
After confirmation of our quoted price, you can place the sample order. The sample will be started after you CHINAMFG back our detailed technical file.
6. What’s your payment terms?
Our payment terms is 30% deposit,balance 70% before shipment. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C5 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 6mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 3-Row |
| Nut Type: | Square Nut |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the limitations of using worm screws in mechanical designs?
While worm screws offer several advantages in mechanical designs, they also have some limitations that should be considered. Here are the key limitations of using worm screws:
- Lower Mechanical Efficiency: Worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower mechanical efficiency compared to other gear systems. This is primarily due to the sliding contact between the worm screw threads and the worm wheel teeth, which results in higher friction and energy losses. The lower mechanical efficiency can lead to heat generation, reduced power transmission, and decreased overall system efficiency. It’s important to consider the trade-off between the desired gear reduction and the mechanical efficiency requirements of the specific application.
- Limited High-Speed Applications: Worm screws are not well-suited for high-speed applications. The sliding contact and meshing action between the threads and teeth can generate heat and cause wear at high rotational speeds. Additionally, the higher friction and lower mechanical efficiency mentioned earlier can limit the maximum achievable speed of the system. If high-speed operation is a requirement, alternative gear systems, such as spur gears or helical gears, may be more suitable.
- Backlash: Worm screw mechanisms can exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which is the lost motion or clearance between the threads and teeth when changing direction. Backlash can negatively impact precision and positioning accuracy in applications that require tight tolerances. It’s important to consider backlash and implement measures to minimize its effects, such as using anti-backlash mechanisms or incorporating backlash compensation techniques.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials for worm screws is crucial to ensure their durability and performance. Worm screws typically require harder materials to withstand the sliding contact and high contact pressures between the threads and teeth. The selection of suitable materials may increase the manufacturing complexity and cost of the worm screw assembly. Additionally, the choice of materials should consider factors such as compatibility, wear resistance, and the specific operating conditions of the application.
- Load Distribution: In worm screw mechanisms, the load is distributed over a limited number of teeth on the worm wheel. This concentrated load distribution can result in higher stresses and wear on the contacting surfaces. It’s important to consider the load capacity and contact area of the worm wheel teeth to ensure that the assembly can handle the anticipated loads without premature failure or excessive wear.
- Required Lubrication: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of worm screw mechanisms. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces. However, the need for lubrication adds complexity to the design and maintenance of the system. It requires regular monitoring of lubricant levels and periodic lubricant replenishment or replacement. Failure to maintain proper lubrication can result in increased friction, wear, and potential system failure.
Despite these limitations, worm screws continue to be widely used in various mechanical designs due to their unique characteristics and advantages. It’s essential to carefully evaluate the specific requirements and constraints of the application and consider alternative gear systems if the limitations of worm screws pose significant challenges to the desired performance and efficiency.

How do you troubleshoot problems in a worm screw gear system?
Troubleshooting problems in a worm screw gear system requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve issues effectively. Here are the steps involved in troubleshooting problems in a worm screw gear system:
- Identify the Symptoms: Start by identifying the specific symptoms or issues that indicate a problem in the worm screw gear system. This can include abnormal noise, reduced performance, increased backlash, erratic motion, or any other noticeable deviations from normal operation. Gather as much information as possible about the symptoms to help narrow down the potential causes.
- Inspect and Clean: Conduct a visual inspection of the worm screw gear system to check for any obvious signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or contamination. Inspect the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel for signs of pitting, scoring, or other surface irregularities. Clean the components if necessary to remove any debris or contaminants that may be affecting the system’s performance.
- Check Lubrication: Review the lubrication of the worm screw gear system. Ensure that the system is adequately lubricated with the recommended lubricant and that the lubricant is in good condition. Insufficient or degraded lubrication can result in increased friction, wear, and inefficiencies. Replenish or replace the lubricant as needed following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Inspect Alignment: Verify the alignment of the worm screw and the worm wheel. Misalignment can cause issues such as increased friction, wear, and reduced efficiency. Check for any signs of misalignment and make adjustments as necessary to ensure proper alignment of the components. This may involve repositioning or realigning the system or addressing any underlying factors contributing to the misalignment.
- Measure Backlash: Measure the amount of backlash present in the system. Excessive backlash can lead to reduced accuracy, loss of motion control, and diminished performance. Use appropriate measuring tools, such as dial indicators, to quantify the amount of backlash. If the backlash exceeds acceptable limits, consider adjusting the system to minimize or eliminate the excessive clearance between the threads and the teeth.
- Check Load and Overloading: Evaluate the loads applied to the worm screw gear system and compare them to the system’s design limits. Overloading the system can lead to accelerated wear, tooth breakage, or component deformation. If the loads exceed the system’s capacity, consider redistributing the load, upgrading the components, or redesigning the system to handle the required loads appropriately.
- Address Specific Issues: Based on the symptoms and findings from the inspection and measurements, address any specific issues identified in the worm screw gear system. This may involve repairing or replacing worn or damaged components, adjusting clearances, realigning the system, improving lubrication, or addressing any other factors contributing to the problems observed.
- Test and Monitor: After addressing the identified issues, test the worm screw gear system to verify that the problems have been resolved. Monitor the system’s performance during operation to ensure that the symptoms have been effectively mitigated. Pay attention to any new or recurring issues that may require further investigation or adjustments.
It is important to note that troubleshooting problems in a worm screw gear system may require expertise and experience. If you encounter complex or persistent issues that you are unable to resolve, it is recommended to seek assistance from qualified technicians or professionals with knowledge in mechanical power transmission systems.
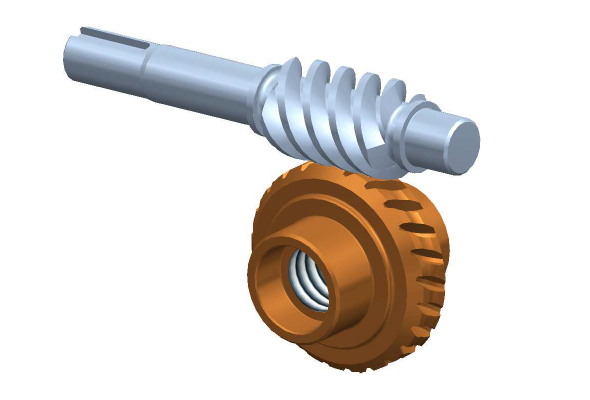
How do you calculate the gear ratio for a worm screw and gear setup?
In a worm screw and gear setup, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the worm wheel (gear) and the number of threads on the worm screw. The gear ratio represents the relationship between the rotational speed of the worm screw and the resulting rotational speed of the worm wheel. The formula to calculate the gear ratio is as follows:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Worm Wheel / Number of Threads on Worm Screw
Here’s a step-by-step process to calculate the gear ratio:
- Count the number of teeth on the worm wheel. This can be done by visually inspecting the gear or referring to its specifications.
- Count the number of threads on the worm screw. The threads refer to the number of complete turns or helical grooves wrapped around the cylindrical body of the worm screw.
- Divide the number of teeth on the worm wheel by the number of threads on the worm screw.
- The result of the division is the gear ratio. It represents the number of revolutions of the worm screw required to complete one revolution of the worm wheel.
For example, let’s say the worm wheel has 40 teeth, and the worm screw has 2 threads. Using the formula, we can calculate the gear ratio as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 teeth / 2 threads = 20
In this case, for every full revolution of the worm screw, the worm wheel will rotate 1/20th of a revolution. This indicates a significant speed reduction, resulting in high torque output at the worm wheel.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio calculated using this formula assumes an ideal scenario without considering factors like friction, efficiency losses, or the pitch diameter of the gears. In practical applications, these factors may affect the actual gear ratio and performance of the worm screw and gear setup.


editor by Dream 2024-05-17
China Custom CHINAMFG Rolled Thread 1.5mm Lead Ball Screw for Auto Controlling Machine (GLR Series, Lead: 1.5mm, Shaft: 8mm)
Product Description
GLR Series Single Nut Ball Screw with Metric Thread (C5/Ct7/Ct10)
| Table of Shaft dia. and Lead combination for Rolled Ball Screw | ||||||||||||||||
| Lead (mm) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 30 | ||
| Shaft dia (mm) | 4 | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 5 | / | |||||||||||||||
| 6 | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 8 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||
| 10 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||
| 12 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 14 | / | / | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||
Accuracy Class & Axial Clearance
Accuracy grade of GLR series(single nut ball screw with metric thread)are based on C5,Ct7 and Ct10(JIS B 1192-3). According to accuracy grade, Axial play 0.005(Preload :C5),0.02(Ct7) and 0.05mm or less(Ct10).
Material & Surface Hardness
GLR series (single nut ball screw with metric thread)of screw shaft screw material S55C (induction hardening), nut material SCM415H (carburizing and hardening), the surface hardness of the ball screw part is HRC58 or higher.
Shaft End Shape
The shaft end shape of the GLR series (single nut ball screw with metric thread) has been standardized.
Application:
1. Medical industry
2.Lithium battery industry
3.Solar photovoltaic industry
4. Semi conductor Industry
5. General industry machinery
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment
9. 3C industry etc
Technical Drawing
Specification List
FACTORY DETAILED PROCESSING PHOTOS
HIGH QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
FAQ
1. Why choose CHINAMFG China?
Over the past 14 years, CHINAMFG has always insisted that “products and services” start from Japanese industry standards,taking ZheJiang standards as the bottom line, actively invest in the development of new transmission components and self-experiment and test. With the service tenet of “exceeding customer expectations”, establish a “trusted” partnership.
2. What is your main products ?
We are a leading manufacturer and distributor of linear motion components in China. Especially miniature size of Ball Screws and Linear Actuators and linear motion guideways. Our brand “KGG” stands for ” Know-how,” ” Great Quality,” and ” Good value” and our factory is located in the most advanced city in China: ZheJiang with the best equipment and sophisticated technology, completely strict quality control system. Our aim is to supply world leader class linear motion components but with most reasonable price in the world.
3. How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
4. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
5. How can I get a sample to check the quality?
After confirmation of our quoted price, you can place the sample order. The sample will be started after you CHINAMFG back our detailed technical file.
6. What’s your payment terms?
Our payment terms is 30% deposit,balance 70% before shipment. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C7 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 8mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 3-Row |
| Nut Type: | Single Nut Ball Screw with Metric Thread |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the common issues or failures associated with worm screws?
Worm screws, like any mechanical component, can experience certain issues or failures over time. Understanding these common problems is important for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Here are some common issues or failures associated with worm screws:
- Wear and Surface Damage: Due to the sliding contact between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel, wear can occur over time. This wear can lead to surface damage, such as pitting, scoring, or galling. Excessive wear and surface damage can affect the performance and efficiency of the worm screw gear system, resulting in increased backlash, decreased torque transmission, and potential failure.
- Lubrication Problems: Inadequate or improper lubrication is a common cause of issues in worm screw systems. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and accelerated wear. On the other hand, over-lubrication can cause excessive drag and fluid churn, leading to inefficient power transmission. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals, types of lubricants, and proper lubrication techniques to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the worm screw system.
- Backlash and Inaccuracy: Backlash refers to the play or clearance between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. Excessive backlash can result in reduced accuracy, loss of motion control, and diminished overall system performance. Backlash can be caused by factors such as wear, misalignment, or improper assembly. Regular inspection and adjustment of backlash are necessary to maintain the desired precision and minimize the effects of backlash-related issues.
- Misalignment: Misalignment between the worm screw and the worm wheel can result in increased friction, wear, and inefficiencies. Misalignment can occur due to factors such as improper installation, component deformation, or external forces. It is essential to ensure proper alignment during installation and periodically check for misalignment during routine maintenance. Adjustments should be made as necessary to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
- Overloading: Subjecting the worm screw gear system to excessive loads beyond its design limits can lead to failure. Overloading can result in accelerated wear, tooth breakage, or component deformation. It is important to operate the system within the specified load limits and consider factors such as shock loads, dynamic loads, and variations in operating conditions. If higher loads are required, it may be necessary to select a worm screw system with a higher load capacity or redesign the system accordingly.
- Corrosion and Contamination: Corrosion and contamination can negatively impact the performance and lifespan of worm screw systems. Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles can lead to corrosion, rusting, or damage to the surfaces of the worm screw and worm wheel. Contamination can interfere with smooth operation and cause accelerated wear. Proper environmental protection, regular cleaning, and appropriate sealing measures can help mitigate the effects of corrosion and contamination.
- Insufficient Stiffness: Worm screws rely on proper support and stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and prevent deflection. Inadequate stiffness in the supporting structure or mounting arrangement can result in excessive deflection, misalignment, and decreased performance. It is crucial to ensure that the worm screw system is properly supported and mounted to maintain the required rigidity and stiffness for optimal operation.
It’s important to note that the specific issues or failures associated with worm screws can vary depending on factors such as the application, operating conditions, maintenance practices, and the quality of the components. Regular inspection, proper lubrication, alignment checks, load monitoring, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for minimizing the occurrence of these issues and ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of worm screw systems.

How does the pitch of a worm screw affect its performance?
The pitch of a worm screw plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics and capabilities. The pitch refers to the axial distance between consecutive threads on the worm screw. Here’s how the pitch of a worm screw affects its performance:
- Speed and Efficiency: The pitch of a worm screw directly influences the speed and efficiency of the worm gear system. A smaller pitch, which means a finer thread, results in a higher gear ratio and slower output speed. Conversely, a larger pitch, or coarser thread, leads to a lower gear ratio and faster output speed. This relationship between pitch and speed allows for speed reduction or multiplication in mechanical power transmission systems.
- Load Capacity: The pitch of a worm screw also affects its load-carrying capacity. A finer pitch tends to distribute the load over more threads, resulting in a larger contact area between the worm screw and the worm wheel. This increased contact area improves load distribution and allows for higher load capacity. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may have a reduced contact area, which can limit the load-carrying capability of the worm gear system.
- Backlash: Backlash is the clearance or play between the threads of the worm screw and the teeth of the worm wheel. The pitch of a worm screw influences the amount of backlash present in the system. A finer pitch generally results in lower backlash due to the smaller clearance between the threads and the teeth. In contrast, coarser pitches may have increased backlash, which can negatively impact the system’s accuracy, precision, and responsiveness.
- Efficiency and Heat Generation: The pitch of a worm screw affects the overall efficiency of the worm gear system. Finer pitches tend to have higher efficiency due to reduced sliding friction between the threads and the teeth. This reduced friction results in less heat generation, contributing to higher overall system efficiency. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may exhibit increased sliding friction, leading to higher energy losses and heat generation.
- Manufacturing and Design Considerations: The pitch of a worm screw also influences the manufacturing process and design considerations. Finer pitches generally require more precise machining or grinding processes to achieve the desired thread geometry. Coarser pitches, on the other hand, may offer advantages in terms of ease of manufacturing and reduced sensitivity to manufacturing tolerances. The selection of the optimal pitch depends on factors such as the desired gear ratio, load requirements, desired efficiency, and manufacturing capabilities.
It’s important to note that the pitch of a worm screw is typically specified by the manufacturer and should be chosen carefully based on the specific application requirements. Consulting with experts or engineers familiar with worm gear systems can help in selecting the appropriate pitch to achieve the desired performance and functionality.

What is a worm screw in mechanical engineering?
In mechanical engineering, a worm screw, also known as a worm gear screw or worm gear, is a type of gear mechanism used to transmit motion and power between non-parallel shafts. It consists of a spiral-shaped screw, called the worm, and a gear wheel, called the worm wheel or worm gear. The worm screw and worm wheel have helical teeth that mesh together to transfer rotational motion.
The worm screw typically has a single thread or multiple threads wrapped around its cylindrical body. The worm wheel, on the other hand, has teeth that are specially shaped to mesh with the worm screw. The orientation of the worm screw and worm wheel is such that the axes of rotation are perpendicular to each other. This configuration allows the worm screw to convert rotational motion along its axis into rotary motion perpendicular to its axis.
One of the defining characteristics of a worm screw is its high gear ratio. Due to the helical nature of the teeth, a worm screw can achieve a high reduction ratio in a single gear stage. This means that a small rotation of the worm screw can result in a substantial rotation of the worm wheel. The ratio of the number of teeth on the worm wheel to the number of threads on the worm screw determines the reduction ratio.
Worm screws have several advantages and applications in mechanical engineering:
- High Reduction Ratio: As mentioned earlier, worm screws offer high gear ratios, making them suitable for applications that require significant speed reduction and torque multiplication. They are commonly used in applications where large gear reductions are needed, such as in conveyor systems, winches, and lifting equipment.
- Self-Locking: A unique characteristic of worm screws is their self-locking property. The angle of the helical teeth creates a wedging effect that prevents the worm wheel from driving the worm screw. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads without the need for additional braking mechanisms, making them suitable for applications where holding positions or preventing back-driving is crucial, such as in elevators or lifting mechanisms.
- Smooth and Quiet Operation: The helical teeth of the worm screw and worm wheel facilitate smooth and quiet operation. The gradual engagement and disengagement of the teeth minimize noise, vibration, and backlash, resulting in a more efficient and reliable gear mechanism.
- Compact Design: Worm screws offer a compact design compared to other gear mechanisms. The perpendicular arrangement of the worm screw and worm wheel allows for a compact and space-saving installation, making them suitable for applications where size constraints are a consideration.
- Reduction of Input Speed: Worm screws are commonly used to reduce the speed of the input shaft while increasing torque. This is advantageous in applications where slower, controlled motion is required, such as in industrial machinery, conveyors, and robotics.
It should be noted that worm screws also have some limitations, including lower efficiency compared to other gear mechanisms, higher friction due to sliding motion, and limited reverse operation capabilities. Therefore, careful consideration of the specific application requirements is necessary when deciding whether to use a worm screw in a mechanical system.


editor by Dream 2024-04-25
China wholesaler CNC Machining Auto Spare Parts Car Accessories Worm Shaft Gears for Machine Part with Best Sales
Product Description
1, production technology: forging machining stamping sand casting die casting investment casting
2,Material: grey iron stainless steel aluminum
3, single process, high precision, little surface roughness,
4, customized, we produce the parts according to drawings or samples,
5, we will inspect the parts strictly and provide material and inspection report.
Packing and Shipping
Grey Iron Housing with Sand Casting Process
1. Standard: crate
2. Delivery: As per contract delivery on time
3. Shipping: As per client request.
Our advantages
1.We can control the products to meet your strict requirement.
2. Different kinds of finish available, like anodized, power coating, painting, polishing, electrophoresis, plating. Etc.
3. Different dimensions according to the requirements
4. Can provide various sizes and packing according to specific requirements
5. We offer the engineer consultation to your design for production improvement and cost saving
Our Service:
1.Your inquiry related to our products or prices will be replied in 24 hours.
2.Individual formula according to customers’ special drawing requests.
3.Manufacturer with large capacity, ensures the fast production cycle after
confirming the order.
4.Protection of sales area and private information for all of our customers.
Screw Sizes and Their Uses
Screws have different sizes and features. This article will discuss screw sizes and their uses. There are 2 main types: right-handed and left-handed screw shafts. Each screw features a point that drills into the object. Flat tipped screws, on the other hand, need a pre-drilled hole. These screw sizes are determined by the major and minor diameters. To determine which size of screw you need, measure the diameter of the hole and the screw bolt’s thread depth.
The major diameter of a screw shaft
The major diameter of a screw shaft is the distance from the outer edge of the thread on 1 side to the tip of the other. The minor diameter is the inner smooth part of the screw shaft. The major diameter of a screw is typically between 2 and 16 inches. A screw with a pointy tip has a smaller major diameter than 1 without. In addition, a screw with a larger major diameter will have a wider head and drive.
The thread of a screw is usually characterized by its pitch and angle of engagement. The pitch is the angle formed by the helix of a thread, while the crest forms the surface of the thread corresponding to the major diameter of the screw. The pitch angle is the angle between the gear axis and the pitch surface. Screws without self-locking threads have multiple starts, or helical threads.
The pitch is a crucial component of a screw’s threading system. Pitch is the distance from a given thread point to the corresponding point of the next thread on the same shaft. The pitch line is 1 element of pitch diameter. The pitch line, or lead, is a crucial dimension for the thread of a screw, as it controls the amount of thread that will advance during a single turn.
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft
When choosing the appropriate screw, it is important to know its pitch diameter and pitch line. The pitch line designates the distance between adjacent thread sides. The pitch diameter is also known as the mean area of the screw shaft. Both of these dimensions are important when choosing the correct screw. A screw with a pitch of 1/8 will have a mechanical advantage of 6.3. For more information, consult an application engineer at Roton.
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft is measured as the distance between the crest and the root of the thread. Threads that are too long or too short will not fit together in an assembly. To measure pitch, use a measuring tool with a metric scale. If the pitch is too small, it will cause the screw to loosen or get stuck. Increasing the pitch will prevent this problem. As a result, screw diameter is critical.
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft is measured from the crest of 1 thread to the corresponding point on the next thread. Measurement is made from 1 thread to another, which is then measured using the pitch. Alternatively, the pitch diameter can be approximated by averaging the major and minor diameters. In most cases, the pitch diameter of a screw shaft is equal to the difference between the two.
The thread depth of a screw shaft
Often referred to as the major diameter, the thread depth is the outermost diameter of the screw. To measure the thread depth of a screw, use a steel rule, micrometer, or caliper. In general, the first number in the thread designation indicates the major diameter of the thread. If a section of the screw is worn, the thread depth will be smaller, and vice versa. Therefore, it is good practice to measure the section of the screw that receives the least amount of use.
In screw manufacturing, the thread depth is measured from the crest of the screw to the root. The pitch diameter is halfway between the major and minor diameters. The lead diameter represents the amount of linear distance traveled in 1 revolution. As the lead increases, the load capacity decreases. This measurement is primarily used in the construction of screws. However, it should not be used for precision machines. The thread depth of a screw shaft is essential for achieving accurate screw installation.
To measure the thread depth of a screw shaft, the manufacturer must first determine how much material the thread is exposed to. If the thread is exposed to side loads, it can cause the nut to wedge. Because the nut will be side loaded, its thread flanks will contact the nut. The less clearance between the nut and the screw, the lower the clearance between the nut and the screw. However, if the thread is centralized, there is no risk of the nut wedgeing.
The lead of a screw shaft
Pitch and lead are 2 measurements of a screw’s linear distance per turn. They’re often used interchangeably, but their definitions are not the same. The difference between them lies in the axial distance between adjacent threads. For single-start screws, the pitch is equal to the lead, while the lead of a multi-start screw is greater than the pitch. This difference is often referred to as backlash.
There are 2 ways to calculate the pitch and lead of a screw. For single-start screws, the lead and pitch are equal. Multiple-start screws, on the other hand, have multiple starts. The pitch of a multiple-start screw is the same as its lead, but with 2 or more threads running the length of the screw shaft. A square-thread screw is a better choice in applications requiring high load-bearing capacity and minimal friction losses.
The PV curve defines the safe operating limits of lead screw assemblies. It describes the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. As the load increases, the lead screw assembly must slow down in order to prevent irreversible damage from frictional heat. Furthermore, a lead screw assembly with a polymer nut must reduce rpm as the load increases. The more speed, the lower the load capacity. But, the PV factor must be below the maximum allowed value of the material used to make the screw shaft.
The thread angle of a screw shaft
The angle between the axes of a thread and the helix of a thread is called the thread angle. A unified thread has a 60-degree angle in all directions. Screws can have either a tapped hole or a captive screw. The screw pitch is measured in millimeters (mm) and is usually equal to the screw major diameter. In most cases, the thread angle will be equal to 60-degrees.
Screws with different angles have various degrees of thread. Originally, this was a problem because of the inconsistency in the threading. However, Sellers’s thread was easier to manufacture and was soon adopted as a standard throughout the United States. The United States government began to adopt this thread standard in the mid-1800s, and several influential corporations in the railroad industry endorsed it. The resulting standard is called the United States Standard thread, and it became part of the ASA’s Vol. 1 publication.
There are 2 types of screw threads: coarse and fine. The latter is easier to tighten and achieves tension at lower torques. On the other hand, the coarse thread is deeper than the fine one, making it easier to apply torque to the screw. The thread angle of a screw shaft will vary from bolt to bolt, but they will both fit in the same screw. This makes it easier to select the correct screw.
The tapped hole (or nut) into which the screw fits
A screw can be re-threaded without having to replace it altogether. The process is different than that of a standard bolt, because it requires threading and tapping. The size of a screw is typically specified by its major and minor diameters, which is the inside distance between threads. The thread pitch, which is the distance between each thread, is also specified. Thread pitch is often expressed in threads per inch.
Screws and bolts have different thread pitches. A coarse thread has fewer threads per inch and a longer distance between threads. It is therefore larger in diameter and longer than the material it is screwed into. A coarse thread is often designated with an “A” or “B” letter. The latter is generally used in smaller-scale metalworking applications. The class of threading is called a “threaded hole” and is designated by a letter.
A tapped hole is often a complication. There is a wide range of variations between the sizes of threaded holes and nut threads, so the tapped hole is a critical dimension in many applications. However, even if you choose a threaded screw that meets the requisite tolerance, there may be a mismatch in the thread pitch. This can prevent the screw from freely rotating.

