Product Description
Material Available: Alloy Steel / SUS / Aluminum
Processing Type: Lathe / Milling / CNC / Extrusion / Machining
Finish Type: Black oxide / Galvanized
Cooperation Type: OEM/ODM
Sollwin has provided OEM to customers and Designs / Solutions are available for supporting as well.
Complex Residential& Commercial metal products are allowed base on our moden equipments and more than 10 years of experiences in our area.
Our processing types have wide range now that included Laser cutting / Forming / Bending / Lathing / Milling / Weldment / Assembly.
All of our products and scrvices are base on Profession, Concentraion, Responsbility and full equipments.
Welcome to contact us for any potential business opportunity.
Q: Is it available to customize 1 piece product?
A: Yes,it is acceptable. Normally we will not need to make tooling if there is no special construction or profile for product.
Q: Can I customize the products even I has sketch or idea only?
A: It is available. We can help you to design the product according to your sketch or idea and provided drawings.
Q: How long is the leading time from development to mass-production?
A: Normally the 1st article can be provided after confirm the design and cost. 30-60 days for first mass-production.
Q: How about your quality control and after-service?
A: We have control plan for all of our products and do this for every processing. We also accept inspection by third party be specified.The warranty should be decided by different products and processings.
Q: Do you do all processing of product in your factory?
A: Honest to say no. We provide complex sheet metal products and manchinery products to our customers. So some processing have to outsourcing by our partners. Some like surface threatment, harding and tempering, special processing which need special machine and so on. But we keep the main processing in our facility. And it will help us to provide competitive products and service.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
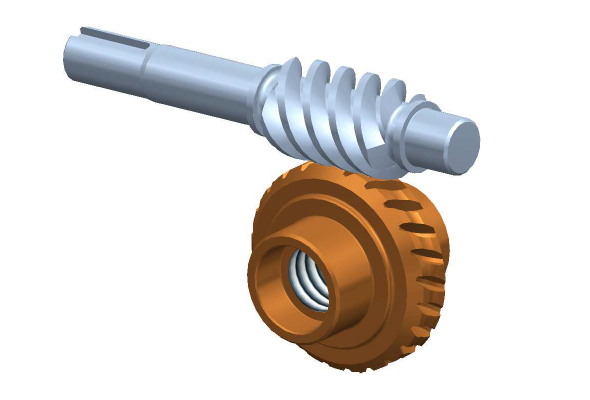
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Mining Equipment |
| Spiral Line: | Right-Handed Rotation |
| Head: | Multiple-Head |
| Reference Surface: | Toroidal Surface |
| Type: | ZK Worm |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can worm screws be used for high torque applications?
Yes, worm screws can be used for high torque applications. The design of a worm screw mechanism allows for efficient torque transmission and multiplication, making it suitable for applications that require high torque output. Here are some key points to consider regarding the use of worm screws in high torque applications:
- Gear Reduction: One of the primary advantages of a worm screw mechanism is its ability to provide a significant gear reduction in a single stage. The helical threads of the worm screw and the meshing teeth of the worm wheel create a high reduction ratio, which results in a lower output speed and higher output torque. This gear reduction capability allows worm screws to generate and transmit substantial torque, making them well-suited for high torque applications.
- Efficiency: While worm screws can provide high torque output, it’s important to consider the mechanical efficiency of the system. The efficiency of a worm screw mechanism can vary depending on factors such as the materials used, lubrication, and design parameters. However, compared to other gear systems, worm screw mechanisms tend to have lower efficiency due to inherent friction between the threads and teeth. It’s crucial to ensure that the efficiency of the worm screw mechanism meets the requirements of the specific high torque application.
- Load Holding: Another advantage of worm screws is their self-locking property. Due to the helical shape of the threads, the worm screw has a wedging effect on the worm wheel, which provides resistance against backward rotation. This self-locking feature allows worm screws to hold loads in a fixed position without the need for additional braking mechanisms. In high torque applications where load holding is required, worm screws can provide reliable and secure positioning.
- Material Selection: The materials used for the worm screw and worm wheel should be carefully selected to withstand high torque loads. Both components should have sufficient strength and wear resistance to handle the transmitted torque without deformation or premature failure. Depending on the specific application requirements, materials such as hardened steel, bronze, or other alloys may be chosen to ensure the durability and performance of the worm screw assembly.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of a worm screw mechanism, especially in high torque applications. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation between the contacting surfaces, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Regular maintenance, including monitoring lubricant levels and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed, is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear or failure.
Overall, worm screws can be effectively used in high torque applications, thanks to their gear reduction capabilities, load-holding properties, and efficient torque transmission. However, it’s important to carefully consider factors such as mechanical efficiency, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance to ensure that the worm screw mechanism can meet the specific requirements and demands of the high torque application.
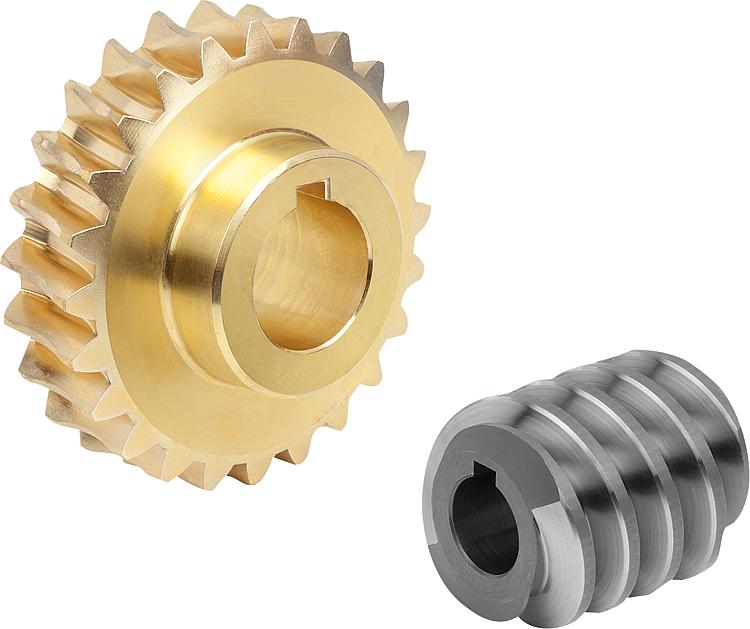

What are the latest innovations in worm screw design and materials?
In recent years, there have been several notable innovations in worm screw design and materials that aim to improve performance, efficiency, durability, and overall functionality. Here are some of the latest advancements in this field:
- Advanced Materials: One of the significant trends in worm screw design is the use of advanced materials. Manufacturers are exploring materials with enhanced strength, wear resistance, and fatigue properties. For example, advanced alloys and composite materials are being employed to improve load capacity, reduce weight, and increase the longevity of worm screws. Additionally, advancements in material science and engineering are leading to the development of self-lubricating materials, which can minimize friction and improve efficiency by reducing the need for external lubrication.
- Improved Thread Geometries: Innovations in thread geometries have focused on optimizing load distribution, reducing friction, and improving efficiency. Researchers and engineers are developing novel thread profiles and forms that enhance contact between the worm screw and the worm wheel. These designs help minimize backlash, increase load-carrying capacity, and improve overall system performance. Additionally, advancements in computer simulations and modeling techniques enable more accurate analysis and optimization of thread geometries for specific applications.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: Surface treatments and coatings are being applied to worm screws to enhance their performance and durability. For instance, advanced coatings such as diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings or specialized lubricious coatings help reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and minimize the need for external lubrication. Surface treatments like nitriding or carburizing can improve hardness and provide resistance against abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of worm screws.
- Precision Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing processes and technologies have enabled the production of worm screws with higher precision and tighter tolerances. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC grinding and high-precision gear hobbing, allow for the creation of worm screws with superior dimensional accuracy, improved surface finish, and better tooth profile control. These manufacturing advancements contribute to enhanced performance, reduced backlash, and increased overall system efficiency.
- Computer-Aided Design and Simulation: The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools has revolutionized worm screw design and optimization. Engineers can now create virtual models, simulate the behavior of worm gear systems, and analyze various design parameters to optimize performance before physical prototypes are manufactured. This iterative design process helps reduce development time, minimize costs, and improve the final design and performance of worm screws.
- Integration with Digitalization and Automation: The integration of worm gear systems with digitalization and automation technologies is another area of innovation. Worm screws are being designed to work seamlessly with sensor technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load. This data can be utilized for predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and optimization of the overall system performance.
It’s important to note that the field of worm screw design and materials is continuously evolving, and new innovations are being introduced regularly. Keeping up with the latest research, advancements, and industry developments is crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers involved in worm gear system applications.
How do you calculate the gear ratio for a worm screw and gear setup?
In a worm screw and gear setup, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the worm wheel (gear) and the number of threads on the worm screw. The gear ratio represents the relationship between the rotational speed of the worm screw and the resulting rotational speed of the worm wheel. The formula to calculate the gear ratio is as follows:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Worm Wheel / Number of Threads on Worm Screw
Here’s a step-by-step process to calculate the gear ratio:
- Count the number of teeth on the worm wheel. This can be done by visually inspecting the gear or referring to its specifications.
- Count the number of threads on the worm screw. The threads refer to the number of complete turns or helical grooves wrapped around the cylindrical body of the worm screw.
- Divide the number of teeth on the worm wheel by the number of threads on the worm screw.
- The result of the division is the gear ratio. It represents the number of revolutions of the worm screw required to complete one revolution of the worm wheel.
For example, let’s say the worm wheel has 40 teeth, and the worm screw has 2 threads. Using the formula, we can calculate the gear ratio as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 teeth / 2 threads = 20
In this case, for every full revolution of the worm screw, the worm wheel will rotate 1/20th of a revolution. This indicates a significant speed reduction, resulting in high torque output at the worm wheel.
It’s important to note that the gear ratio calculated using this formula assumes an ideal scenario without considering factors like friction, efficiency losses, or the pitch diameter of the gears. In practical applications, these factors may affect the actual gear ratio and performance of the worm screw and gear setup.


editor by CX 2024-01-16